Abstract
We have identified 7-[3H]hydroxy-N,N-di-n-propyl-2-aminotetralin ([3H]7-OH-DPAT) as a selective probe for the recently cloned dopamine D3 receptor and used it to assess the presence of this receptor and establish its distribution and properties in brain. In transfected Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, it binds to D3 receptors with subnanomolar affinity, whereas its affinity is approximately 100-, 1000-, and 10,000-fold lower at D2, D4, and D1 receptors, respectively. Specific [3H]7-OH-DPAT binding sites, with a Kd of 0.8 nM and a pharmacology similar to those at reference D3 receptors of CHO cells, were identified in rat brain. D3 receptors differ from D2 receptors in brain by their lower abundance (2 orders of magnitude) and distribution, restricted to a few mainly phylogenetically ancient areas--e.g., paleostriatum and archicerebellum--as evidenced by membrane binding are autoradiography studies. Native D3 receptors in brain are characterized by an unusually high nanomolar affinity for dopamine and a low modulatory influence of guanyl nucleotides on agonist binding. These various features suggest that D3 receptors are involved in a peculiar mode of neurotransmission in a restricted subpopulation of dopamine neurons.
Full text
PDF
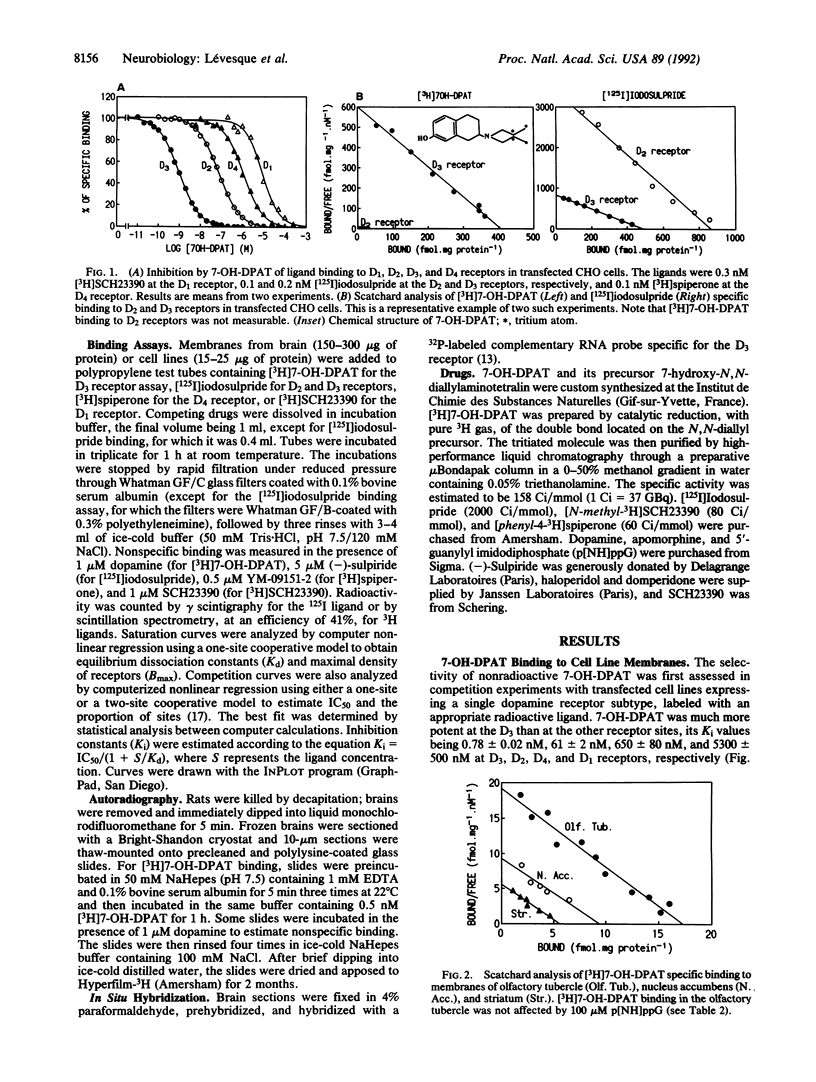
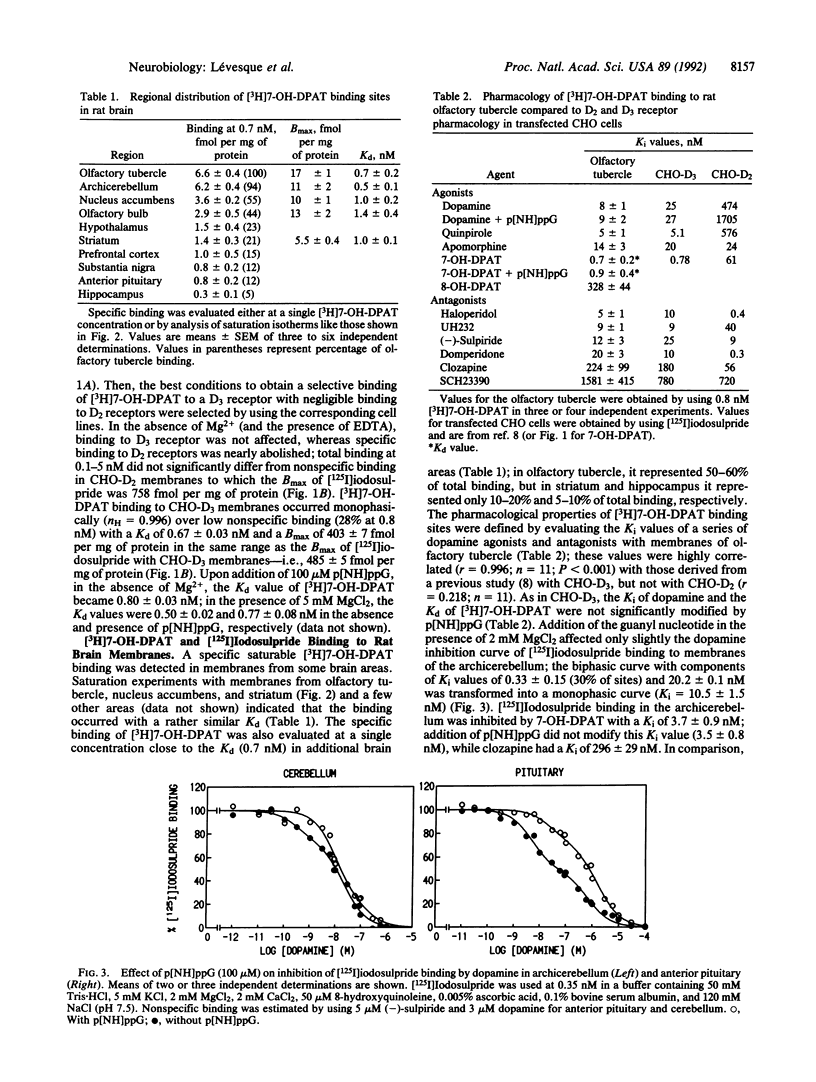
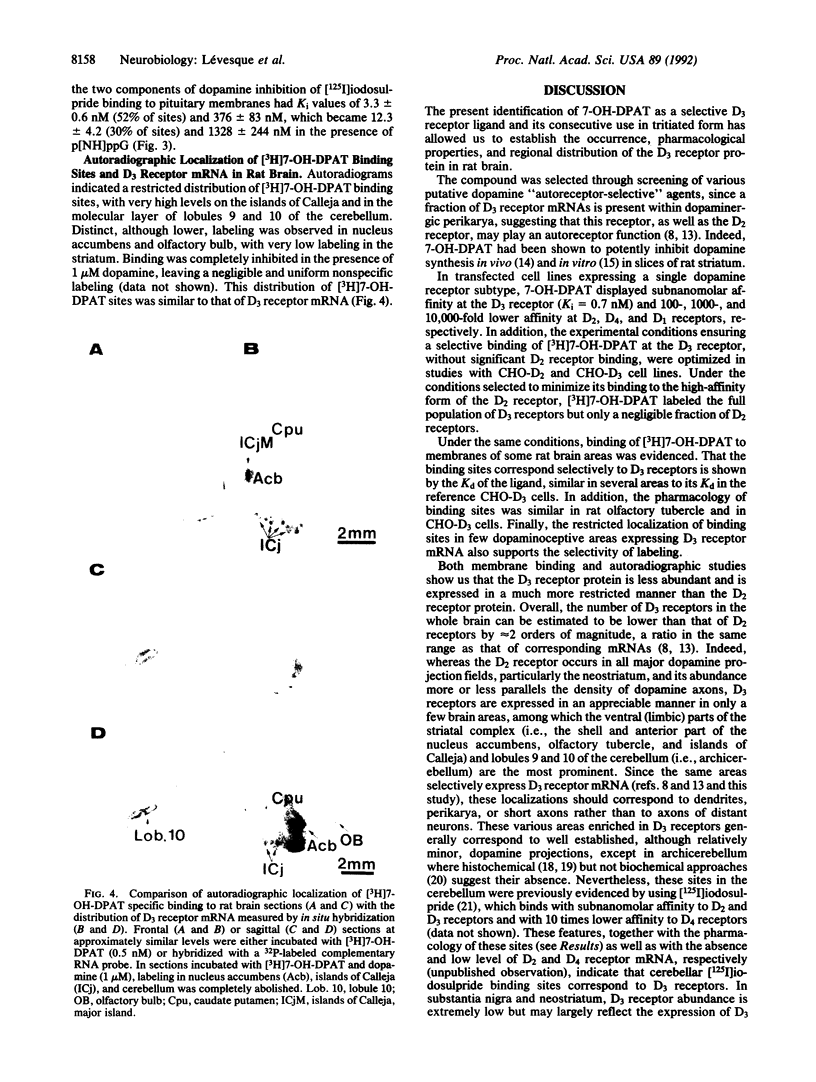

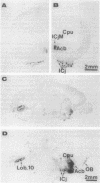
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckstead R. M., Domesick V. B., Nauta W. J. Efferent connections of the substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area in the rat. Brain Res. 1979 Oct 19;175(2):191–217. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)91001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouthenet M. L., Martres M. P., Sales N., Schwartz J. C. A detailed mapping of dopamine D-2 receptors in rat central nervous system by autoradiography with [125I]iodosulpride. Neuroscience. 1987 Jan;20(1):117–155. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouthenet M. L., Souil E., Martres M. P., Sokoloff P., Giros B., Schwartz J. C. Localization of dopamine D3 receptor mRNA in the rat brain using in situ hybridization histochemistry: comparison with dopamine D2 receptor mRNA. Brain Res. 1991 Nov 15;564(2):203–219. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91456-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunzow J. R., Van Tol H. H., Grandy D. K., Albert P., Salon J., Christie M., Machida C. A., Neve K. A., Civelli O. Cloning and expression of a rat D2 dopamine receptor cDNA. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):783–787. doi: 10.1038/336783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dearry A., Gingrich J. A., Falardeau P., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Bates M. D., Caron M. G. Molecular cloning and expression of the gene for a human D1 dopamine receptor. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):72–76. doi: 10.1038/347072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon J. H., Loughlin S. E., Ribak C. E. The islands of Calleja complex of rat basal forebrain. III. Histochemical evidence for a striatopallidal system. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Jul 20;218(1):91–120. doi: 10.1002/cne.902180106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feenstra M. G., Sumners C., Goedemoed J. H., de Vries J. B., Rollema H., Horn A. S. A comparison of the potencies of various dopamine receptor agonists in models for pre- and postsynaptic receptor activity. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Sep;324(2):108–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00497015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamblin M. W., Creese I. 3H-dopamine binding to rat striatal D-2 and D-3 sites: enhancement by magnesium and inhibition by guanine nucleotides and sodium. Life Sci. 1982 May 3;30(18):1587–1595. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90248-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Calne D. B. Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):93–96. doi: 10.1038/277093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kizer J. S., Palkovits M., Brownstein M. J. The projections of the A8, A9 and A10 dopaminergic cell bodies: evidence for a nigral-hypothalamic-median eminence dopaminergic pathway. Brain Res. 1976 May 28;108(2):363–370. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90192-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martres M. P., Sokoloff P., Delandre M., Schwartz J. C., Protais P., Costentin J. Selection of dopamine antagonists discriminating various behavioral responses and radioligand binding sites. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Feb;325(2):102–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00506189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monsma F. J., Jr, Mahan L. C., McVittie L. D., Gerfen C. R., Sibley D. R. Molecular cloning and expression of a D1 dopamine receptor linked to adenylyl cyclase activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6723–6727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder T. B., de Vries J. B., Dijkstra D., Wiechers J. W., Grol C. J., Horn A. S. Further in vitro and in vivo studies with the putative presynaptic dopamine agonist N,N-dipropyl-7-hydroxy-2-aminotetralin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;336(5):494–501. doi: 10.1007/BF00169305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piomelli D., Pilon C., Giros B., Sokoloff P., Martres M. P., Schwartz J. C. Dopamine activation of the arachidonic acid cascade as a basis for D1/D2 receptor synergism. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):164–167. doi: 10.1038/353164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff P., Andrieux M., Besançon R., Pilon C., Martres M. P., Giros B., Schwartz J. C. Pharmacology of human dopamine D3 receptor expressed in a mammalian cell line: comparison with D2 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr 10;225(4):331–337. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(92)90107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff P., Giros B., Martres M. P., Bouthenet M. L., Schwartz J. C. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dopamine receptor (D3) as a target for neuroleptics. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):146–151. doi: 10.1038/347146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spano P. F., Govoni S., Trabucchi M. Studies on the pharmacological properties of dopamine receptors in various areas of the central nervous system. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1978;19:155–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunahara R. K., Guan H. C., O'Dowd B. F., Seeman P., Laurier L. G., Ng G., George S. R., Torchia J., Van Tol H. H., Niznik H. B. Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D5 receptor with higher affinity for dopamine than D1. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):614–619. doi: 10.1038/350614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunahara R. K., Niznik H. B., Weiner D. M., Stormann T. M., Brann M. R., Kennedy J. L., Gelernter J. E., Rozmahel R., Yang Y. L., Israel Y. Human dopamine D1 receptor encoded by an intronless gene on chromosome 5. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):80–83. doi: 10.1038/347080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson L. W. The projections of the ventral tegmental area and adjacent regions: a combined fluorescent retrograde tracer and immunofluorescence study in the rat. Brain Res Bull. 1982 Jul-Dec;9(1-6):321–353. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(82)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiberi M., Jarvie K. R., Silvia C., Falardeau P., Gingrich J. A., Godinot N., Bertrand L., Yang-Feng T. L., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Caron M. G. Cloning, molecular characterization, and chromosomal assignment of a gene encoding a second D1 dopamine receptor subtype: differential expression pattern in rat brain compared with the D1A receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7491–7495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Tol H. H., Bunzow J. R., Guan H. C., Sunahara R. K., Seeman P., Niznik H. B., Civelli O. Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D4 receptor with high affinity for the antipsychotic clozapine. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):610–614. doi: 10.1038/350610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetterström T., Sharp T., Marsden C. A., Ungerstedt U. In vivo measurement of dopamine and its metabolites by intracerebral dialysis: changes after d-amphetamine. J Neurochem. 1983 Dec;41(6):1769–1773. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb00893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q. Y., Grandy D. K., Thambi L., Kushner J. A., Van Tol H. H., Cone R., Pribnow D., Salon J., Bunzow J. R., Civelli O. Cloning and expression of human and rat D1 dopamine receptors. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):76–80. doi: 10.1038/347076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Mestikawy S., Glowinski J., Hamon M. Presynaptic dopamine autoreceptors control tyrosine hydroxylase activation in depolarized striatal dopaminergic terminals. J Neurochem. 1986 Jan;46(1):12–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb12919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]