Abstract
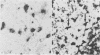
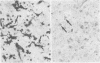
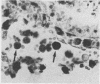
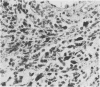
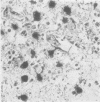
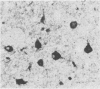
The macrophage markers non-specific esterase, alpha 1-antitrypsin, alpha 1-antichymotrypsin, and lysozyme were compared with conventional microglial and macrophage stains in the human central nervous system. In a series of specimens from cases of head trauma, conventionally fixed and embedded, the modified Weil-Davenport stain was unequivocally best for demonstrating reactive microglia. alpha 1-antichymotrypsin, however, was the most effective for showing macrophages in a series of specimens from patients with other conditions, which included inflammatory, neoplastic, and non-inflammatory diseases. The non-specific esterase reaction was unsatisfactory in tissues fixed in neutral formalin but was successful in fresh frozen tissue. In a series of specimens from cases of multiple sclerosis, non-specific esterase showed demyelination clearly and stained neuronal cytoplasm. It also stained macrophages but was less satisfactory for lipid-bearing phagocytes in multiple sclerosis than oil red 0.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brierley J. B., Brown A. W. The origin of lipid phagocytes in the central nervous system: I. The intrinsic microglia. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Nov 10;211(4):397–406. doi: 10.1002/cne.902110406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker J. The enzyme histochemistry of lymphoid and non-lymphoid cells of the human palatine tonsil: a basis for the study of lymphomas. J Pathol. 1981 May;134(1):81–95. doi: 10.1002/path.1711340109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran R. C., Jones E. L. Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas: an immunohistochemical and histological study. J Pathol. 1979 Dec;129(4):179–190. doi: 10.1002/path.1711290404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A., Allison A. C., Ward P., Kight N. Identification of human mononuclear leucocyte populations by esterase staining. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Nov;30(2):289–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume D. A., Gordon S. Mononuclear phagocyte system of the mouse defined by immunohistochemical localization of antigen F4/80. Identification of resident macrophages in renal medullary and cortical interstitium and the juxtaglomerular complex. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1704–1709. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson P., Jones D. B., Millward-Sadler G. H., Judd M. A., Payne S. Alpha-1-antitrypsin in human macrophages. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Sep;34(9):982–990. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.9.982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. Y., Lam K. W., Yam L. T. Esterases in human leukocytes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Jan;21(1):1–12. doi: 10.1177/21.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. Y., Taylor C. R. The distribution of muramidase (lysozyme) in human tissues. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Feb;28(2):124–132. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.2.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehmichen M., Wiethölter H., Greaves M. F. Immunological analysis of human microglia: lack of monocytic and lymphoid membrane differentiation antigens. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1979 Mar;38(2):99–103. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197903000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer D. R. Microscopic lesions in the brain following head injury. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Aug;31(4):299–306. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.4.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadimitriou C. S., Stein H., Papacharalampous N. X. Presence of alpha1-antichymotrypsin and alpha1-antitrypsin in haematopoietic and lymphoid tissue cells as revealed by the immunoperoxidase method. Pathol Res Pract. 1980 Nov;169(3-4):287–297. doi: 10.1016/s0344-0338(80)80007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]