Abstract
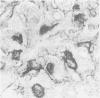
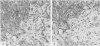
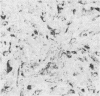
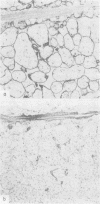
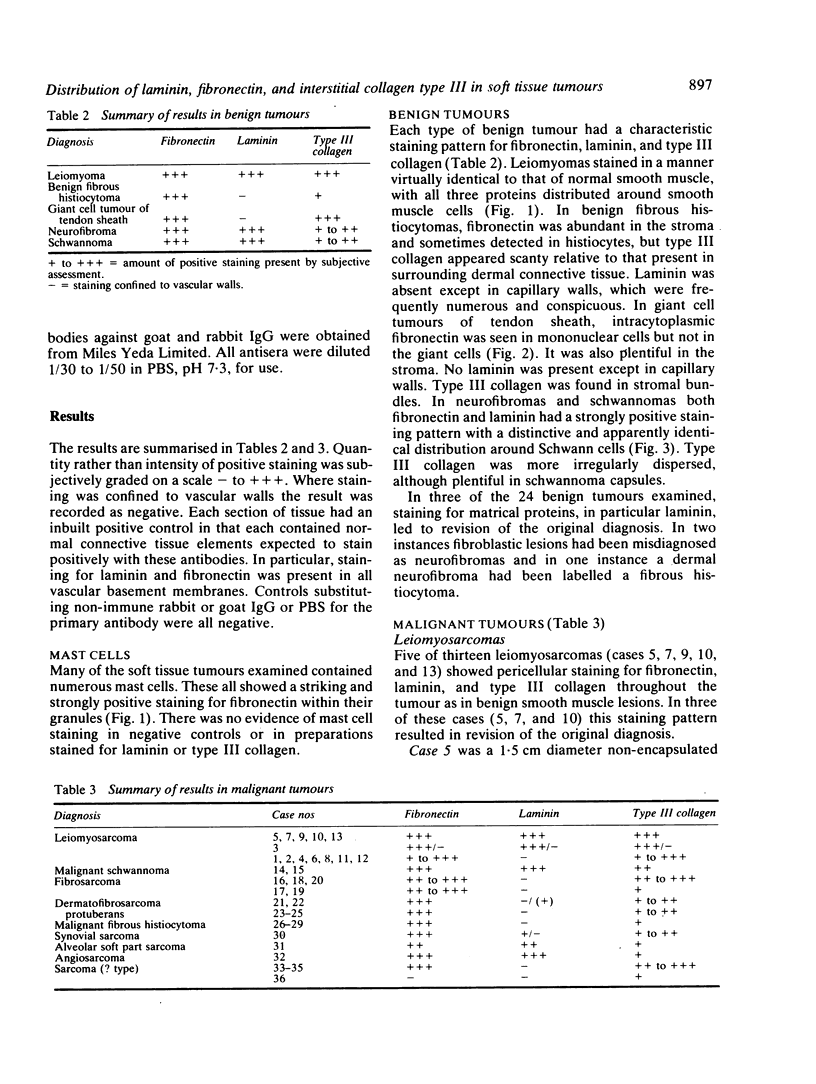
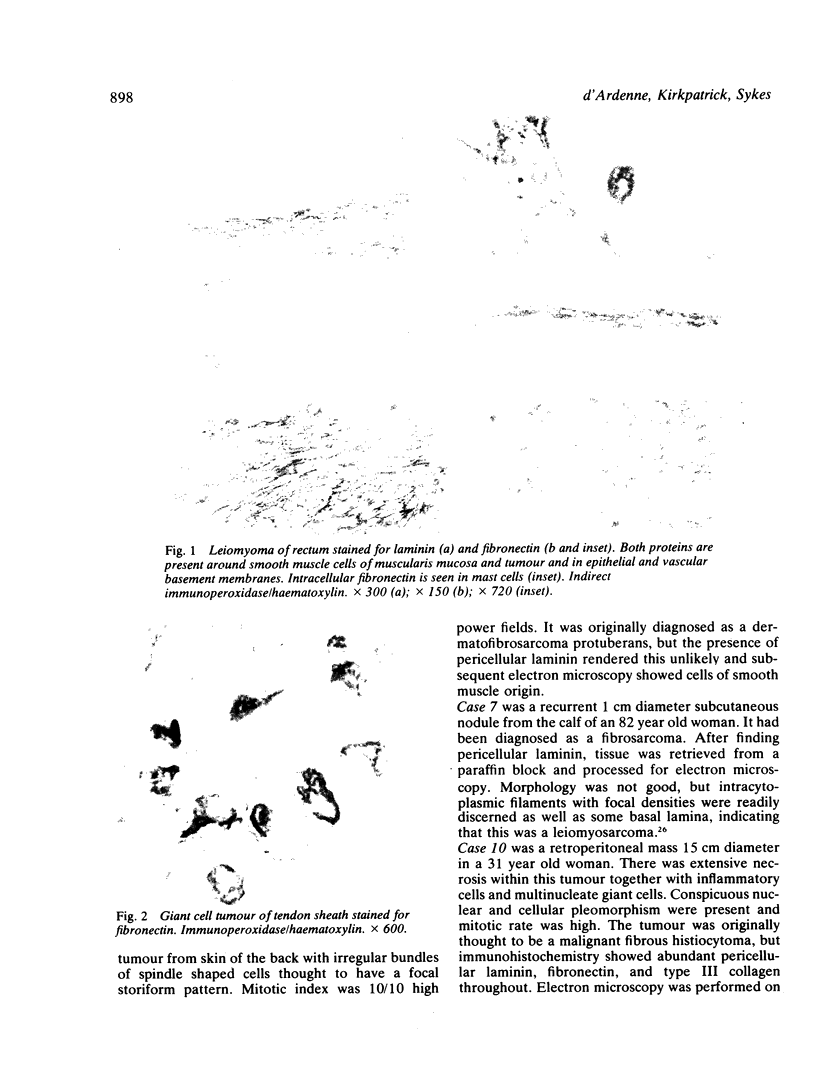
The distributions of laminin, fibronectin, and interstitial collagen type III have been investigated in a series of 60 soft tissue tumours by immunochemistry. Positive laminin staining was seen in sites predicted by the distribution of ultrastructurally visible basal lamina. Pericellular laminin was present in all benign tumours of Schwann cell and smooth muscle origin examined, in the two malignant Schwannomas examined, and in six of 13 leiomyosarcomas. It was also evident around nests of cells in an alveolar soft part sarcoma and around malignant endothelial cells in an angiosarcoma. In fibroblastic and fibrohistiocytic tumours it was found only in blood vessel walls. The results of laminin staining led to revision of the original histopathological diagnosis in seven of the 60 cases studied. Fibronectin was abundant in the stroma of most neoplasms, both benign and malignant. It was also found in a distribution parallel to that of laminin. In some tumours this was clearly distinguishable from the distribution of interstitial collagen. Intracellular fibronectin was shown consistently only in mast cell granules. Its demonstration in synovial cells, fibroblasts, and histiocytes was more variable. Interstitial collagen type II had the most irregular distribution of the three proteins. It was as plentiful in tumours of smooth muscle origin as in tumours of fibroblastic origin, but was scanty in fibrous histiocytomas. Its distribution appeared similar to that of laminin and fibronectin in leiomyomas, but differed from these two proteins in Schwann cell tumours and other neoplasms. In one leiomyosarcoma fibronectin, laminin, and type III collagen appeared to be lost concomitantly from tumour cell peripheries.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrechtsen R., Nielsen M., Wewer U., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Basement membrane changes in breast cancer detected by immunohistochemical staining for laminin. Cancer Res. 1981 Dec;41(12 Pt 1):5076–5081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birembaut P., Caron Y., van Cauwenberge D., Foidart J. M. Distribution of laminin, a basement membrane glycoprotein in epithelial proliferations. A preliminary study in the breast, the lungs and uterine cervix. Coll Relat Res. 1983;3(1):25–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boselli J. M., Macarak E. J., Clark C. C., Brownell A. G., Martinez-Hernandez A. Fibronectin: its relationship to basement membranes. I. Light microscopic studies. Coll Relat Res. 1981 Sep;1(5):391–404. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(81)80024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn R. H., Banerjee S. D., Bernfield M. R. Basal lamina of embryonic salivary epithelia. Nature of glycosaminoglycan and organization of extracellular materials. J Cell Biol. 1977 May;73(2):464–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.2.