Abstract
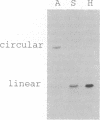
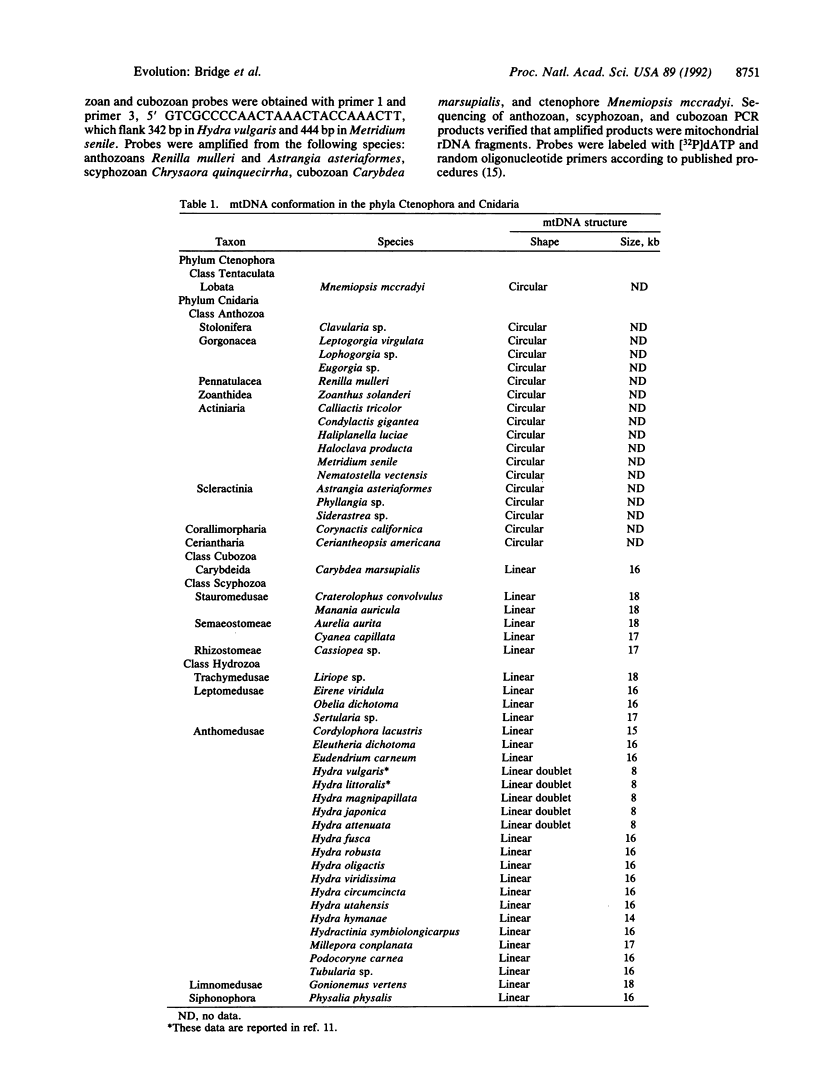
The phylogenetic relationships of the Recent cnidarian classes remain one of the classic problems in invertebrate zoology. We survey the structure of the mitochondrial genome in representatives of the four extant cnidarian classes and in the phylum Ctenophora. We find that all anthozoan species tested possess mtDNA in the form of circular molecules, whereas all scyphozoan, cubozoan, and hydrozoan species tested display mtDNA in the form of linear molecules. Because ctenophore and all other known metazoan mtDNA is circular, the shared occurrence of linear mtDNA in three of the four cnidarian classes suggests a basal position for the Anthozoa within the phylum.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chomet P. S., Wessler S., Dellaporta S. L. Inactivation of the maize transposable element Activator (Ac) is associated with its DNA modification. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):295–302. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04753.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christen R., Ratto A., Baroin A., Perasso R., Grell K. G., Adoutte A. An analysis of the origin of metazoans, using comparisons of partial sequences of the 28S RNA, reveals an early emergence of triploblasts. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):499–503. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07975.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garey J. R., Wolstenholme D. R. Platyhelminth mitochondrial DNA: evidence for early evolutionary origin of a tRNA(serAGN) that contains a dihydrouridine arm replacement loop, and of serine-specifying AGA and AGG codons. J Mol Evol. 1989 May;28(5):374–387. doi: 10.1007/BF02603072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W. Origin and evolution of mitochondrial DNA. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:25–50. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lansman R. A., Shade R. O., Shapira J. F., Avise J. C. The use of restriction endonucleases to measure mitochondrial DNA sequence relatedness in natural populations. III. Techniques and potential applications. J Mol Evol. 1981;17(4):214–226. doi: 10.1007/BF01732759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shure M., Wessler S., Fedoroff N. Molecular identification and isolation of the Waxy locus in maize. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]