Abstract
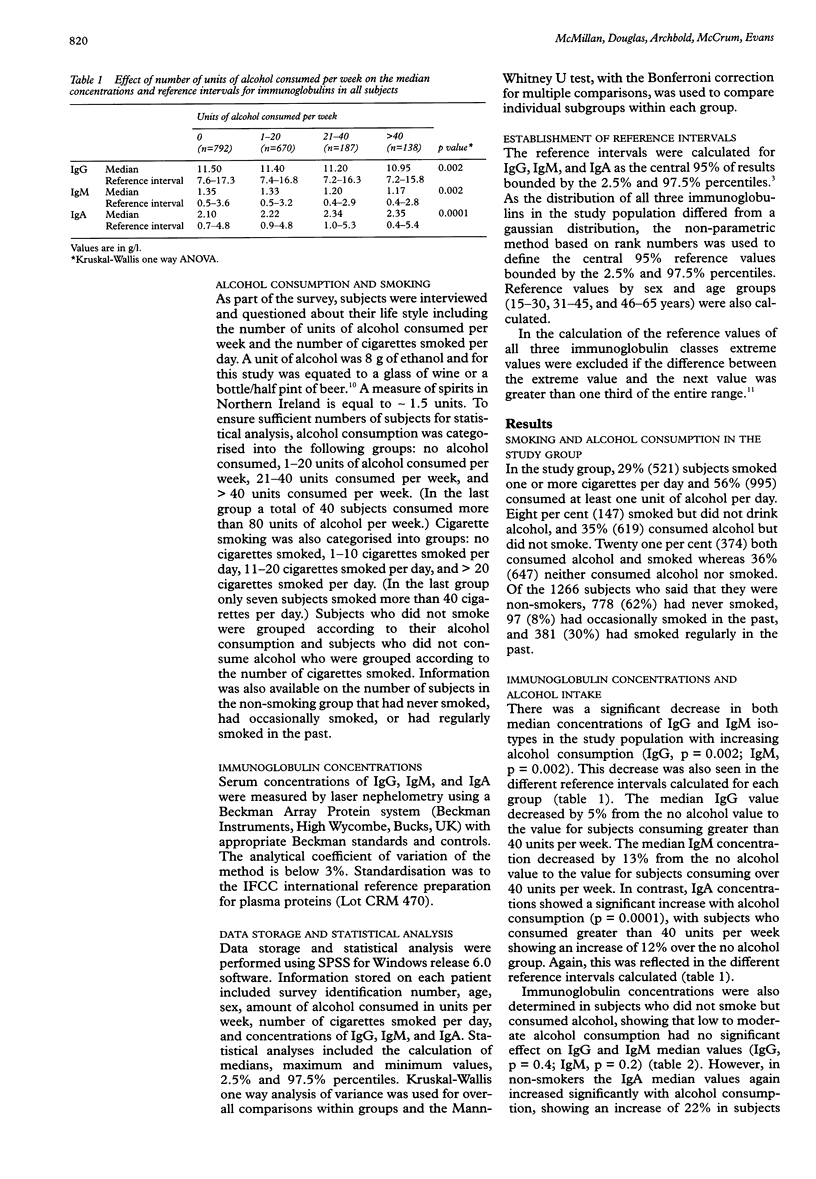
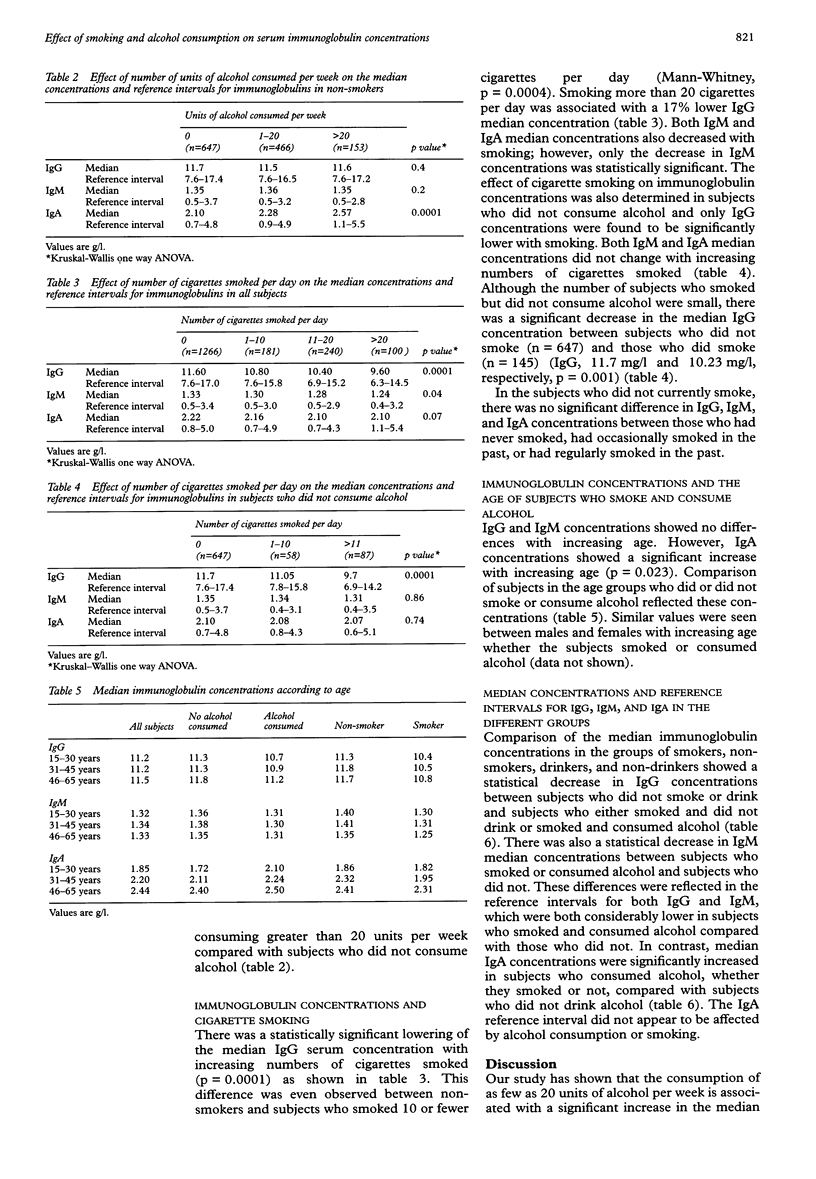
AIM: To determine the effect of low to moderate levels of smoking and alcohol consumption on immunoglobulin concentrations. METHODS: Serum samples from 1787 subjects with approximately equal numbers in each five year group from 15 to 64 years were obtained from a large random population survey in Northern Ireland. Details were available on each subject concerning the number of units of alcohol consumed per week and the number of cigarettes smoked per day. IgG, IgM, and IgA concentrations were measured by laser nephelometry on all serum samples. RESULTS: Low to moderate consumption of alcohol was associated with a decrease in IgG and IgM median concentrations in contrast to an increase in IgA median concentrations. The decrease in IgM and especially IgG median concentrations appeared to be related to the smoking habits of the subjects. Alcohol consumption alone was associated with increased IgA median concentrations whereas cigarette smoking alone was associated with reduced IgG median concentrations. CONCLUSION: Low levels of alcohol consumption and cigarette smoking influence IgG, IgM, and IgA serum concentrations. This should be borne in mind when selecting subjects for use in research and clinical settings.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen P., Pedersen O. F., Bach B., Bonde G. J. Serum antibodies and immunoglobulins in smokers and nonsmokers. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Feb;47(2):467–473. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulsvik A., Fagerhoi M. K. Smoking and immunoglobulin levels. Lancet. 1979 Feb 24;1(8113):449–449. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90934-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulsvik A., Fagerhoi M. K. Smoking and immunoglobulin levels. Lancet. 1979 Feb 24;1(8113):449–449. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90934-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. G. Immune and inflammatory function in cigarette smokers. Thorax. 1987 Apr;42(4):241–249. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.4.