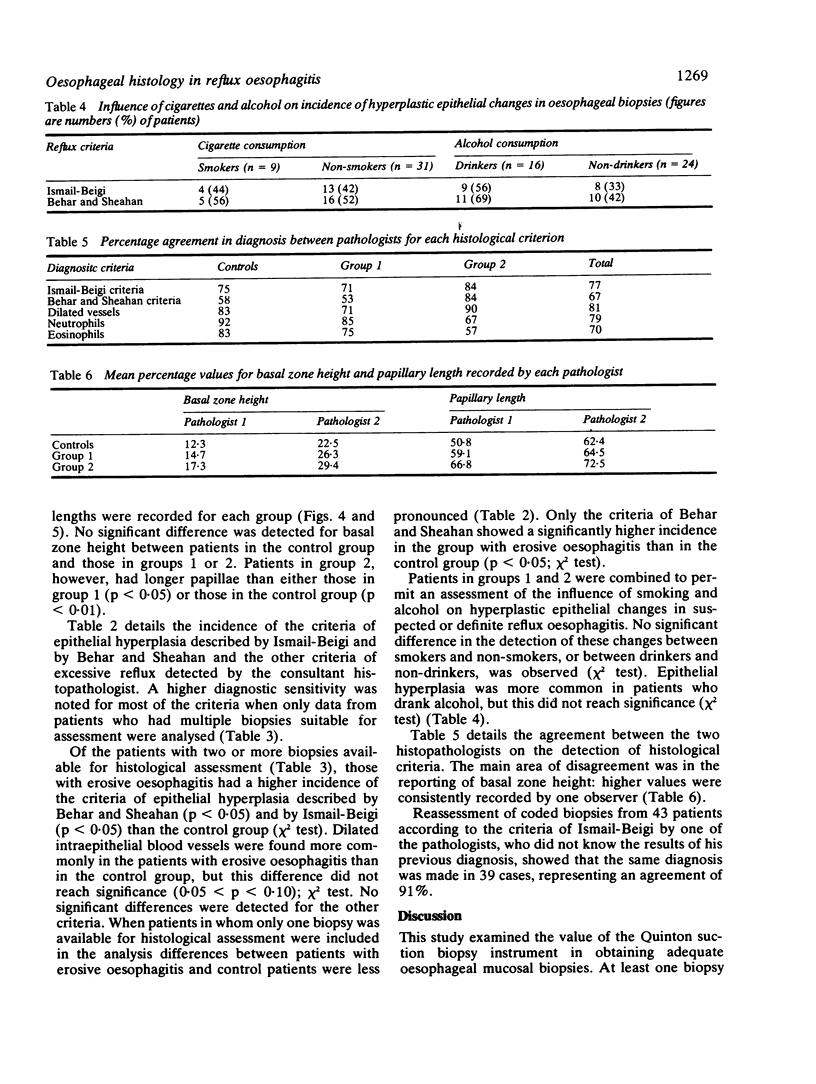
Abstract
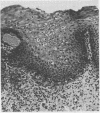
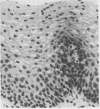
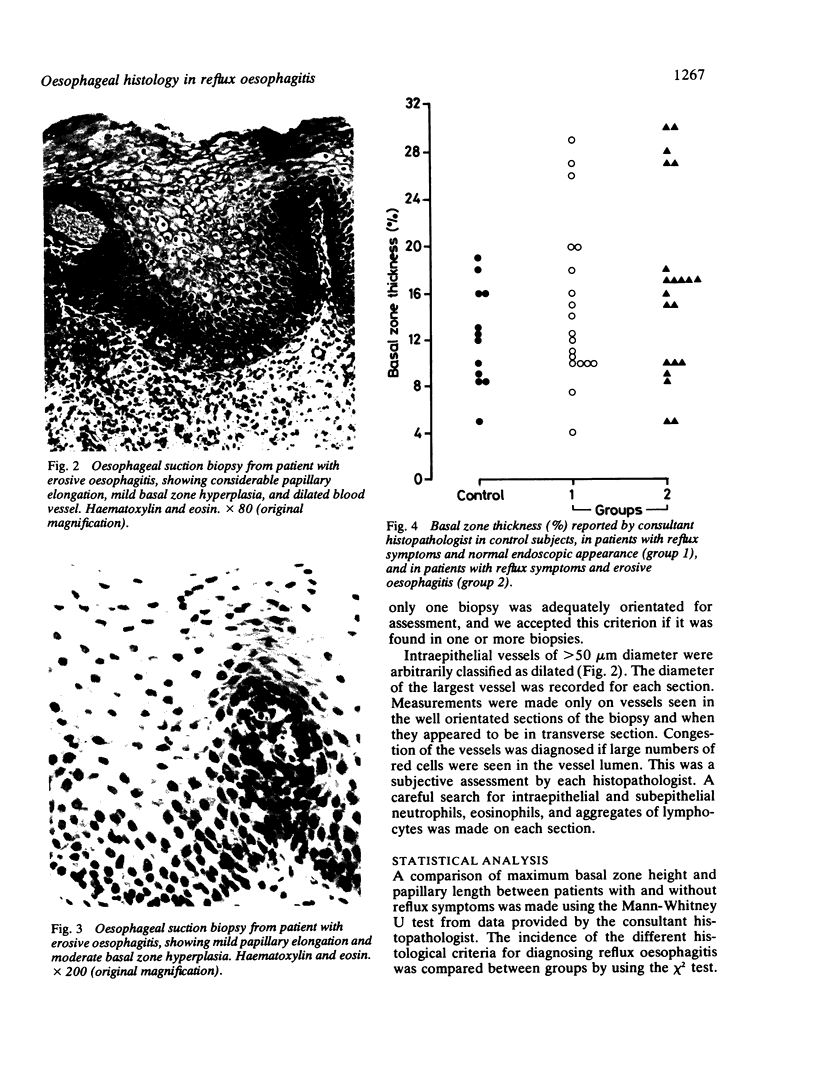
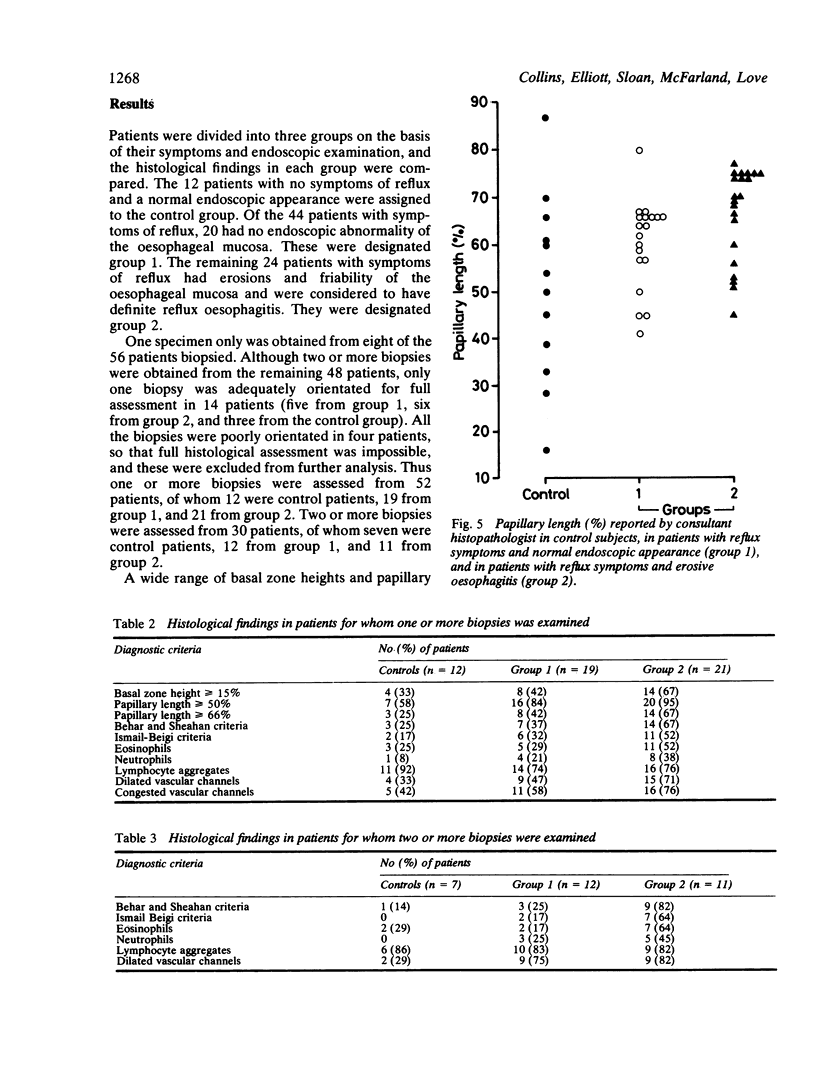
Multiple specimens taken at oesophageal suction biopsy were obtained from 56 patients, of whom 44 had symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux and 24 had endoscopic evidence of erosive oesophagitis. Biopsies were examined independently by two histopathologists for the following criteria for reflux: epithelial hyperplasia, vascular dilatation and congestion, neutrophil infiltration, and eosinophil infiltration. The incidence of these criteria in patients with and without endoscopic evidence of oesophagitis or symptoms of reflux was investigated. It was concluded that vascular dilatation and epithelial hyperplasia, defined as basal zone thickness greater than or equal to 15% and papillary elongation greater than or equal to 66%, can be detected most reliably, but their diagnostic accuracy is limited unless multiple biopsies are examined.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALLEM C. M., FLETCHER H. W., McKENNA R. D. The diagnosis of esophagitis. Am J Dig Dis. 1960 Feb;5:88–93. doi: 10.1007/BF02232017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behar J., Sheahan D. Histologic abnormalities in reflux esophagitis. Arch Pathol. 1975 Jul;99(7):387–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branicki F. J., Evans D. F., Ogilvie A. L., Atkinson M., Hardcastle J. D. Ambulatory monitoring of oesophageal pH in reflux oesophagitis using a portable radiotelemetry system. Gut. 1982 Nov;23(11):992–998. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.11.992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breen K. J., Whelan G. The diagnosis of reflux oesophagitis: an evaluation of five investigative procedures. Aust N Z J Surg. 1978 Apr;48(2):156–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1978.tb07294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester T. R., Johnson L. F. The evaluation of objective measurements of gastroesophageal reflux and their contribution to patient management. Surg Clin North Am. 1976 Feb;56(1):39–53. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)40834-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester T. R., Wang C. I., Wernly J. A., Pellegrini C. A., Little A. G., Klementschitsch P., Bermudez G., Johnson L. F., Skinner D. B. Technique, indications, and clinical use of 24 hour esophageal pH monitoring. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1980 May;79(5):656–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geboes K., Desmet V., Vantrappen G., Mebis J. Vascular changes in the esophageal mucosa. An early histologic sign of esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 1980 May;26(2):29–32. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(80)73261-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail-Beigi F., Horton P. F., Pope C. E., 2nd Histological consequences of gastroesophageal reflux in man. Gastroenterology. 1970 Feb;58(2):163–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail-Beigi F., Pope C. E., 2nd Distribution of the histological changes of gastroesophageal reflux in the distal esophagus of man. Gastroenterology. 1974 Jun;66(6):1109–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis L. R., Dent J., Whitehead R. Morphometric assessment of reflux oesophagitis in fibreoptic biopsy specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Jan;38(1):44–48. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F., DeMeester T. R., Haggitt R. C. Endoscopic signs for gastroesophageal reflux objectively evaluated. Gastrointest Endosc. 1976 Feb;22(3):151–155. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(76)73731-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komorowski R. A., Leinicke J. A. Comparison of fiberoptic endoscope and Quinton tube esophageal biopsies in esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 1978 May;24(4):154–155. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(78)73492-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Man M., Bryant R. G. Nuclear magnetic resonance investigation of rhodanese sulfhydryl groups. A chloride ion probe study. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1109–1112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seefeld U., Krejs G. J., Siebenmann R. E., Blum A. L. Esophageal histology in gastroesophageal reflux. Morphometric findings in suction biopsies. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Nov;22(11):956–964. doi: 10.1007/BF01076193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladen G. E., Riddell R. H., Willoughby J. M. Oesophagoscopy, biopsy, and acid perfusion test in diagnosis of "reflux oesophagitis". Br Med J. 1975 Jan 11;1(5949):71–76. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5949.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spence R. A., Sloan J. M., Johnston G. W., Greenfield A. Oesophageal mucosal changes in patients with varices. Gut. 1983 Nov;24(11):1024–1029. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.11.1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein W. M., Bogoch E. R., Bowes K. L. The normal human esophageal mucosa: a histological reappraisal. Gastroenterology. 1975 Jan;68(1):40–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter H. S., Madara J. L., Stafford R. J., Grand R. J., Quinlan J. E., Goldman H. Intraepithelial eosinophils: a new diagnostic criterion for reflux esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1982 Oct;83(4):818–823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wranne B., Areskog M., Tibbling L. The acid perfusion test as differential diagnostic aid in patients with chest pain. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1981;644:59–61. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1981.tb03122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]