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtoy P. J., Timpl R., Farquhar M. G. Comparative distribution of laminin, type IV collagen, and fibronectin in the rat glomerulus. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Sep;30(9):874–886. doi: 10.1177/30.9.7130672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ardenne A. J., Burns J., Sykes B. C., Bennett M. K. Fibronectin and type III collagen in epithelial neoplasms of gastrointestinal tract and salivary gland. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jul;36(7):756–763. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.7.756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ardenne A. J., Burns J., Sykes B. C., Kirkpatrick P. Comparative distribution of fibronectin and type III collagen in normal human tissues. J Pathol. 1983 Sep;141(1):55–69. doi: 10.1002/path.1711410107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ardenne A. J., McGee J. O. Fibronectin in disease. J Pathol. 1984 Apr;142(4):235–251. doi: 10.1002/path.1711420402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner L., de Lanerolle P., Costa J. Immunoreactivity of paraffin-embedded normal tissues and mesenchymal tumors for smooth muscle myosin. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Nov;80(5):677–681. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/80.5.677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Boulay C. E. Demonstration of fibronectin in soft tissue tumours using the immunoperoxidase technique. Diagn Histopathol. 1982 Oct-Dec;5(4):283–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foidart J. M., Bere E. W., Jr, Yaar M., Rennard S. I., Gullino M., Martin G. R., Katz S. I. Distribution and immunoelectron microscopic localization of laminin, a noncollagenous basement membrane glycoprotein. Lab Invest. 1980 Mar;42(3):336–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forni M., Klatt E. C., Shaw S. T., Jr, Taylor C. R., Lukes R. J., Meyer P. R. Immunohistochemical characterization of reactive and neoplastic mast cells. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Nov;80(5):660–665. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/80.5.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. R., Bernfield M. R. The basal lamina of the postnatal mammary epithelium contains glycosaminoglycans in a precise ultrastructural organization. Dev Biol. 1980 Jan;74(1):118–135. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman E. G., Oldberg A., Martin G. R., Ruoslahti E. Codistribution of heparan sulfate proteoglycan, laminin, and fibronectin in the extracellular matrix of normal rat kidney cells and their coordinate absence in transformed cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;94(1):28–35. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick P., d'Ardenne A. J. Effects of fixation and enzymatic digestion on the immunohistochemical demonstration of laminin and fibronectin in paraffin embedded tissue. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jun;37(6):639–644. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.6.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., Klebe R. J., Martin G. R. Role of collagenous matrices in the adhesion and growth of cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;88(3):473–485. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.3.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labat-Robert J., Birembaut P., Robert L., Adnet J. J. Modification of fibronectin distribution pattern in solid human tumours. Diagn Histopathol. 1981 Oct-Dec;4(4):299–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Foidart J. M., Ekblom P. Immunohistochemical demonstration of laminin, the major glycoprotein of basement membranes, as an aid in the diagnosis of soft tissue tumors. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Mar;79(3):306–311. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/79.3.306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller P., Achtsätter H., Butzengeiger M., Schüle B. The distribution of fibronectin in lymph nodes infiltrated by Hodgkin's disease. An immunoperoxidase study on paraffin sections. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1983;400(3):319–329. doi: 10.1007/BF00612193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R. Laminin, fibronectin, and collagen in synaptic and extrasynaptic portions of muscle fiber basement membrane. J Cell Biol. 1982 May;93(2):442–451. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.2.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenman S., Vaheri A. Fibronectin in human solid tumors. Int J Cancer. 1981;27(4):427–435. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910270403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Rohde H., Robey P. G., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., Martin G. R. Laminin--a glycoprotein from basement membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9933–9937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaheri A., Mosher D. F. High molecular weight, cell surface-associated glycoprotein (fibronectin) lost in malignant transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 18;516(1):1–25. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartio T., Seppä H., Vaheri A. Susceptibility of soluble and matrix fibronectins to degradation by tissue proteinases, mast cell chymase and cathepsin G. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):471–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. A., Meyer A. T. Ultrastructure of gastric leiomyoma. Arch Pathol. 1969 Jan;87(1):71–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yurt R., Austen K. F. Preparative purification of the rat mast cell chymase: characterization and interaction with granule components. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1405–1419. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]