Abstract
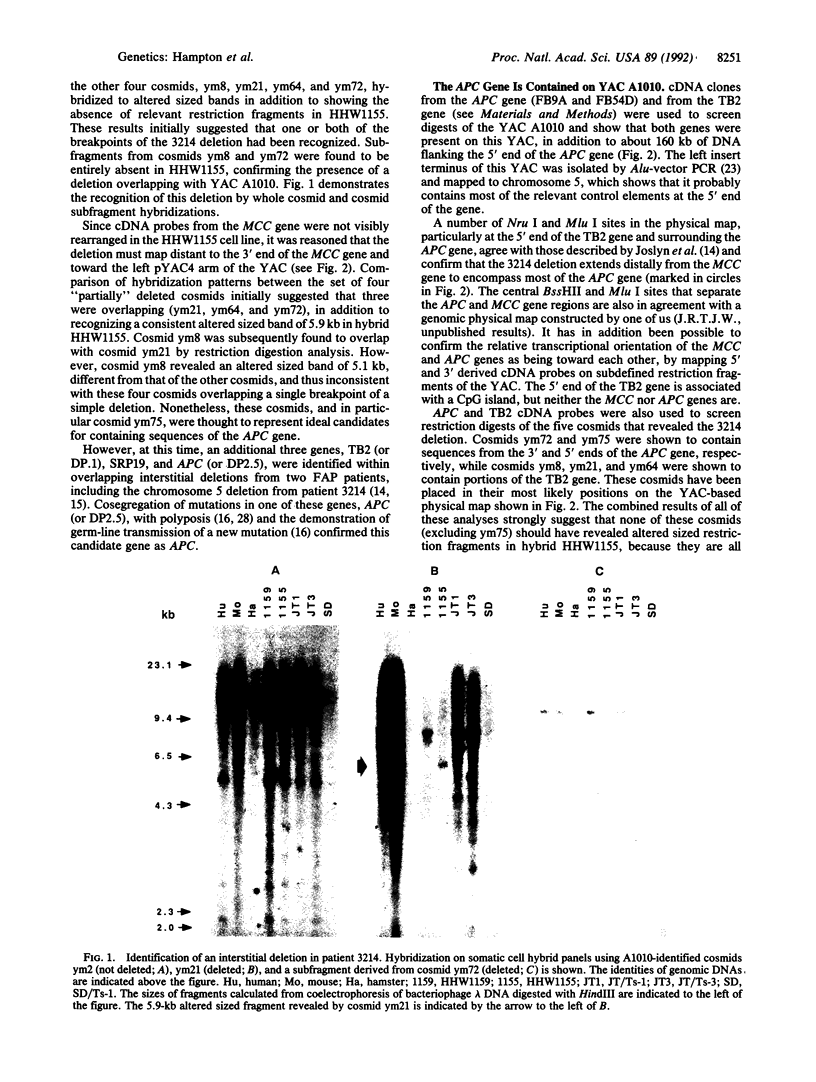
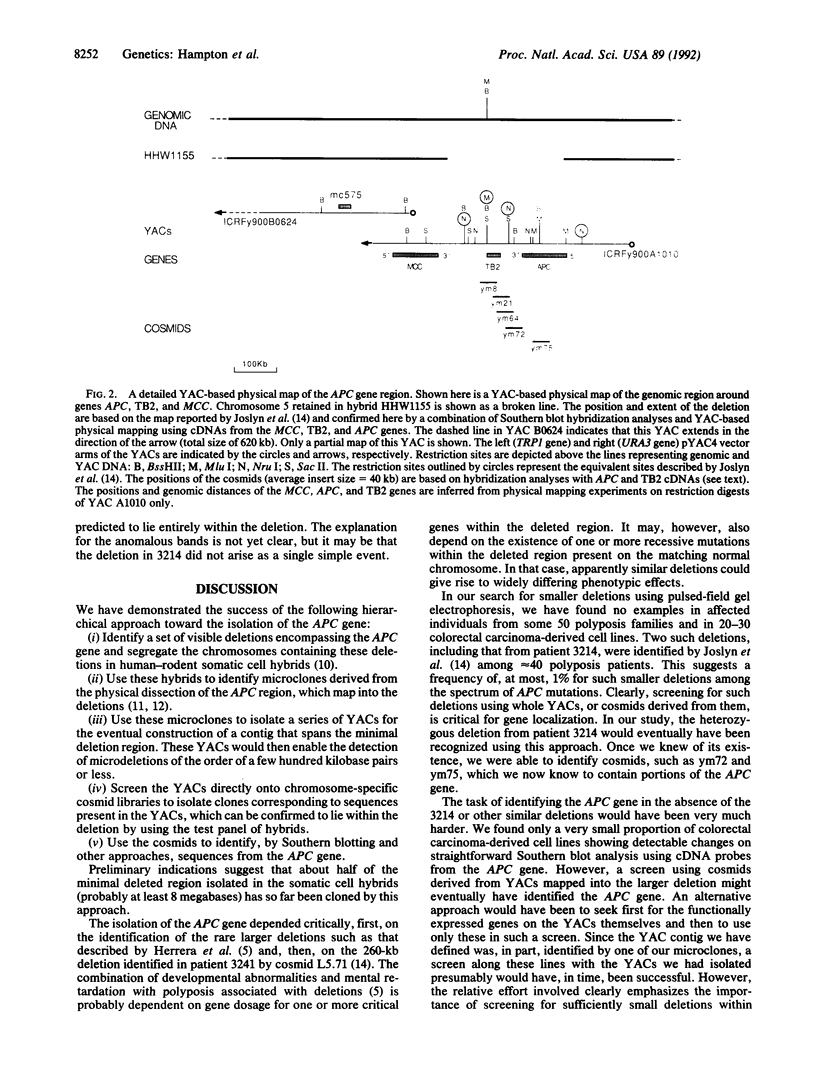
Two yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) spanning a total distance of 1.1 megabase pairs of DNA around the MCC (for mutated in colorectal carcinoma) and APC (for adenomatous polyposis coli) genes at 5q21 have been isolated and characterized. Starting from the MCC gene, a strategy was undertaken to identify constitutional submicroscopic deletions in familial adenomatous polyposis patients that might considerably narrow down the position of the APC gene. To this end, YACs identified by the MCC gene were screened across a chromosome 5-specific cosmid library to provide a source of DNA probes for genomic scanning. The cosmids isolated from these experiments were used to screen a panel of somatic cell hybrids containing chromosome 5 segregated from patients suspected to carry putative interstitial deletions. This screening approach led to the confirmation of a small heterozygous deletion in a polyposis patient that overlaps one of the two isolated YACs. This YAC has been shown to contain the entire APC gene, in addition to a significant portion of DNA flanking the 5' end of the gene, and should therefore prove a valuable resource for functional studies by transfer to colorectal tumor-derived cell lines.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashton-Rickardt P. G., Dunlop M. G., Nakamura Y., Morris R. G., Purdie C. A., Steel C. M., Evans H. J., Bird C. C., Wyllie A. H. High frequency of APC loss in sporadic colorectal carcinoma due to breaks clustered in 5q21-22. Oncogene. 1989 Oct;4(10):1169–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton-Rickardt P. G., Wyllie A. H., Bird C. C., Dunlop M. G., Steel C. M., Morris R. G., Piris J., Romanowski P., Wood R., White R. MCC, a candidate familial polyposis gene in 5q.21, shows frequent allele loss in colorectal and lung cancer. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1881–1886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer W. F., Bailey C. J., Bodmer J., Bussey H. J., Ellis A., Gorman P., Lucibello F. C., Murday V. A., Rider S. H., Scambler P. Localization of the gene for familial adenomatous polyposis on chromosome 5. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):614–616. doi: 10.1038/328614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A., Waterston R., Kiff J., Sulston J., Kohara Y. Genome linking with yeast artificial chromosomes. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):184–186. doi: 10.1038/335184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyette M. C., Cho K., Fasching C. L., Levy D. B., Kinzler K. W., Paraskeva C., Vogelstein B., Stanbridge E. J. Progression of colorectal cancer is associated with multiple tumor suppressor gene defects but inhibition of tumorigenicity is accomplished by correction of any single defect via chromosome transfer. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1387–1395. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groden J., Thliveris A., Samowitz W., Carlson M., Gelbert L., Albertsen H., Joslyn G., Stevens J., Spirio L., Robertson M. Identification and characterization of the familial adenomatous polyposis coli gene. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):589–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampton G. M., Howe C., Leuteritz G., Thomas H., Bodmer W. F., Solomon E., Ballhausen W. G. Regional mapping of 22 microclones around the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) locus on chromosome 5q. Hum Genet. 1991 Nov;88(1):112–114. doi: 10.1007/BF00204940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampton G., Leuteritz G., Lüdecke H. J., Senger G., Trautmann U., Thomas H., Solomon E., Bodmer W. F., Horsthemke B., Claussen U. Characterization and mapping of microdissected genomic clones from the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) region. Genomics. 1991 Oct;11(2):247–251. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90130-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera L., Kakati S., Gibas L., Pietrzak E., Sandberg A. A. Gardner syndrome in a man with an interstitial deletion of 5q. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Nov;25(3):473–476. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320250309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockey K. A., Mulcahy M. T., Montgomery P., Levitt S. Deletion of chromosome 5q and familial adenomatous polyposis. J Med Genet. 1989 Jan;26(1):61–62. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joslyn G., Carlson M., Thliveris A., Albertsen H., Gelbert L., Samowitz W., Groden J., Stevens J., Spirio L., Robertson M. Identification of deletion mutations and three new genes at the familial polyposis locus. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):601–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Nilbert M. C., Su L. K., Vogelstein B., Bryan T. M., Levy D. B., Smith K. J., Preisinger A. C., Hedge P., McKechnie D. Identification of FAP locus genes from chromosome 5q21. Science. 1991 Aug 9;253(5020):661–665. doi: 10.1126/science.1651562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Nilbert M. C., Vogelstein B., Bryan T. M., Levy D. B., Smith K. J., Preisinger A. C., Hamilton S. R., Hedge P., Markham A. Identification of a gene located at chromosome 5q21 that is mutated in colorectal cancers. Science. 1991 Mar 15;251(4999):1366–1370. doi: 10.1126/science.1848370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larin Z., Monaco A. P., Lehrach H. Yeast artificial chromosome libraries containing large inserts from mouse and human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4123–4127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppert M., Dobbs M., Scambler P., O'Connell P., Nakamura Y., Stauffer D., Woodward S., Burt R., Hughes J., Gardner E. The gene for familial polyposis coli maps to the long arm of chromosome 5. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1411–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.3479843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAlpine P. J., Van Cong N., Boucheix C., Pakstis A. J., Doute R. C., Shows T. B. The 1987 Catalog of mapped genes and report of the nomenclature committee. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;46(1-4):29–101. doi: 10.1159/000132472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. L., Ledbetter S. A., Corbo L., Victoria M. F., Ramírez-Solis R., Webster T. D., Ledbetter D. H., Caskey C. T. Alu polymerase chain reaction: a method for rapid isolation of human-specific sequences from complex DNA sources. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6686–6690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nizetić D., Zehetner G., Monaco A. P., Gellen L., Young B. D., Lehrach H. Construction, arraying, and high-density screening of large insert libraries of human chromosomes X and 21: their potential use as reference libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3233–3237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragoussis J., Monaco A., Mockridge I., Kendall E., Campbell R. D., Trowsdale J. Cloning of the HLA class II region in yeast artificial chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3753–3757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubock M. J., Larin Z., Cook M., Papalopulu N., Krumlauf R., Lehrach H. A yeast artificial chromosome containing the mouse homeobox cluster Hox-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4751–4755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon E., Voss R., Hall V., Bodmer W. F., Jass J. R., Jeffreys A. J., Lucibello F. C., Patel I., Rider S. H. Chromosome 5 allele loss in human colorectal carcinomas. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):616–619. doi: 10.1038/328616a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Oshimura M., Kikuchi R., Seki M., Hayashi T., Miyaki M. Suppression of tumorigenicity in human colon carcinoma cells by introduction of normal chromosome 5 or 18. Nature. 1991 Jan 24;349(6307):340–342. doi: 10.1038/349340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varesco L., Thomas H. J., Cottrell S., Murday V., Fennell S. J., Williams S., Searle S., Sheer D., Bodmer W. F., Frischauf A. M. CpG island clones from a deletion encompassing the gene for adenomatous polyposis coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10118–10122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Kern S. E., Preisinger A. C., Leppert M., Nakamura Y., White R., Smits A. M., Bos J. L. Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 1;319(9):525–532. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809013190901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. V., Jones T. A., Cottrell S., Zehetner G., Varesco L., Ward T., Thomas H., Lawson P. A., Solomon E., Bodmer W. F. Fine mapping of probes in the adenomatous polyposis coli region of chromosome 5 by in situ hybridization. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1991 Sep;3(5):382–389. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870030509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]