Abstract
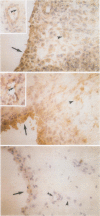
AIM: To determine whether the urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (u-PAR; CD87) exhibits a possible pathogenic role in rheumatoid and osteoarthritis. METHODS: A semiquantitative, indirect immunoperoxidase histochemical analysis was performed on frozen synovial tissue sections. The recently characterised monoclonal antibody 10G7 recognising transfectants bearing u-PAR was used. Synovial tissue was obtained from 10 patients with rheumatoid arthritis, 10 patients with osteoarthritis, and four normal subjects. RESULTS: u-PAR was expressed on 70-90% of synovial tissue lining cells and subsynovial, interstitial macrophages from the arthritis patients, but only on a few myeloid cells from the normal subjects. It was also present on more endothelial cells from the rheumatoid and osteoarthritis patients, than from normal synovial tissue. CONCLUSIONS: Plasminogen activators are important in joint destruction underlying arthritis. The up-regulated expression of u-PAR in diseased versus normal synovial tissue suggests a role for this antigen in the inflammatory and angiogenic mechanisms underlying rheumatoid and osteoarthritis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman R., Asch E., Bloch D., Bole G., Borenstein D., Brandt K., Christy W., Cooke T. D., Greenwald R., Hochberg M. Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis. Classification of osteoarthritis of the knee. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee of the American Rheumatism Association. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Aug;29(8):1039–1049. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi E., Ferrero E., Fazioli F., Mangili F., Wang J., Bender J. R., Blasi F., Pardi R. Integrin-dependent induction of functional urokinase receptors in primary T lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1996 Sep 1;98(5):1133–1141. doi: 10.1172/JCI118896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasi F. Urokinase and urokinase receptor: a paracrine/autocrine system regulating cell migration and invasiveness. Bioessays. 1993 Feb;15(2):105–111. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohuslav J., Horejsí V., Hansmann C., Stöckl J., Weidle U. H., Majdic O., Bartke I., Knapp W., Stockinger H. Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor, beta 2-integrins, and Src-kinases within a single receptor complex of human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1995 Apr 1;181(4):1381–1390. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.4.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle M. D., Chiodo V. A., Lawman M. J., Gee A. P., Young M. Urokinase: a chemotactic factor for polymorphonuclear leukocytes in vivo. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):169–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brommer E. J., Dooijewaard G., Dijkmans B. A., Breedveld F. C. Depression of tissue-type plasminogen activator and enhancement of urokinase-type plasminogen activator as an expression of local inflammation. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Aug 3;68(2):180–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. K., Piccoli D. S., Roberts M. J., Muirden K. D., Hamilton J. A. Effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha and beta on resorption of human articular cartilage and production of plasminogen activator by human articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Apr;33(4):542–552. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciambrone G. J., McKeown-Longo P. J. Vitronectin regulates the synthesis and localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in HT-1080 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13617–13622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colville-Nash P. R., Scott D. L. Angiogenesis and rheumatoid arthritis: pathogenic and therapeutic implications. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Jul;51(7):919–925. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.7.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dore-Duffy P., Washington R., Dragovic L. Expression of endothelial cell activation antigens in microvessels from patients with multiple sclerosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1993;331:243–248. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-2920-0_38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcone D. J., McCaffrey T. A., Haimovitz-Friedman A., Garcia M. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 stimulates macrophage urokinase expression and release of matrix-bound basic fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Jun;155(3):595–605. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041550317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerritsen M. E., Niedbala M. J., Szczepanski A., Carley W. W. Cytokine activation of human macro- and microvessel-derived endothelial cells. Blood Cells. 1993;19(2):325–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb R. H., Ziche M., Murano G., Liotta L. A. Plasminogen activators (urokinase) mediate neovascularization: possible role in tumor angiogenesis. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1986 Oct;12(4):337–338. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyetko M. R., Chen G. H., McDonald R. A., Goodman R., Huffnagle G. B., Wilkinson C. C., Fuller J. A., Toews G. B. Urokinase is required for the pulmonary inflammatory response to Cryptococcus neoformans. A murine transgenic model. J Clin Invest. 1996 Apr 15;97(8):1818–1826. doi: 10.1172/JCI118611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. A., Hart P. H., Leizer T., Vitti G. F., Campbell I. K. Regulation of plasminogen activator activity in arthritic joints. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1991 Feb;27:106–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Hale L. P., Denning S. M., Le P. T., Singer K. H. The role of leukocyte adhesion molecules in cellular interactions: implications for the pathogenesis of inflammatory synovitis. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1989;11(2):163–185. doi: 10.1007/BF00197187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildenbrand R., Dilger I., Hörlin A., Stutte H. J. Urokinase and macrophages in tumour angiogenesis. Br J Cancer. 1995 Oct;72(4):818–823. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen S. Leukocyte-endothelial cell interaction and the control of leukocyte migration into inflamed synovium. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1989;11(2):187–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00197188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi H., Tanaka S., Matsuo O. Plasminogen activator in synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1987 Jun;14(3):439–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchheimer J. C. Modulation of receptor bound urokinase-type plasminogen activator on human monocytes by non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Scand J Rheumatol. 1993;22(2):53–57. doi: 10.3109/03009749309095115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchheimer J. C., Nong Y. H., Remold H. G. IFN-gamma, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and urokinase regulate the expression of urokinase receptors on human monocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4229–4234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchheimer J. C., Remold H. G., Wanivenhaus A., Binder B. R. Increased proteolytic activity on the surface of monocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Nov;34(11):1430–1433. doi: 10.1002/art.1780341114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. E., Burrows J. C., Haines G. K., Carlos T. M., Harlan J. M., Leibovich S. J. Immunolocalization of endothelial and leukocyte adhesion molecules in human rheumatoid and osteoarthritic synovial tissues. Lab Invest. 1991 Mar;64(3):313–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. E., Kunkel S. L., Strieter R. M. Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. J Investig Med. 1995 Feb;43(1):28–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer D. J., Kuo A., Kariko K., Ahuja M., Klugherz B. D., Ivanics K. M., Hoxie J. A., Williams W. V., Liang B. T., Cines D. B. Regulation of the endothelial cell urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor. Evidence for cyclic AMP-dependent and protein kinase C-dependent pathways. Circ Res. 1993 Feb;72(2):330–340. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.2.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
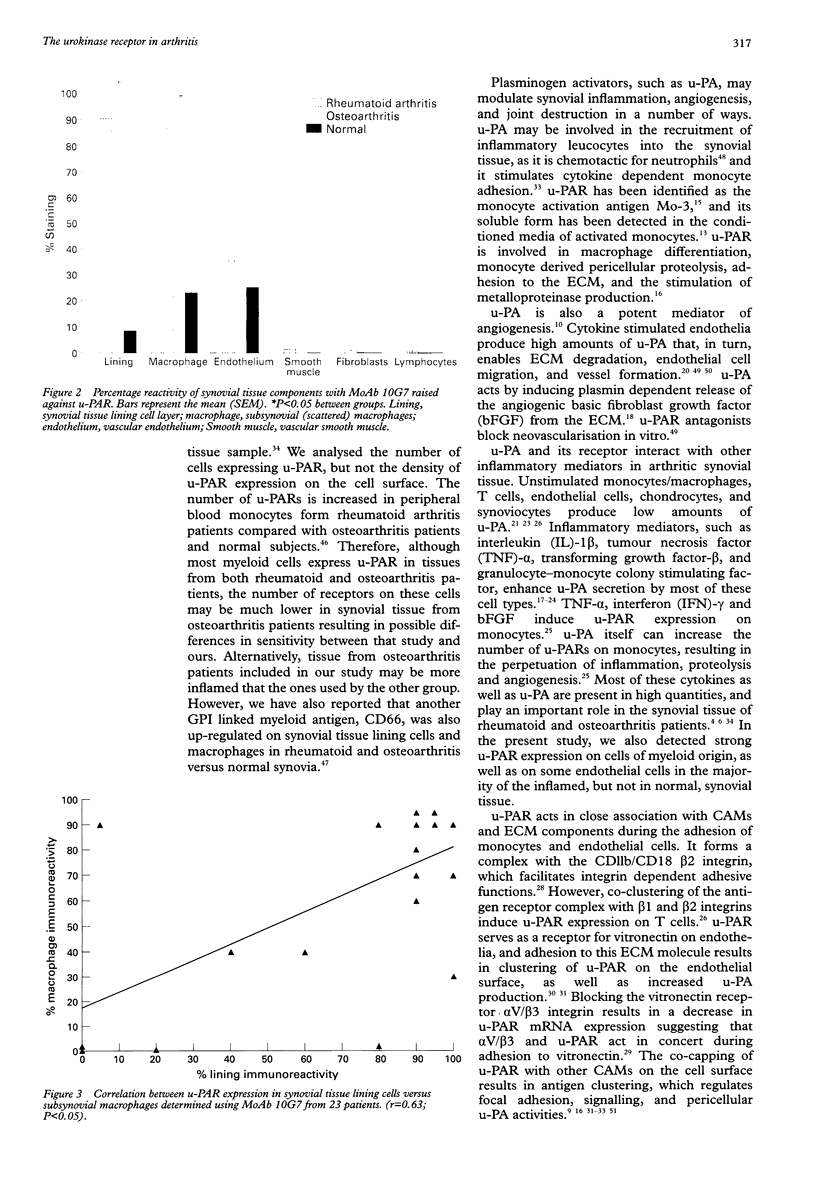
- Lu H., Mabilat C., Yeh P., Guitton J. D., Li H., Pouchelet M., Shoevaert D., Legrand Y., Soria J., Soria C. Blockage of urokinase receptor reduces in vitro the motility and the deformability of endothelial cells. FEBS Lett. 1996 Feb 12;380(1-2):21–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)01540-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magdolen V., Rettenberger P., Koppitz M., Goretzki L., Kessler H., Weidle U. H., König B., Graeff H., Schmitt M., Wilhelm O. Systematic mutational analysis of the receptor-binding region of the human urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Eur J Biochem. 1996 May 1;237(3):743–751. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0743p.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Mazzieri R., Rifkin D. B. Expression of the urokinase receptor in vascular endothelial cells is stimulated by basic fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):1193–1201. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min H. Y., Doyle L. V., Vitt C. R., Zandonella C. L., Stratton-Thomas J. R., Shuman M. A., Rosenberg S. Urokinase receptor antagonists inhibit angiogenesis and primary tumor growth in syngeneic mice. Cancer Res. 1996 May 15;56(10):2428–2433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizukami I. F., Faulkner N. E., Gyetko M. R., Sitrin R. G., Todd R. F., 3rd Enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assay detection of a soluble form of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor in vivo. Blood. 1995 Jul 1;86(1):203–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizukami I. F., Garni-Wagner B. A., DeAngelo L. M., Liebert M., Flint A., Lawrence D. A., Cohen R. L., Todd R. F., 3rd Immunologic detection of the cellular receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1994 Apr;71(1):96–104. doi: 10.1006/clin.1994.1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nip J., Rabbani S. A., Shibata H. R., Brodt P. Coordinated expression of the vitronectin receptor and the urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor in metastatic melanoma cells. J Clin Invest. 