Abstract
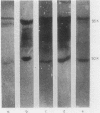
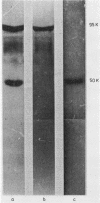
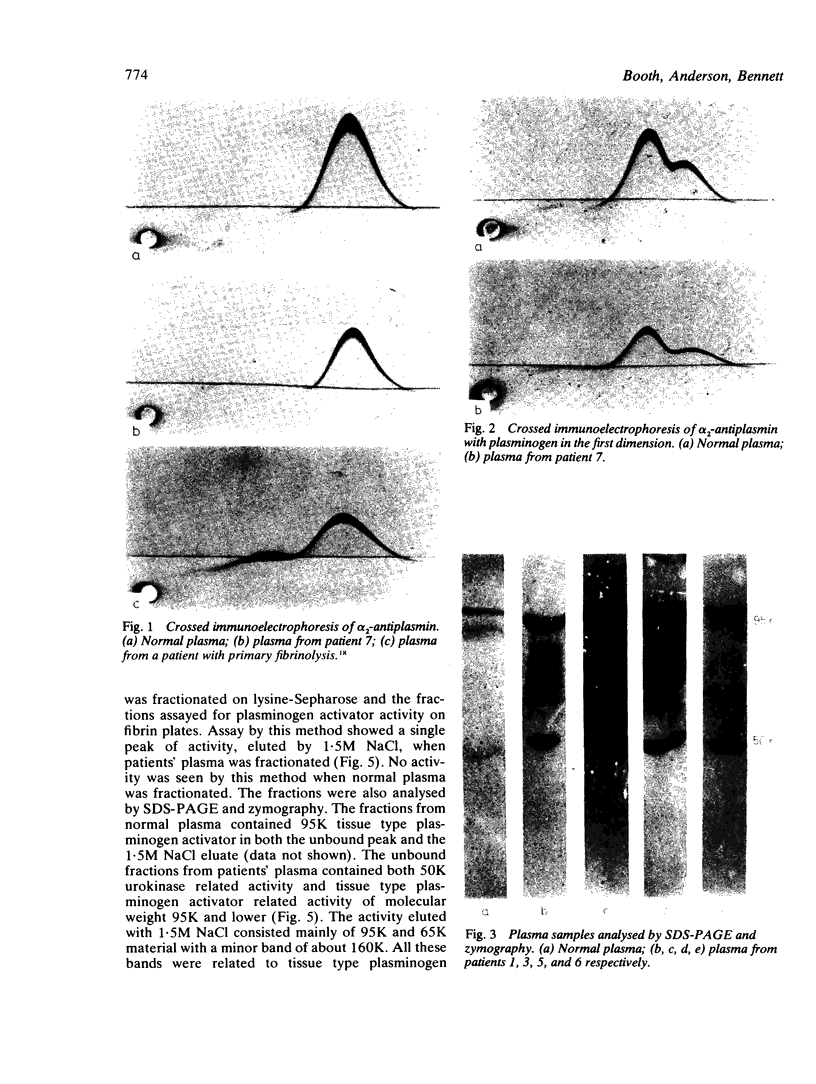
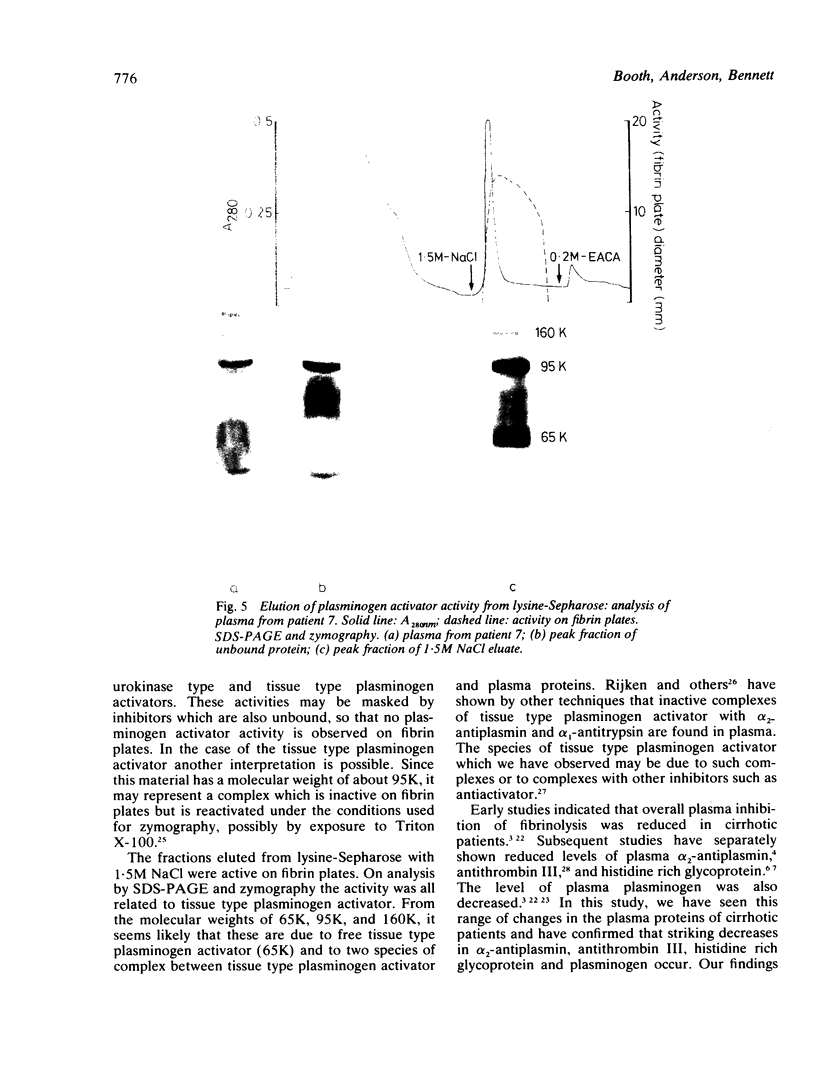
Plasma samples from patients with alcoholic cirrhosis were analysed for plasminogen activators and for inhibitors of the fibrinolytic system. Plasminogen activator activity was considerably increased in patients' plasma compared with normal. Immunochemical characterisation of these plasminogen activators showed that they included both tissue type and urokinase type plasminogen activator. The major inhibitor of plasmin, alpha 2-antiplasmin, was decreased in the patients, but no evidence for the generation of plasmin was found.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki N., Yamanaka T. The alpha2-plasmin inhibitor levels in liver diseases. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 Mar 1;84(1-2):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90481-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth N. A., Bennett B. Plasmin--alpha 2-antiplasmin complex as an indicator of in vivo fibrinolysis. Br J Haematol. 1982 Mar;50(3):537–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1982.tb01950.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth N. A., Bennett B. Plasmin-alpha 2-antiplasmin complexes in bleeding disorders characterized by primary or secondary fibrinolysis. Br J Haematol. 1984 Apr;56(4):545–556. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1984.tb02179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth N. A., Bennett B., Wijngaards G., Grieve J. H. A new life-long hemorrhagic disorder due to excess plasminogen activator. Blood. 1983 Feb;61(2):267–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLETCHER A. P., BIEDERMAN O., MOORE D., ALKJAERSIG N., SHERRY S. ABNORMAL PLASMINOGEN-PLASMIN SYSTEM ACTIVITY (FIBRINOLYSIS) IN PATIENTS WITH HEPATIC CIRRHOSIS: ITS CAUSE AND CONSEQUENCES. J Clin Invest. 1964 Apr;43:681–695. doi: 10.1172/JCI104953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Reich E. A study of proteases and protease-inhibitor complexes in biological fluids. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):223–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluft C., Los N. Demonstration of two forms of alpha 2-antiplasmin in plasma by modified crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Thromb Res. 1981 Jan 1;21(1-2):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korninger C., Stassen J. M., Collen D. Turnover of human extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator in rabbits. Thromb Haemost. 