Abstract
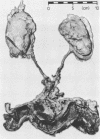
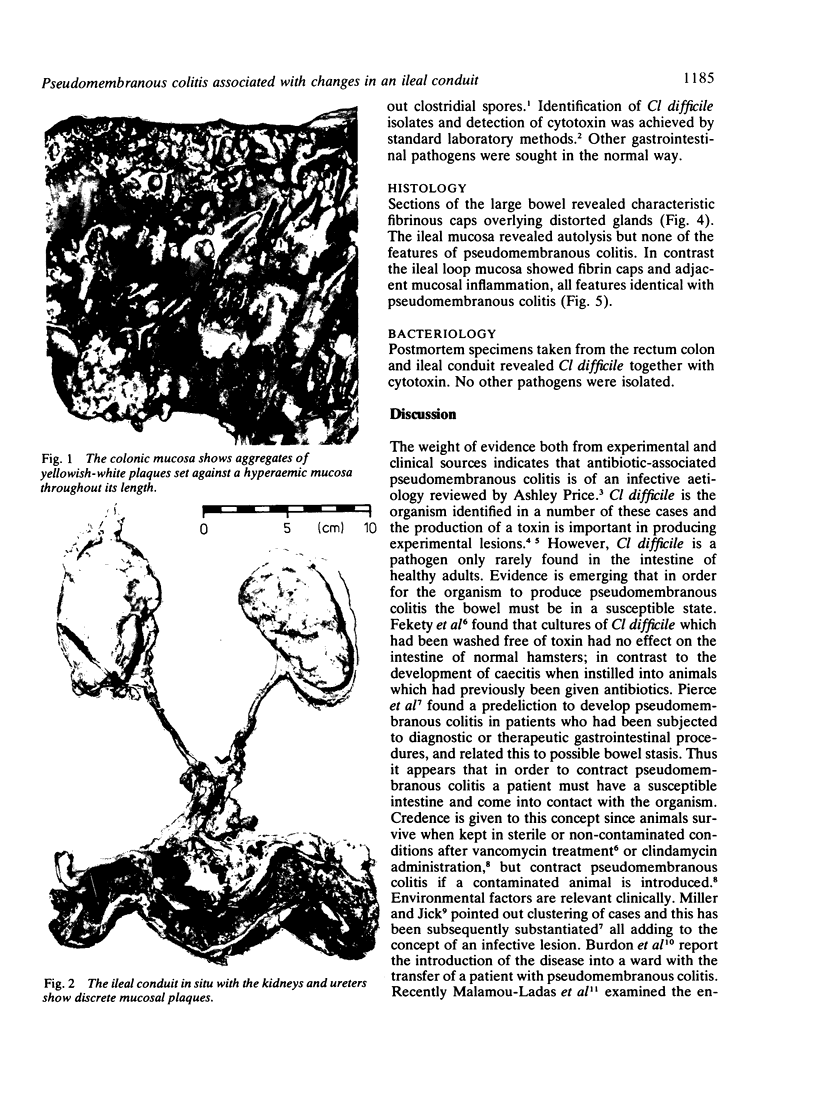
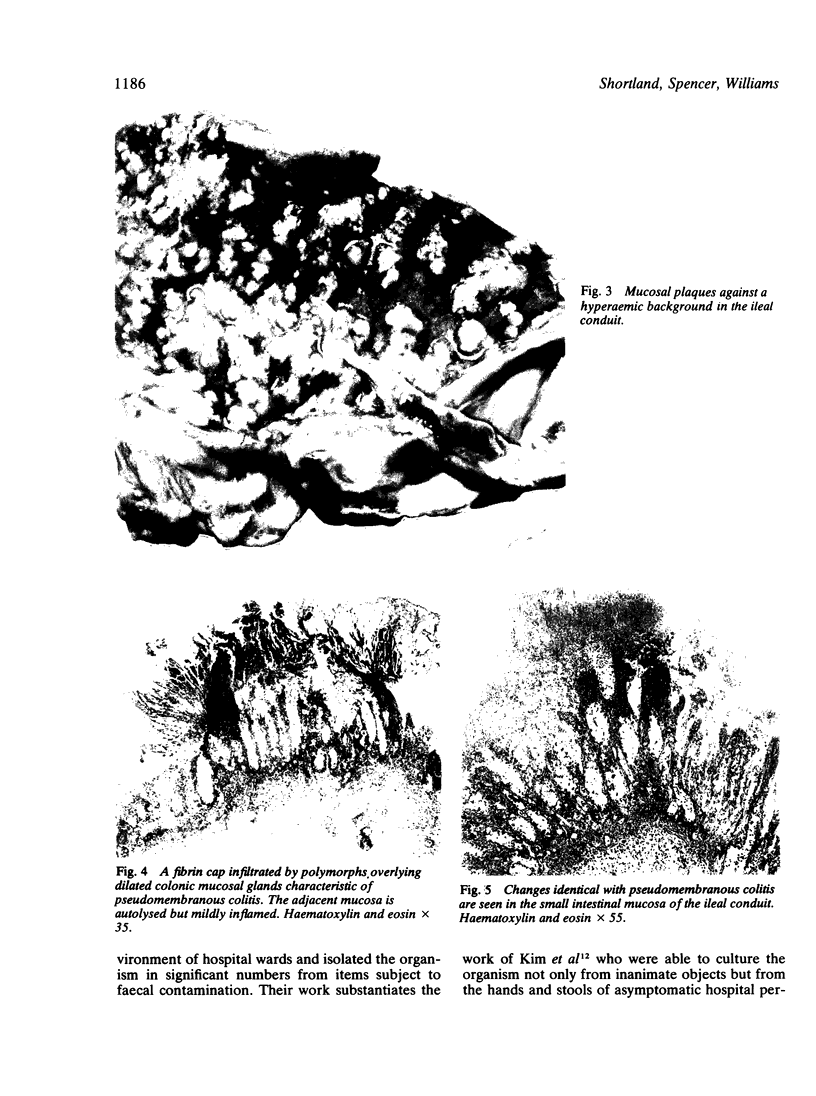
A case of antibiotic associated pseudomembranous colitis following total cystectomy is reported, in which there was involvement of the ileal conduit. The small bowel remaining in situ was uninvolved. Bacteriological studies revealed Clostridium difficile and the toxin in both colon and ileal conduit. Relevant publications concerning pathogenesis are discussed, in relation to the unusual site described in this case. Epidemiological evidence is reviewed which suggests that isolation of patients with pseudomembranous colitis is a logical course of action.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett J. G. Antimicrobial agents implicated in Clostridium difficile toxin-associated diarrhea of colitis. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1981 Jul;149(1):6–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behan W. M., Mills P. R. Possible evidence for a Shwartzman reaction in pseudomembranous colitis. Digestion. 1982;23(3):141–150. doi: 10.1159/000198721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borriello S. P., Honour P. Simplified procedure for the routine isolation of Clostridium difficile from faeces. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Oct;34(10):1124–1127. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.10.1124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fekety R., Silva J., Toshniwal R., Allo M., Armstrong J., Browne R., Ebright J., Rifkin G. Antibiotic-associated colitis: effects of antibiotics on Clostridium difficile and the disease in hamsters. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Mar-Apr;1(2):386–397. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.2.386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F. Bile acids, diarrhea, and antibiotics: data, speculation, and a unifying hypothesis. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135 (Suppl):S126–S132. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.supplement.s126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. H., Fekety R., Batts D. H., Brown D., Cudmore M., Silva J., Jr, Waters D. Isolation of Clostridium difficile from the environment and contacts of patients with antibiotic-associated colitis. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jan;143(1):42–50. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.1.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langham P. Parental consent: its justification and limitations. Clin Res. 1979 Dec;27(5):349–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson H. E., Price A. B., Honour P., Borriello S. P. Clostridium difficile and the aetiology of pseudomembranous colitis. Lancet. 1978 May 20;1(8073):1063–1066. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90912-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malamou-Ladas H., O'Farrell S., Nash J. Q., Tabaqchali S. Isolation of Clostridium difficile from patients and the environment of hospital wards. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jan;36(1):88–92. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. R., Jick H. Antibiotic-associated colitis. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 Jul;22(1):1–6. doi: 10.1002/cpt19772211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce P. F., Jr, Wilson R., Silva J., Jr, Garagusi V. F., Rifkin G. D., Fekety R., Nunez-Montiel O., Dowell V. R., Jr, Hughes J. M. Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis: an epidemiologic investigation of a cluster of cases. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):269–274. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin G. D., Silva J., Jr, Fekety R. Gastrointestinal and systemic toxicity of fecal extracts from hamsters with clindamycin-induced colitis. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jan;74(1):52–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):475–500. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.475-500.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]