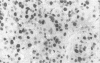
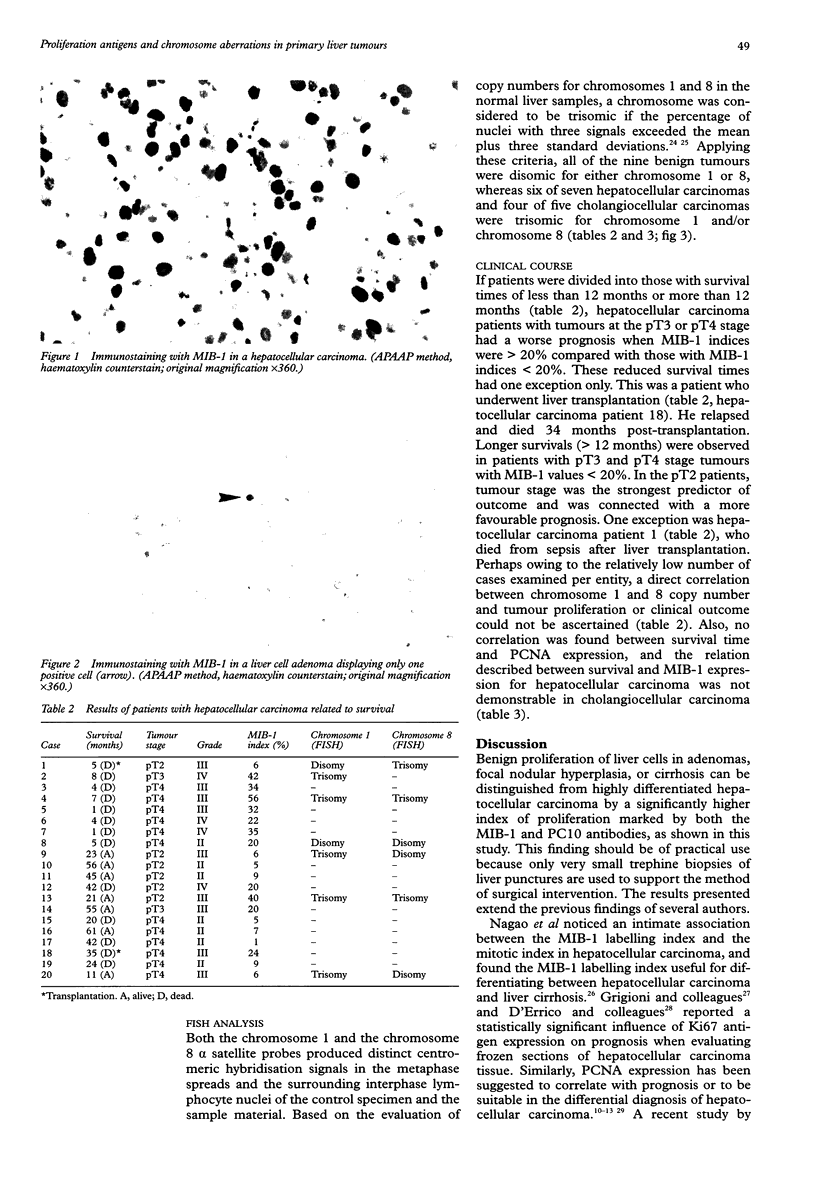
Abstract
AIMS: To assess cell proliferation and the presence of numerical chromosome aberrations involving chromosomes 1 and 8 in benign and malignant liver tumours. METHODS: Cell proliferation was studied immunohistochemically in paraffin wax embedded material from 62 primary liver tumours (20 hepatocellular carcinomas, 16 cholangiocellular carcinomas, 15 liver cell adenomas, 11 focal nodular hyperplasias), and the results were compared with histological characteristics and clinical data. Copy numbers of chromosomes 1 and 8 were assessed by interphase fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) with satellite probes in fresh tumour material. RESULTS: The expression of proliferation associated antigen Ki67, using the monoclonal antibody MIB-1, and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), using the antibody PC10, was found to be significantly higher in malignant versus benign liver tumours. Neither Ki67 nor PCNA expression were independent prognostic parameters. However, there was a tendency for a worse outcome (survival < 12 months) for patients with a high MIB-1 labelling index (> 20%) compared with patients having the same tumour stage and a low MIB-1 index. Aneusomy for chromosomes 1 and 8 was demonstrated by FISH in malignant tumours (six of seven hepatocellular carcinomas, four of five cholangiocellular carcinomas) but not in benign tumours (none of nine) or non-neoplastic liver (none of nine). CONCLUSION: Both the determination of the proliferating cell fraction and FISH analysis are useful for distinguishing hepatocellular carcinoma from liver cell adenoma or focal nodular hyperplasia; high fractions of proliferating cells are predictive of an early relapse.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi E., Hashimoto H., Tsuneyoshi M. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen in hepatocellular carcinoma and small cell liver dysplasia. Cancer. 1993 Nov 15;72(10):2902–2909. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19931115)72:10<2902::aid-cncr2820721008>3.0.co;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardi G., Johansson B., Pandis N., Heim S., Mandahl N., Andrén-Sandberg A., Hägerstrand I., Mitelman F. Cytogenetic findings in three primary hepatocellular carcinomas. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1992 Feb;58(2):191–195. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(92)90111-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesterfeld S., Gerres K., Fischer-Wein G., Böcking A. Polyploidy in non-neoplastic tissues. J Clin Pathol. 1994 Jan;47(1):38–42. doi: 10.1136/jcp.47.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Frank R., Blundell P. A., Macdonald-Bravo H. Cyclin/PCNA is the auxiliary protein of DNA polymerase-delta. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):515–517. doi: 10.1038/326515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Macdonald-Bravo H. Existence of two populations of cyclin/proliferating cell nuclear antigen during the cell cycle: association with DNA replication sites. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1549–1554. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. C., Gatter K. C. Monoclonal antibody Ki-67: its use in histopathology. Histopathology. 1990 Dec;17(6):489–503. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1990.tb00788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattoretti G., Becker M. H., Key G., Duchrow M., Schlüter C., Galle J., Gerdes J. Monoclonal antibodies against recombinant parts of the Ki-67 antigen (MIB 1 and MIB 3) detect proliferating cells in microwave-processed formalin-fixed paraffin sections. J Pathol. 1992 Dec;168(4):357–363. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell J. L., Falini B., Erber W. N., Ghosh A. K., Abdulaziz Z., MacDonald S., Pulford K. A., Stein H., Mason D. Y. Immunoenzymatic labeling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP complexes). J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Feb;32(2):219–229. doi: 10.1177/32.2.6198355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Errico A., Grigioni W. F., Fiorentino M., Baccarini P., Grazi G. L., Mancini A. M. Overexpression of p53 protein and Ki67 proliferative index in hepatocellular carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study on 109 Italian patients. Pathol Int. 1994 Sep;44(9):682–687. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1994.tb02947.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDMONDSON H. A., STEINER P. E. Primary carcinoma of the liver: a study of 100 cases among 48,900 necropsies. Cancer. 1954 May;7(3):462–503. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195405)7:3<462::aid-cncr2820070308>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara Y., Monden M., Mori T., Nakamura Y., Emi M. Frequent multiplication of the long arm of chromosome 8 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1993 Feb 15;53(4):857–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigioni W. F., Garbisa S., D'Errico A., Baccarini P., Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Liotta L. A., Mancini A. M. Evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma aggressiveness by a panel of extracellular matrix antigens. Am J Pathol. 1991 Mar;138(3):647–654. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamon-Benais C., Ingster O., Terris B., Couturier-Turpin M. H., Bernheim A., Feldmann G. Interphase cytogenetic studies of human hepatocellular carcinomas by fluorescent in situ hybridization. Hepatology. 1996 Mar;23(3):429–435. doi: 10.1002/hep.510230306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopman A. H., Poddighe P. J., Smeets A. W., Moesker O., Beck J. L., Vooijs G. P., Ramaekers F. C. Detection of numerical chromosome aberrations in bladder cancer by in situ hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1989 Dec;135(6):1105–1117. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain S., Filipe M. I., Hall P. A., Waseem N., Lane D. P., Levison D. A. Prognostic value of proliferating cell nuclear antigen in gastric carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 1991 Aug;44(8):655–659. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.8.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakita N., Seki S., Sakaguchi H., Yanai A., Kuroki T., Mizoguchi Y., Kobayashi K., Monna T. Analysis of proliferating hepatocytes using a monoclonal antibody against proliferating cell nuclear antigen/cyclin in embedded tissues from various liver diseases fixed in formaldehyde. Am J Pathol. 1992 Feb;140(2):513–520. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., Kagawa K., Deguchi T., Nakajima T., Kakusui M., Ohkawara T., Katagishi T., Okanoue T., Kashima K., Ashihara T. Cytogenetic analyses of hepatocellular carcinoma by in situ hybridization with a chromosome-specific DNA probe. Cancer. 1996 Jan 15;77(2):271–277. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19960115)77:2<271::AID-CNCR8>3.0.CO;2-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto M., Nakanishi T., Kira S., Kawaguchi M., Nakashio R., Suemori S., Kajiyama G., Asahara T., Dohi K. The assessment of proliferating cell nuclear antigen immunohistochemical staining in small hepatocellular carcinoma and its relationship to histologic characteristics and prognosis. Cancer. 1993 Sep 15;72(6):1859–1865. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930915)72:6<1859::aid-cncr2820720612>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick D., Hall P. A. The complexities of proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Histopathology. 1992 Dec;21(6):591–594. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1992.tb00454.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick D., Yu C., Hobbs C., Hall P. A. The relevance of antibody concentration to the immunohistological quantification of cell proliferation-associated antigens. Histopathology. 1993 Jun;22(6):543–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1993.tb00174.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao T., Kondo F., Sato T., Nagato Y., Kondo Y. Immunohistochemical detection of aberrant p53 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation with cell proliferative activity indices, including mitotic index and MIB-1 immunostaining. Hum Pathol. 