Abstract
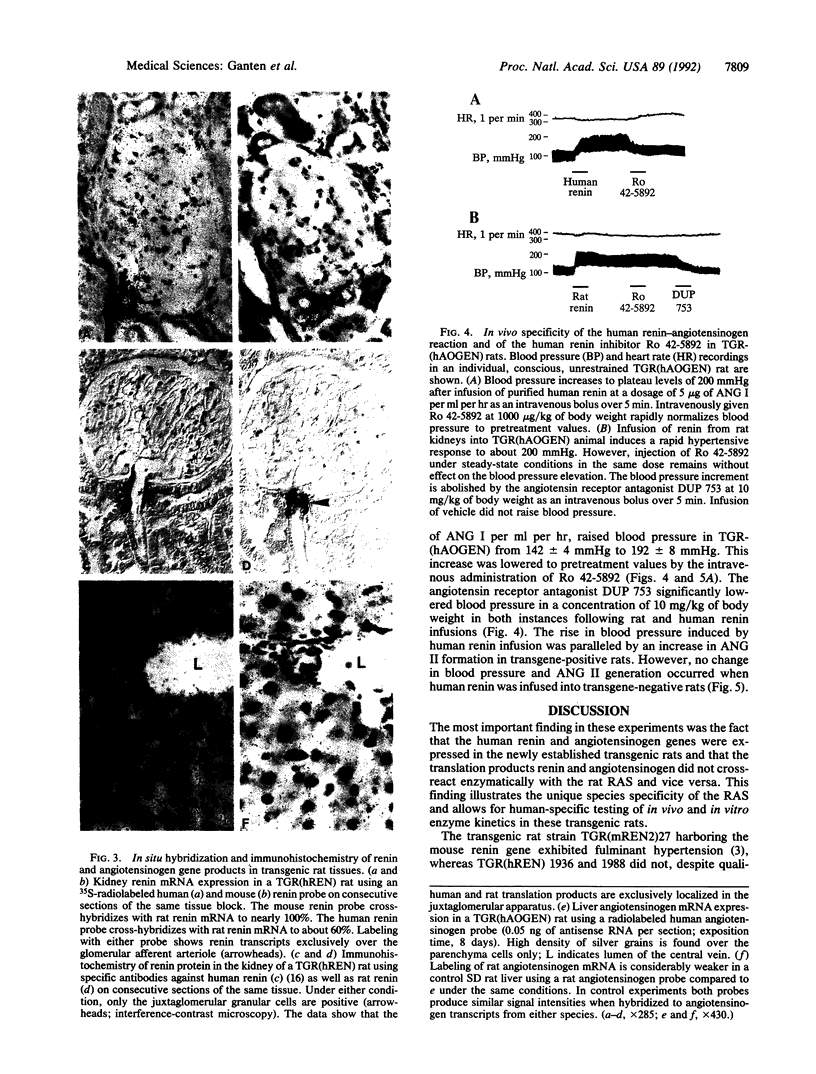
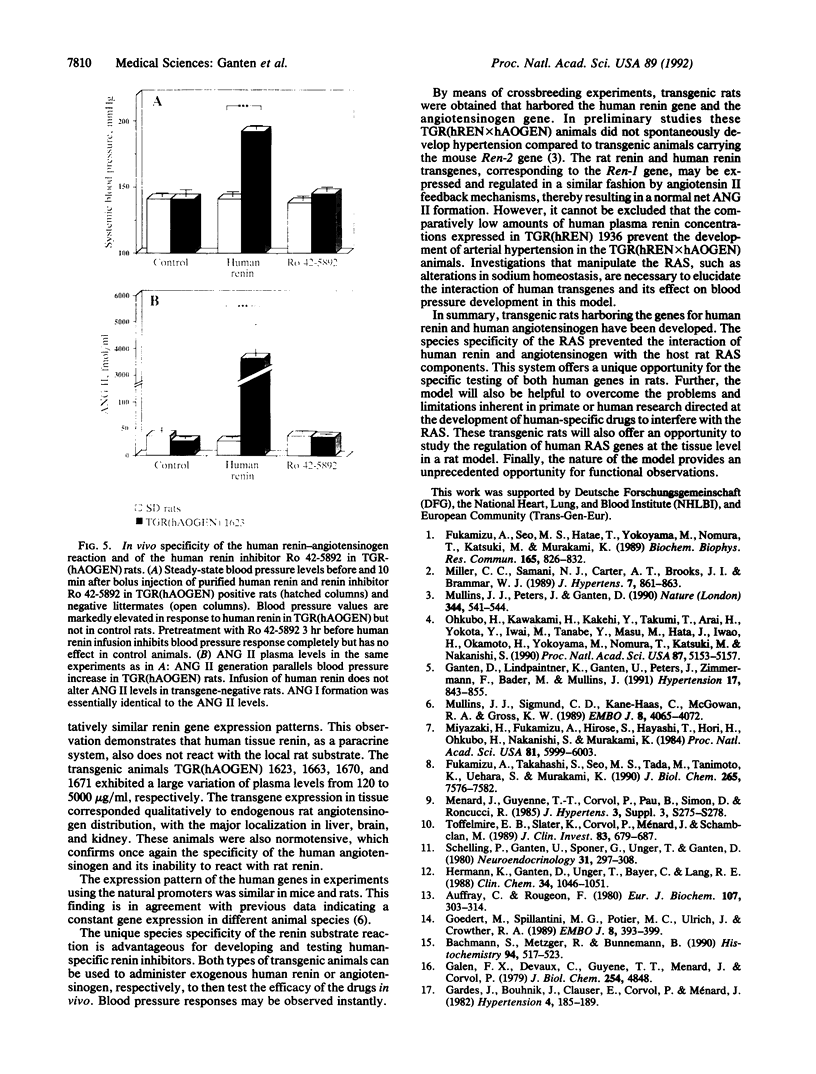
The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is the most important regulatory system of electrolyte homeostasis and blood pressure. We report here the development of transgenic rats carrying the human angiotensinogen TGR-(hAOGEN) and human renin TGR(hREN) genes. The plasma levels and tissue distribution of the transcription and translation products from both genes are described. A unique species specificity of the enzyme kinetics was observed. The human RAS components in the transgenic rats did not interact with the endogenous rat RAS in vivo. Instead, infusions of exogenous human RAS components specifically interacted with human transgene translation products. Thus, infusion of human renin in TGR(hAOGEN) led to an increase of angiotensin II and an elevation of blood pressure, which could not be antagonized by the human-specific renin enzyme inhibitor Ro 42-5892. Rat renin also elevated blood pressure and angiotensin II in TGR(hAOGEN); however, this effect was not antagonized by the human renin inhibitor. Compared to mice, rats offer the advantage of chronic instrumentation and repetitive, sophisticated, hemodynamic, and endocrinological investigations. Thus, transgenic rat models with human-specific enzyme kinetics permit primate-specific analyses in non-primate in vivo and in vitro experimental systems.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann S., Metzger R., Bunnemann B. Tamm-Horsfall protein-mRNA synthesis is localized to the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop in rat kidney. Histochemistry. 1990;94(5):517–523. doi: 10.1007/BF00272616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukamizu A., Seo M. S., Hatae T., Yokoyama M., Nomura T., Katsuki M., Murakami K. Tissue-specific expression of the human renin gene in transgenic mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 15;165(2):826–832. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukamizu A., Takahashi S., Seo M. S., Tada M., Tanimoto K., Uehara S., Murakami K. Structure and expression of the human angiotensinogen gene. Identification of a unique and highly active promoter. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7576–7582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galen F. X., Devaux C., Guyenne T., Menard J., Corvol P. Multiple forms of human renin. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4848–4855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganten D., Lindpaintner K., Ganten U., Peters J., Zimmermann F., Bader M., Mullins J. Transgenic rats: new animal models in hypertension research. Invited lecture. Hypertension. 1991 Jun;17(6 Pt 2):843–855. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.17.6.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardes J., Bouhnik J., Clauser E., Corvol P., Menard J. Role of angiotensinogen in blood pressure homeostasis. Hypertension. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):185–189. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.4.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Spillantini M. G., Potier M. C., Ulrich J., Crowther R. A. Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding an isoform of microtubule-associated protein tau containing four tandem repeats: differential expression of tau protein mRNAs in human brain. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):393–399. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann K., Ganten D., Unger T., Bayer C., Lang R. E. Measurement and characterization of angiotensin peptides in plasma. Clin Chem. 1988 Jun;34(6):1046–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. C., Samani N. J., Carter A. T., Brooks J. I., Brammar W. J. Modulation of mouse renin gene expression by dietary sodium chloride intake in one-gene, two-gene and transgenic animals. J Hypertens. 1989 Nov;7(11):861–863. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198911000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki H., Fukamizu A., Hirose S., Hayashi T., Hori H., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S., Murakami K. Structure of the human renin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5999–6003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. J., Peters J., Ganten D. Fulminant hypertension in transgenic rats harbouring the mouse Ren-2 gene. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):541–544. doi: 10.1038/344541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. J., Sigmund C. D., Kane-Haas C., Gross K. W., McGowan R. A. Expression of the DBA/2J Ren-2 gene in the adrenal gland of transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4065–4072. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08590.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ménard J., Guyenne T. T., Corvol P., Pau B., Simon D., Roncucci R. Direct immunometric assay of active renin in human plasma. J Hypertens Suppl. 1985 Dec;3(3):S275–S278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkubo H., Kawakami H., Kakehi Y., Takumi T., Arai H., Yokota Y., Iwai M., Tanabe Y., Masu M., Hata J. Generation of transgenic mice with elevated blood pressure by introduction of the rat renin and angiotensinogen genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5153–5157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schelling P., Ganten U., Sponer G., Unger T., Ganten D. Components of the renin-angiotensin system in the cerebrospinal fluid of rats and dogs with special consideration of the origin and the fate of angiotensin II. Neuroendocrinology. 1980 Nov;31(5):297–308. doi: 10.1159/000123092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toffelmire E. B., Slater K., Corvol P., Menard J., Schambelan M. Response of plasma prorenin and active renin to chronic and acute alterations of renin secretion in normal humans. Studies using a direct immunoradiometric assay. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):679–687. doi: 10.1172/JCI113932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]