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. G. Immune and inflammatory function in cigarette smokers. Thorax. 1987 Apr;42(4):241–249. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.4.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meliska C. J., Stunkard M. E., Gilbert D. G., Jensen R. A., Martinko J. M. Immune function in cigarette smokers who quit smoking for 31 days. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995 Apr;95(4):901–910. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(95)70135-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mili F., Flanders W. D., Boring J. R., Annest J. L., DeStefano F. The associations of alcohol drinking and drinking cessation to measures of the immune system in middle-aged men. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1992 Aug;16(4):688–694. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1992.tb00662.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasse E. A. Determination of reference intervals in the clinical laboratory using the proposed guideline National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards C28-P. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1992 Jul;116(7):710–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollerud D. J., Brown L. M., Blattner W. A., Weiss S. T., Maloney E. M., Kurman C. C., Nelson D. L., Hoover R. N. Racial differences in serum immunoglobulin levels: relationship to cigarette smoking, T-cell subsets, and soluble interleukin-2 receptors. J Clin Lab Anal. 1995;9(1):37–41. doi: 10.1002/jcla.1860090107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollerud D. J., Brown L. M., Blattner W. A., Weiss S. T., Maloney E. M., Kurman C. C., Nelson D. L., Hoover R. N. Racial differences in serum immunoglobulin levels: relationship to cigarette smoking, T-cell subsets, and soluble interleukin-2 receptors. J Clin Lab Anal. 1995;9(1):37–41. doi: 10.1002/jcla.1860090107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Wiel A., van Hattum J., Schuurman H. J., Kater L. Immunoglobulin A in the diagnosis of alcoholic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1988 Feb;94(2):457–462. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90437-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


