Abstract
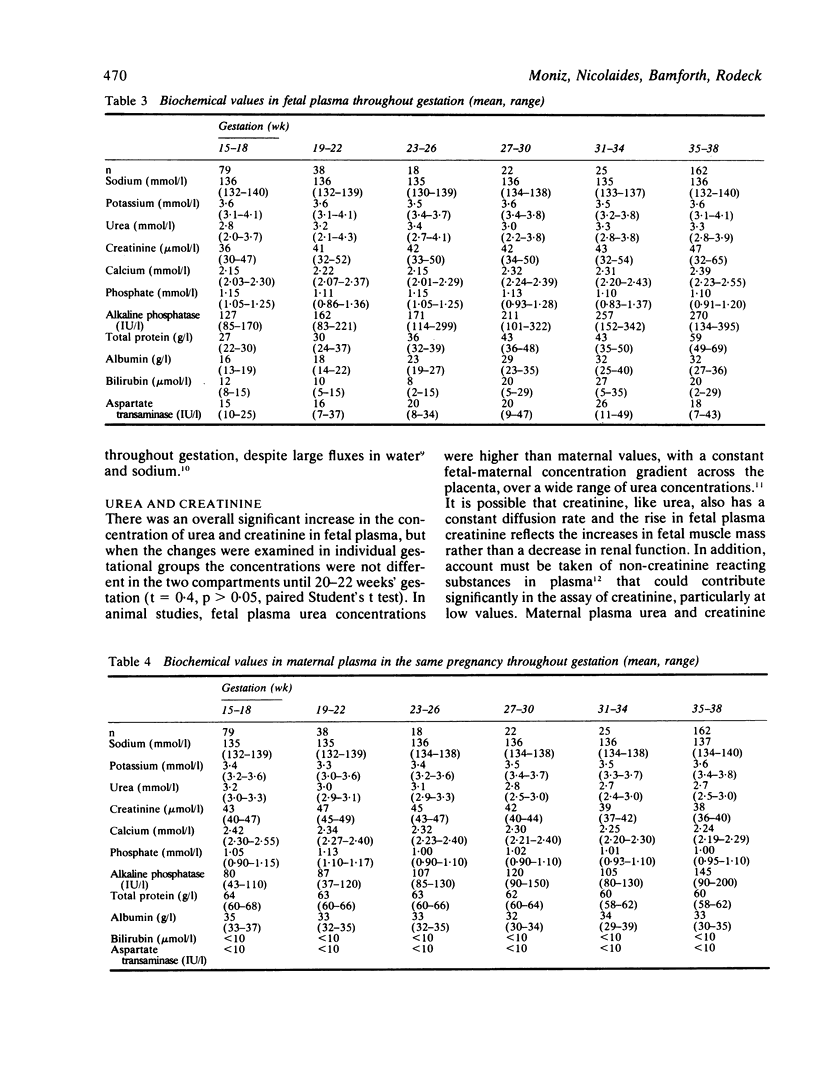
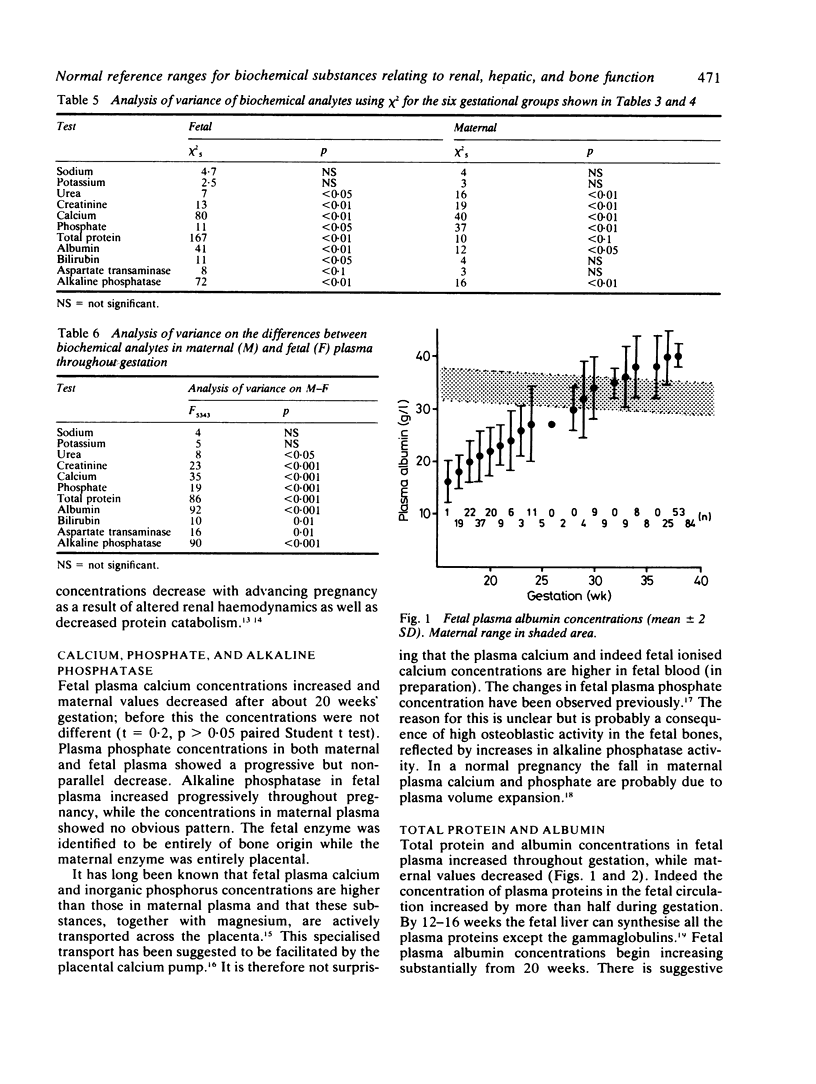
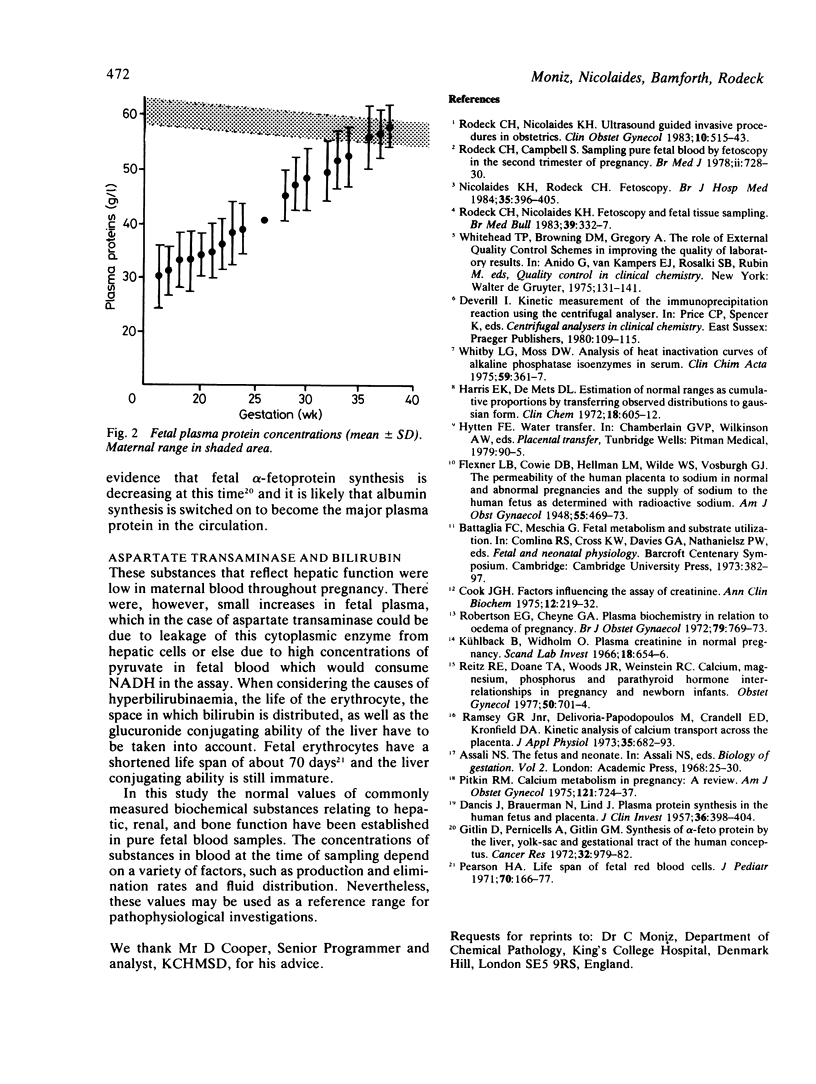
Normal reference ranges for sodium, potassium, urea, creatinine, calcium, phosphate, total protein, albumin, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, and aspartate transaminase were determined from 344 fetal and maternal plasma samples between 15 and 38 weeks' gestation. Pure fetal blood was obtained by fetoscopy in the second trimester and in the third trimester by umbilical cord puncture at delivery. All biochemical substances were measured by continuous flow (SMAC, Technicon) except albumin, which was measured by turbidimetry (CobasBio, Roche). The resulting data were analysed on an AMDAHL 470A computer and reference ranges covering 2.5 to 97.5 percentiles were defined. Analysis of variance was performed to examine the overall effect of gestational age on the analytes measured and on the changes in the fetal compartment relative to the mothers'. A paired t test was performed to examine how these biochemical substances in fetal plasma related to maternal plasma from the same pregnancy.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cook J. G., Association of clinical Biochemists' Scientific and Technica Committee Factors influencing the assay of creatinine. Ann Clin Biochem. 1975 Nov;12(6):219–232. doi: 10.1177/000456327501200162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANCIS J., BRAVERMAN N., LIND J. Plasma protein synthesis in the human fetus and placenta. J Clin Invest. 