Abstract
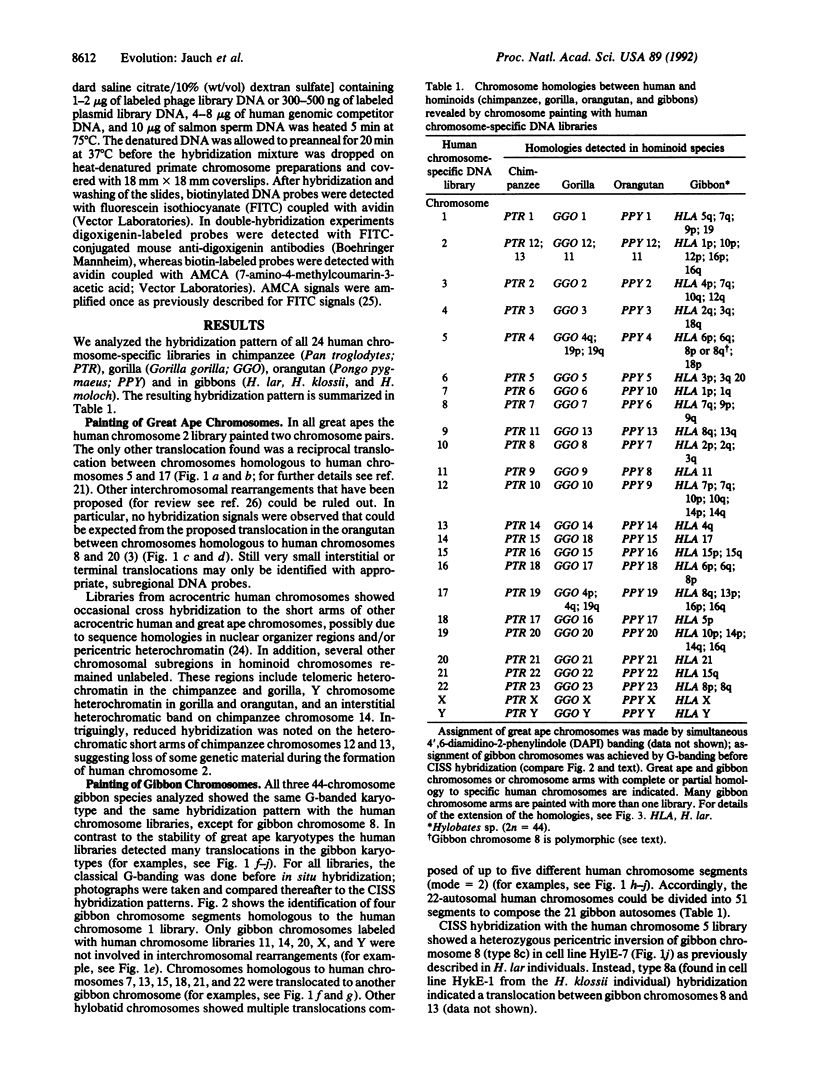
The homology between hylobatid chromosomes and other primates has long remained elusive. We used chromosomal in situ suppression hybridization of all human chromosome-specific DNA libraries to "paint" the chromosomes of primates and establish homologies between the human, great ape (chimpanzee, gorilla, and orangutan), and gibbon karyotypes (Hylobates lar species group, 2n = 44). The hybridization patterns unequivocally demonstrate the high degree of chromosomal homology and synteny of great ape and human chromosomes. Relative to human, no translocations were detected in great apes, except for the well-known fusion-origin of human chromosome 2 and a 5;17 translocation in the gorilla. In contrast, numerous translocations were detected that have led to the massive reorganization of the gibbon karyotype: the 22 autosomal human chromosomes have been divided into 51 elements to compose the 21 gibbon autosomes. Molecular cytogenetics promises to finally allow hylobatids to be integrated into the overall picture of chromosomal evolution in the primates.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collins C., Kuo W. L., Segraves R., Fuscoe J., Pinkel D., Gray J. W. Construction and characterization of plasmid libraries enriched in sequences from single human chromosomes. Genomics. 1991 Dec;11(4):997–1006. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90025-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couturier J., Dutrillaux B., Turleau C., de Grouchy J. Comparaisons chromosomiques chez quatrae espèces ou sous-espèces de gibbons. Ann Genet. 1982;25(1):5–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couturier J., Lernould J. M. Karyotypic study of four gibbon forms provisionally considered as subspecies of Hylobates (Nomascus) concolor (Primates, Hylobatidae). Folia Primatol (Basel) 1991;56(2):95–104. doi: 10.1159/000156533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer T., Lichter P., Borden J., Ward D. C., Manuelidis L. Detection of chromosome aberrations in metaphase and interphase tumor cells by in situ hybridization using chromosome-specific library probes. Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;80(3):235–246. doi: 10.1007/BF01790091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haimoff E. H., Chivers D. J., Gittins S. P., Whitten T. A phylogeny of gibbons (Hylobates spp.) based on morphological and behavioural characters. Folia Primatol (Basel) 1982;39(3-4):213–237. doi: 10.1159/000156079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klever M., Grond-Ginsbach C., Scherthan H., Schroeder-Kurth T. M. Chromosomal in situ suppression hybridization after Giemsa banding. Hum Genet. 1991 Mar;86(5):484–486. doi: 10.1007/BF00194638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Cremer T., Borden J., Manuelidis L., Ward D. C. Delineation of individual human chromosomes in metaphase and interphase cells by in situ suppression hybridization using recombinant DNA libraries. Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;80(3):224–234. doi: 10.1007/BF01790090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. Evolutionary tempo and phylogenetic inference based on primate karyotypes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1982;34(3):261–264. doi: 10.1159/000131814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien S. J., Graves J. A. Report of the committee on comparative gene mapping. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1990;55(1-4):406–433. doi: 10.1159/000133025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Gray J. W., Trask B., van den Engh G., Fuscoe J., van Dekken H. Cytogenetic analysis by in situ hybridization with fluorescently labeled nucleic acid probes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):151–157. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Landegent J., Collins C., Fuscoe J., Segraves R., Lucas J., Gray J. Fluorescence in situ hybridization with human chromosome-specific libraries: detection of trisomy 21 and translocations of chromosome 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9138–9142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley C. G., Ahlquist J. E. DNA hybridization evidence of hominoid phylogeny: results from an expanded data set. J Mol Evol. 1987;26(1-2):99–121. doi: 10.1007/BF02111285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tantravahi R., Dev V. G., Firschein I. L., Miller D. A., Miller O. J. Karyotype of the gibbons hylobates lar and h. moloch inversion in chromosome 7. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1975;15(2):92–102. doi: 10.1159/000130505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Tuinen P., Ledbetter D. H. Cytogenetic comparison and phylogeny of three species of Hylobatidae. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1983 Aug;61(4):453–466. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330610408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienberg J., Jauch A., Stanyon R., Cremer T. Molecular cytotaxonomy of primates by chromosomal in situ suppression hybridization. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90292-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienberg J., Stanyon R., Jauch A., Cremer T. Homologies in human and Macaca fuscata chromosomes revealed by in situ suppression hybridization with human chromosome specific DNA libraries. Chromosoma. 1992 Mar;101(5-6):265–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00346004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J., Prakash O. The origin of man: a chromosomal pictorial legacy. Science. 1982 Mar 19;215(4539):1525–1530. doi: 10.1126/science.7063861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]