Abstract
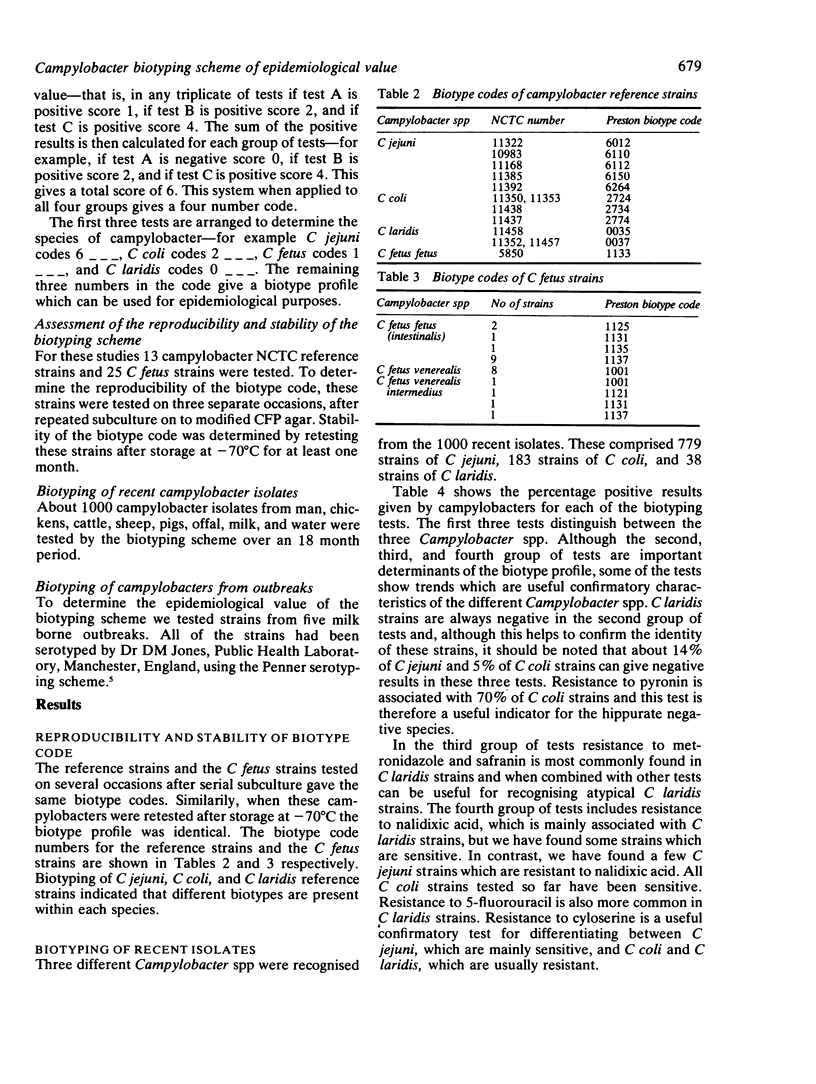
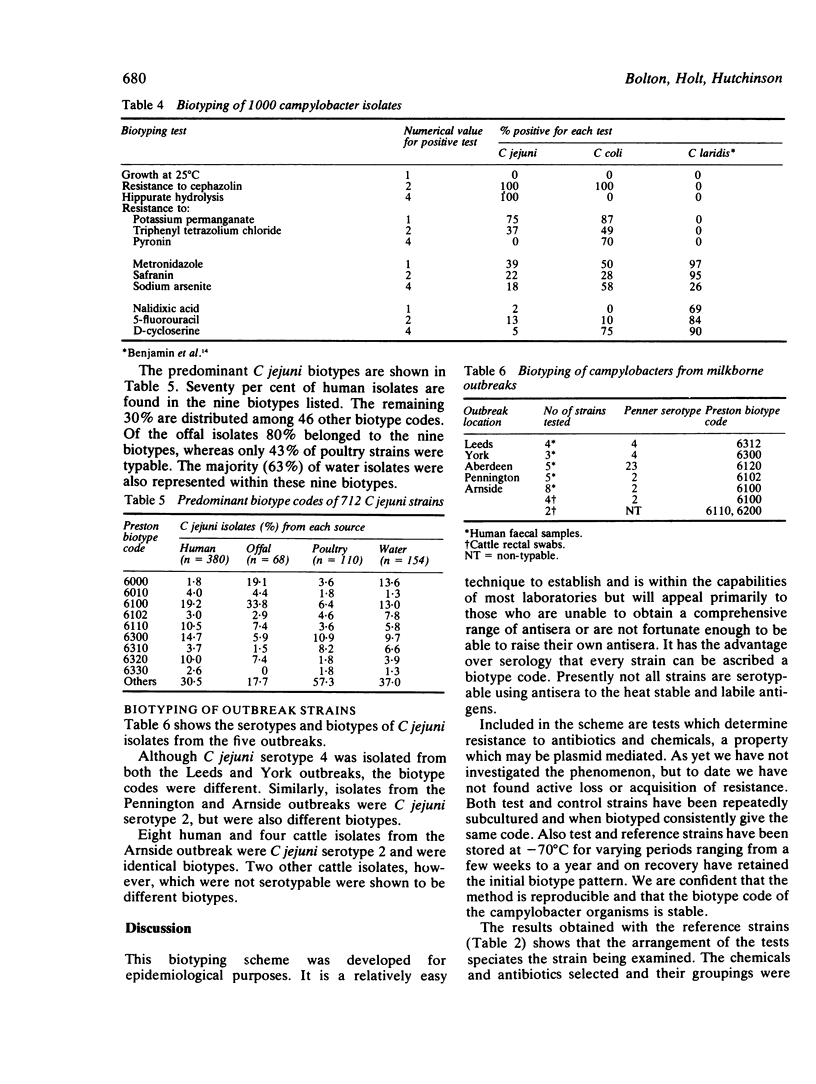
A biotyping scheme has been developed which utilises 12 tests, including growth at 28 degrees C, hippurate hydrolysis, and 10 resistotyping tests. These tests are arranged in groups of three, and by assigning a numerical value to each positive test a four figure code is produced for each strain. The order of the tests is such that campylobacters are both speciated and biotyped . This scheme recognises Campylobacter jejuni, C coli, "C laridis ," C fetus fetus, and C fetus subspecies venerealis. The reproducibility of the biotyping technique and the stability of the biotype code have been determined by testing campylobacter reference strains. The routine application of the scheme has also been evaluated by biotyping 1000 recent campylobacter isolates, and the epidemiological value has been confirmed by testing serotyped isolates from several milk borne outbreaks.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolton F. J., Coates D. Development of a blood-free Campylobacter medium: screening tests on basal media and supplements, and the ability of selected supplements to facilitate aerotolerance. J Appl Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;54(1):115–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1983.tb01308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey S. M. Hippurate hydrolysis by Campylobacter fetus. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):435–437. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.435-437.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert G. A., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Lambert M. A., Blaser M. J., Moss C. W. 30 years of campylobacters: biochemical characteristics and a biotyping proposal for Campylobacter jejuni. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1065–1073. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1065-1073.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., De Grandis S., Fleming P. C. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus to eight cephalosporins with special reference to species differentiation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Dec;18(6):948–951. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.6.948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H., Woodward D. L., Edgar J. A., Laroche L. J., Gill P. Serotyping of Campylobacter jejuni by slide agglutination based on heat-labile antigenic factors. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):761–768. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.761-768.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N. Passive hemagglutination technique for serotyping Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni on the basis of soluble heat-stable antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):732–737. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.732-737.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piot P., Van Dyck E., Totten P. A., Holmes K. K. Identification of Gardnerella (Haemophilus) vaginalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):19–24. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.19-24.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B., Benjamin J. '1001' Campylobacters: cultural characteristics of intestinal campylobacters from man and animals. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Dec;85(3):427–442. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400063506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B., Benjamin J. Differentiation of enteropathogenic Campylobacter. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Nov;33(11):1122–1122. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.11.1122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