1981 Oct;46(3):658–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen H. R., Hoylaerts M., Collen D. Isolation and characterization of a human plasma protein with affinity for the lysine binding sites in plasminogen. Role in the regulation of fibrinolysis and identification as histidine-rich glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10214–10222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen H. R., Jacobs G., Collen D. Histidine-rich glycoprotein in a normal and a clinical population. Thromb Res. 1981 May 15;22(4):519–523. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(81)90115-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie M., Booth N. A., Bennett B. Comparative studies on human activators of plasminogen. Br J Haematol. 1981 Jan;47(1):77–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1981.tb02763.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllertz S., Clemmensen I. The primary inhibitor of plasmin in human plasma. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):545–553. doi: 10.1042/bj1590545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogston C. M., Ogston D. Plasma fibrinogen and plasminogen levels in health and in ischaemic heart disease. J Clin Pathol. 1966 Jul;19(4):352–356. doi: 10.1136/jcp.19.4.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogston D., Bennett N. B., Ogston C. M. The fibrinolytic enzyme system in hepatic cirrhosis and malignant metastases. J Clin Pathol. 1971 Dec;24(9):822–826. doi: 10.1136/jcp.24.9.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PURCELL G., Jr, PHILLIPS L. L. FIBRINOLYTIC ACTIVITY IN CIRRHOSIS OF THE LIVER. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1963 Aug;117:139–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., MENZIE C. A new method for the determination of fibrinogen in small samples of plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Feb;37(2):316–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radcliffe R., Heinze T. Isolation of plasminogen activator from human plasma by chromatography on lysine-sepharose. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jul;189(1):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Juhan-Vague I., Collen D. Complexes between tissue-type plasminogen activator and proteinase inhibitors in human plasma, identified with an immunoradiometric assay. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Feb;101(2):285–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Goodnough L. T., Boyle J. M., Heimburger N. Reduced histidine-rich glycoprotein levels in plasma of patients with advanced liver cirrhosis. Possible implications for enhanced fibrinolysis. Am J Med. 1982 Aug;73(2):179–182. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]