Abstract
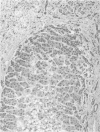
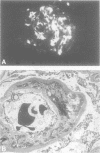
Lysinuric protein intolerance (LPI) is a rare autosomal recessive inborn error of metabolism, characterised by defective transport of the cationic amino acids lysine, arginine and ornithine. To date there are few reported necropsy cases. This report describes the necropsy findings in a 21 year old female patient originally diagnosed as having LPI in 1973. Liver function tests deteriorated and immediately before death jaundice, hyperammonaemia, coma, metabolic acidosis, and a severe bleeding diathesis developed. At necropsy, there was micronodular cirrhosis of the liver with extensive fatty change in hepatocytes. The lungs showed pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Immunofluorescence and electron microscopy revealed the presence of a glomerulonephritis with predominant IgA deposition. These necropsy findings reflect the spectrum of lesions reported in LPI, providing further evidence of an association between this condition and pulmonary alveolar proteinosis, cirrhosis and glomerulonephritis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carson N. A., Redmond O. A. Lysinuric protein intolerance. Ann Clin Biochem. 1977 May;14(3):135–135. doi: 10.1177/000456327701400127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata M., Suzuki M., Kawamura G., Kono S., Koda N., Yamaguchi S., Aoki K. Immunological abnormalities in a patient with lysinuric protein intolerance. Eur J Pediatr. 1987 Jul;146(4):427–428. doi: 10.1007/BF00444955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parto K., Kallajoki M., Aho H., Simell O. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis and glomerulonephritis in lysinuric protein intolerance: case reports and autopsy findings of four pediatric patients. Hum Pathol. 1994 Apr;25(4):400–407. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]