1995 May;95(5):2096–2103. doi: 10.1172/JCI117897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper M. S., Belin D., Montesano R., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 modulates basic fibroblast growth factor-induced proteolytic and angiogenic properties of endothelial cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):743–755. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper M. S., Vassalli J. D., Wilks J. W., Schweigerer L., Orci L., Montesano R. Modulation of bovine microvascular endothelial cell proteolytic properties by inhibitors of angiogenesis. J Cell Biochem. 1994 Aug;55(4):419–434. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240550403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao N. K., Shi G. P., Chapman H. A. Urokinase receptor is a multifunctional protein: influence of receptor occupancy on macrophage gene expression. J Clin Invest. 1995 Jul;96(1):465–474. doi: 10.1172/JCI118057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roldan A. L., Cubellis M. V., Masucci M. T., Behrendt N., Lund L. R., Danø K., Appella E., Blasi F. Cloning and expression of the receptor for human urokinase plasminogen activator, a central molecule in cell surface, plasmin dependent proteolysis. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):467–474. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08132.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronday H. K., Smits H. H., Van Muijen G. N., Pruszczynski M. S., Dolhain R. J., Van Langelaan E. J., Breedveld F. C., Verheijen J. H. Difference in expression of the plasminogen activation system in synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 May;35(5):416–423. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.5.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxne T., Lecander I., Geborek P. Plasminogen activators and plasminogen activator inhibitors in synovial fluid. Difference between inflammatory joint disorders and osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 1993 Jan;20(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M., Wilhelm O., Jänicke F., Magdolen V., Reuning U., Ohi H., Moniwa N., Kobayashi H., Weidle U., Graeff H. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and its receptor (CD87): a new target in tumor invasion and metastasis. J Obstet Gynaecol (Tokyo 1995) 1995 Apr;21(2):151–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0756.1995.tb01089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitrin R. G., Todd R. F., 3rd, Albrecht E., Gyetko M. R. The urokinase receptor (CD87) facilitates CD11b/CD18-mediated adhesion of human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1996 Apr 15;97(8):1942–1951. doi: 10.1172/JCI118626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szekanecz Z., Haines G. K., Harlow L. A., Shah M. R., Fong T. W., Fu R., Lin S. J., Koch A. E. Increased synovial expression of the adhesion molecules CD66a, CD66b, and CD31 in rheumatoid and osteoarthritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1995 Aug;76(2):180–186. doi: 10.1006/clin.1995.1113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szekanecz Z., Haines G. K., Lin T. R., Harlow L. A., Goerdt S., Rayan G., Koch A. E. Differential distribution of intercellular adhesion molecules (ICAM-1, ICAM-2, and ICAM-3) and the MS-1 antigen in normal and diseased human synovia. Their possible pathogenetic and clinical significance in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Feb;37(2):221–231. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szekanecz Z., Szegedi G., Koch A. E. Cellular adhesion molecules in rheumatoid arthritis: regulation by cytokines and possible clinical importance. J Investig Med. 1996 Apr;44(4):124–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waltz D. A., Sailor L. Z., Chapman H. A. Cytokines induce urokinase-dependent adhesion of human myeloid cells. A regulatory role for plasminogen activator inhibitors. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1541–1552. doi: 10.1172/JCI116360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei Y., Waltz D. A., Rao N., Drummond R. J., Rosenberg S., Chapman H. A. Identification of the urokinase receptor as an adhesion receptor for vitronectin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 23;269(51):32380–32388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharski L. R., Brown F. E., Memoli V. A., Kisiel W., Kudryk B. J., Rousseau S. M., Hunt J. A., Dunwiddie C., Nutt E. M. Pathways of coagulation activation in situ in rheumatoid synovial tissue. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1992 May;63(2):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(92)90008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hinsbergh V. W., van den Berg E. A., Fiers W., Dooijewaard G. Tumor necrosis factor induces the production of urokinase-type plasminogen activator by human endothelial cells. Blood. 1990 May 15;75(10):1991–1998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]