Abstract
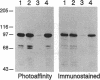
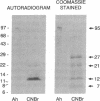
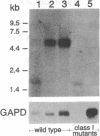
A cDNA encoding the murine Ah receptor (Ahb-1 allele for aromatic hydrocarbon responsiveness) has been isolated and characterized. Analysis of the deduced protein sequence revealed a region with similarity to the basic region/helix-loop-helix (BR/HLH) motif found in many transcription factors that undergo dimerization for function. In addition to the BR/HLH domain, the N-terminal domain of the Ah receptor has extensive sequence similarity to the human ARNT (aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator) protein and two regulatory proteins of Drosophila, Sim and Per. Photoaffinity labeling and peptide mapping studies indicate that the Ah receptor binds agonist at a domain that lies within this conserved N-terminal domain. The Ah receptor appears to be a ligand-activated transcription factor with a helix-loop-helix motif similar to those found in a variety of DNA-binding proteins, including Myc and MyoD.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradfield C. A., Glover E., Poland A. Purification and N-terminal amino acid sequence of the Ah receptor from the C57BL/6J mouse. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;39(1):13–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb R. R., Stoming T. A., Whitney J. B., 3rd The aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase (Ah) locus and a novel restriction-fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) are located on mouse chromosome 12. Biochem Genet. 1987 Jun;25(5-6):401–413. doi: 10.1007/BF00554549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Tjian R. Analysis of Sp1 in vivo reveals multiple transcriptional domains, including a novel glutamine-rich activation motif. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink C. J., Gasiewicz T. A., Whitlock J. P., Jr Protein-DNA interactions at a dioxin-responsive enhancer. Evidence that the transformed Ah receptor is heteromeric. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20708–20712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favreau L. V., Pickett C. B. Transcriptional regulation of the rat NAD(P)H:quinone reductase gene. Identification of regulatory elements controlling basal level expression and inducible expression by planar aromatic compounds and phenolic antioxidants. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4556–4561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hankinson O. Dominant and recessive aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase-deficient mutants of mouse hepatoma line, Hepa-1, and assignment of recessive mutants to three complementation groups. Somatic Cell Genet. 1983 Jul;9(4):497–514. doi: 10.1007/BF01543050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. C., Reyes H., Chu F. F., Sander F., Conley L. H., Brooks B. A., Hankinson O. Cloning of a factor required for activity of the Ah (dioxin) receptor. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):954–958. doi: 10.1126/science.1852076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel D. I., Whitlock J. P., Jr Induction of mRNA specific for cytochrome P1-450 in wild type and variant mouse hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10390–10394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. B., Miller A. G., Israel D. I., Galeazzi D. R., Whitlock J. P., Jr Biochemical and genetic analysis of variant mouse hepatoma cells which overtranscribe the cytochrome P1-450 gene in response to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12357–12363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent B. C., Treitel M. A., Carlson M. The SNF5 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a glutamine- and proline-rich transcriptional activator that affects expression of a broad spectrum of genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5616–5625. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legraverend C., Hannah R. R., Eisen H. J., Owens I. S., Nebert D. W., Hankinson O. Regulatory gene product of the Ah locus. Characterization of receptor mutants among mouse hepatoma clones. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6402–6407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. G., Israel D., Whitlock J. P., Jr Biochemical and genetic analysis of variant mouse hepatoma cells defective in the induction of benzo(a)pyrene-metabolizing enzyme activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3523–3527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K., Faloona F., Scharf S., Saiki R., Horn G., Erlich H. Specific enzymatic amplification of DNA in vitro: the polymerase chain reaction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):263–273. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nambu J. R., Lewis J. O., Wharton K. A., Jr, Crews S. T. The Drosophila single-minded gene encodes a helix-loop-helix protein that acts as a master regulator of CNS midline development. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1157–1167. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90292-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Gonzalez F. J. P450 genes: structure, evolution, and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:945–993. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okey A. B., Vella L. M., Harper P. A. Detection and characterization of a low affinity form of cytosolic Ah receptor in livers of mice nonresponsive to induction of cytochrome P1-450 by 3-methylcholanthrene. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;35(6):823–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdew G. H., Hollenback C. E. Analysis of photoaffinity-labeled aryl hydrocarbon receptor heterogeneity by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 3;29(26):6210–6214. doi: 10.1021/bi00478a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Glover E., Bradfield C. A. Characterization of polyclonal antibodies to the Ah receptor prepared by immunization with a synthetic peptide hapten. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;39(1):20–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Glover E., Taylor B. A. The murine Ah locus: a new allele and mapping to chromosome 12. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;32(4):471–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Glover E. Variation in the molecular mass of the Ah receptor among vertebrate species and strains of rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 14;146(3):1439–1449. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90811-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongratz I., Strömstedt P. E., Mason G. G., Poellinger L. Inhibition of the specific DNA binding activity of the dioxin receptor by phosphatase treatment. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16813–16817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder W. A., Shelton J. B., Shelton J. R. An examination of conditions for the cleavage of polypeptide chains with cyanogen bromide: application to catalase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):551–556. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telakowski-Hopkins C. A., King R. G., Pickett C. B. Glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene: identification of regulatory elements required for basal level and inducible expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1000–1004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Tapscott S., Thayer M., Krause M., Benezra R., Blackwell T. K., Turner D., Rupp R., Hollenberg S. The myoD gene family: nodal point during specification of the muscle cell lineage. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):761–766. doi: 10.1126/science.1846704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton K. A., Yedvobnick B., Finnerty V. G., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. opa: a novel family of transcribed repeats shared by the Notch locus and other developmentally regulated loci in D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]