1995 Mar;26(3):326–333. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(95)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasarek A., Werner M., Nolte M., Klempnauer J., Georgii A. Trisomy 1 and 8 occur frequently in hepatocellular carcinoma but not in liver cell adenoma and focal nodular hyperplasia. A fluorescence in situ hybridization study. Virchows Arch. 1995;427(4):373–378. doi: 10.1007/BF00199385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng I. O., Lai E. C., Fan S. T., Ng M., Chan A. S., So M. K. Prognostic significance of proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 1994 May 1;73(9):2268–2274. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19940501)73:9<2268::aid-cncr2820730906>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojanguren I., Ariza A., Llatjós M., Castellà E., Mate J. L., Navas-Palacios J. J. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression in normal, regenerative, and neoplastic liver: a fine-needle aspiration cytology and biopsy study. Hum Pathol. 1993 Aug;24(8):905–908. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(93)90141-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Tan C. K., Kostura M., Mathews M. B., So A. G., Downey K. M., Stillman B. Functional identity of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and a DNA polymerase-delta auxiliary protein. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):517–520. doi: 10.1038/326517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg A. A., Turc-Carel C. The cytogenetics of solid tumors. Relation to diagnosis, classification and pathology. Cancer. 1987 Feb 1;59(3):387–395. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19870201)59:3<387::aid-cncr2820590306>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon D., Munoz S. J., Maddrey W. C., Knowles B. B. Chromosomal rearrangements in a primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1990 Apr;45(2):255–260. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(90)90091-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soini Y., Virkajärvi N., Lehto V. P., Päkkö P. Hepatocellular carcinomas with a high proliferation index and a low degree of apoptosis and necrosis are associated with a shortened survival. Br J Cancer. 1996 May;73(9):1025–1030. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1996.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suehiro T., Matsumata T., Itasaka H., Yamamoto K., Kawahara N., Sugimachi K. Clinicopathologic features and prognosis of resected hepatocellular carcinomas of varied sizes with special reference to proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Cancer. 1995 Aug 1;76(3):399–405. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19950801)76:3<399::aid-cncr2820760309>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi S., Qian J., Brown J. A., Alcaraz A., Bostwick D. G., Lieber M. M., Jenkins R. B. Potential markers of prostate cancer aggressiveness detected by fluorescence in situ hybridization in needle biopsies. Cancer Res. 1994 Jul 1;54(13):3574–3579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada T., Nakanuma Y. Cell proliferative activity in adenomatous hyperplasia of the liver and small hepatocellular carcinoma. An immunohistochemical study demonstrating proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Cancer. 1992 Aug 1;70(3):591–598. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19920801)70:3<591::aid-cncr2820700309>3.0.co;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward B. E., Gersen S. L., Carelli M. P., McGuire N. M., Dackowski W. R., Weinstein M., Sandlin C., Warren R., Klinger K. W. Rapid prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal aneuploidies by fluorescence in situ hybridization: clinical experience with 4,500 specimens. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 May;52(5):854–865. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. C., Woods A. L., Levison D. A. The assessment of cellular proliferation by immunohistochemistry: a review of currently available methods and their applications. Histochem J. 1992 Mar;24(3):121–131. doi: 10.1007/BF01047461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]