Abstract
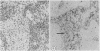
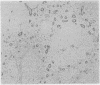
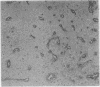
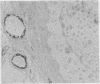
Forty six lymph nodes were examined with the indirect immunoperoxidase technique for the distribution of fibronectin and laminin. Fibronectin was present in the framework of the tissue and the basal lamina of blood vessels, giving a clear outline of nodal architecture. Intracellular fibronectin was observed in cases of reactive sinus histiocytosis, when about a third of macrophages exhibited strong positivity. Mast cells were positive. A pronounced increase in extracellular fibronectin was seen in nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease, although heavily hyalinised areas exhibited only superficial positivity. Reed-Sternberg and mononuclear Hodgkin's cells were consistently negative for fibronectin. Laminin staining was localised to vascular and marginal sinus basement membranes. No cellular positivity was evident. The distribution of laminin indicated a pronounced increase in vascularity in nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease, which was especially prevalent within the dense fibrous trabeculae. In contrast, however, examination of the other Rye subtypes showed a lesser degree of vascularity with numbers of vessels similar to those observed in reactive follicular hyperplasia. Laminin was found to be more efficient than factor VIII related antigen as a vascular marker.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahamson D. R., Caulfield J. P. Proteinuria and structural alterations in rat glomerular basement membranes induced by intravenously injected anti-laminin immunoglobulin G. J Exp Med. 1982 Jul 1;156(1):128–145. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom A. L., Giddings J. C. Value of factor VIII related antigen as a means of demonstrating extramedullary megakaryopoiesis. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Nov;37(11):1317–1317. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.11.1317-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom A. L., Giddings J. C., Wilks C. J. Factor 8 on the vascular intima: possible importance in haemostasis and thrombosis. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 14;241(111):217–219. doi: 10.1038/newbio241217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorf W. H., Mukai K., Rosai J. Immunohistochemical identification of factor VIII-related antigen in endothelial cells of cutaneous lesions of alleged vascular nature. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 Feb;75(2):167–171. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/75.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker J., Smith P. J. Immunohistochemical localisation of factor VIII-related antigen in Hodgkin's disease. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jan;37(1):37–44. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ardenne A. J., Burns J., Sykes B. C., Kirkpatrick P. Comparative distribution of fibronectin and type III collagen in normal human tissues. J Pathol. 1983 Sep;141(1):55–69. doi: 10.1002/path.1711410107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ardenne A. J., McGee J. O. Fibronectin in disease. J Pathol. 1984 Apr;142(4):235–251. doi: 10.1002/path.1711420402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foidart J. M., Bere E. W., Jr, Yaar M., Rennard S. I., Gullino M., Martin G. R., Katz S. I. Distribution and immunoelectron microscopic localization of laminin, a noncollagenous basement membrane glycoprotein. Lab Invest. 1980 Mar;42(3):336–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. H., Painter R. G., Birdwell C., Plow E. F. The detection, immunofluorescent localization, and thrombin induced release of human platelet-associated fibronectin antigen. J Supramol Struct. 1979;11(2):167–174. doi: 10.1002/jss.400110206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W., De los Santos R. P., Hoyer J. R. Antihemophilic factor antigen. Localization in endothelial cells by immunofluorescent microscopy. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2737–2744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innes D. J., Jr, Mills S. E., Walker G. K. Megakaryocytic leukemia; identification utilizing anti-factor VIII immunoperoxidase. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Jan;77(1):107–110. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/77.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Hoyer L. W., Nachman R. L. Synthesis of antihemophilic factor antigen by cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2757–2764. doi: 10.1172/JCI107471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson S., Rubin K., Hök M., Ahlgren T., Seljelid R. In vitro biosynthesis of cold insoluble globulin (fibronectin) by mouse peritoneal macrophages. FEBS Lett. 1979 Sep 15;105(2):313–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80637-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. L., Crocker J., Gregory J., Guibarra M., Curran R. C. Angiofollicular lymph node hyperplasia (Castleman's disease): an immunohistochemical and enzyme-histochemical study of the hyaline-vascular form of lesion. J Pathol. 1984 Oct;144(2):131–147. doi: 10.1002/path.1711440208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick P., d'Ardenne A. J. Effects of fixation and enzymatic digestion on the immunohistochemical demonstration of laminin and fibronectin in paraffin embedded tissue. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jun;37(6):639–644. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.6.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurkinen M., Vaheri A., Roberts P. J., Stenman S. Sequential appearance of fibronectin and collagen in experimental granulation tissue. Lab Invest. 1980 Jul;43(1):47–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Rao C. N., Barsky S. H. Tumor invasion and the extracellular matrix. Lab Invest. 1983 Dec;49(6):636–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Hernandez A. The hepatic extracellular matrix. I. Electron immunohistochemical studies in normal rat liver. Lab Invest. 1984 Jul;51(1):57–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Umfleet R. A. The cold-insoluble globulin of human plasma. I. Purification, primary characterization, and relationship to fibrinogen and other cold-insoluble fraction components. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5728–5736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller P., Achtsätter H., Butzengeiger M., Schüle B. The distribution of fibronectin in lymph nodes infiltrated by Hodgkin's disease. An immunoperoxidase study on paraffin sections. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1983;400(3):319–329. doi: 10.1007/BF00612193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao N. C., Barsky S. H., Terranova V. P., Liotta L. A. Isolation of a tumor cell laminin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 29;111(3):804–808. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91370-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly J. T., Nash J. R., Mackie M. J., McVerry B. A. Immuno-enzymatic detection of fibronectin in normal and pathological haematopoietic tissue. Br J Haematol. 1985 Mar;59(3):497–504. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb07336.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick G. D., Nachman R. L. Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease contain fibronectin. Blood. 1981 Feb;57(2):339–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenman S., Vaheri A. Distribution of a major connective tissue protein, fibronectin, in normal human tissues. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1054–1064. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenman S., Vaheri A. Fibronectin in human solid tumors. Int J Cancer. 1981;27(4):427–435. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910270403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Rohde H., Robey P. G., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., Martin G. R. Laminin--a glycoprotein from basement membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9933–9937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartiovaara J., Linder E., Ruoslahti E., Vaheri A. Distribution of fibroblast surface antigen: association with fibrillar structures of normal cells and loss upon viral transformation. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1522–1533. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Weston J. A. Isolation of a major cell surface glycoprotein from fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3492–3496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- d'Ardenne A. J., Kirkpatrick P., Sykes B. C. Distribution of laminin, fibronectin, and interstitial collagen type III in soft tissue tumours. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Aug;37(8):895–904. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.8.895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]