1957 Mar;36(3):398–404. doi: 10.1172/JCI103436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin D., Perricelli A., Gitlin G. M. Synthesis of -fetoprotein by liver, yolk sac, and gastrointestinal tract of the human conceptus. Cancer Res. 1972 May;32(5):979–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. K., DeMets D. L. Estimation of normal ranges and cumulative proportions by transforming observed distributions to gaussian form. Clin Chem. 1972 Jul;18(7):605–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlbäck B., Widholm O. Plasma creatinine in normal pregnancy. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1966;18(6):654–656. doi: 10.3109/00365516609049049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaides K., Rodeck C. H. Prenatal diagnosis. Fetoscopy. Br J Hosp Med. 1984 Jun;31(6):396–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson H. A. Life-span of the fetal red blood cell. J Pediatr. 1967 Feb;70(2):166–171. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(67)80410-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitkin R. M. Calcium metabolism in pregnancy: a review. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1975 Mar 1;121(5):724–737. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(75)90481-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramberg C. F., Jr, Delivoria-Papadopoulos M., Crandall E. D., Kronfeld D. S. Kinetic analysis of calcium transport across the placenta. J Appl Physiol. 1973 Nov;35(5):682–688. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1973.35.5.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitz R. E., Daane T. A., Woods J. R., Weinstein R. L. Calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and parathyroid hormone interrelationships in pregnancy and newborn infants. Obstet Gynecol. 1977 Dec;50(6):701–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson E. G., Cheyne G. A. Plasma biochemistry in relation to oedema of pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1972 Sep;79(9):769–776. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1972.tb12918.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodeck C. H., Campbell S. Sampling pure fetal blood by fetoscopy in second trimester of pregnancy. Br Med J. 1978 Sep 9;2(6139):728–730. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6139.728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodeck C. H., Nicolaides K. H. Fetoscopy and fetal tissue sampling. Br Med Bull. 1983 Oct;39(4):332–337. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodeck C. H., Nicolaides K. H. Ultrasound guided invasive procedures in obstetrics. Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 1983 Dec;10(3):515–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitby L. G., Moss D. W. Analysis of heat inactivation curves of alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes in serum. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 Mar 24;59(3):361–367. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


