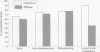Abstract
AIMS: To assess whether standard and variant isoforms of CD44 (CD44s, CD44v5, and CD44v6) have a differential expression profile in early versus advanced gastric adenocarcinoma of the diffuse and intestinal types and their metastases. METHODS: Immunohistochemical expression of CD44s, CD44v5, and CD44v6 was evaluated in 14 early gastric cancers (nine intestinal and five diffuse) and 37 advanced adenocarcinomas (21 intestinal and 16 diffuse) as well as in 18 cases of perigastric lymph node metastasis. Ten normal and five metaplastic gastric mucosa samples were also included in the study. RESULTS: Although no significant association was found between the degree of invasion and the CD44 expression profile, CD44v6 positivity was detected more frequently in metastases of intestinal-type carcinomas (66%) than in metastases of diffuse-type neoplasms (11%) (p < 0.05). Weak CD44s, CD44v5, and CD44v6 expression was observed focally in both normal and metaplastic gastric mucosa samples. CONCLUSIONS: These data suggest that CD44v6 expression may be involved in the production of lymph node metastases in intestinal-type gastric carcinoma but not in the diffuse-type disease, the metastatic potential of which is most likely unrelated to the CD44 family of adhesion molecules.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Denning S. M., Le P. T., Singer K. H., Haynes B. F. Antibodies against the CD44 p80, lymphocyte homing receptor molecule augment human peripheral blood T cell activation. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):7–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dämmrich J., Vollmers H. P., Heider K. H., Müller-Hermelink H. K. Importance of different CD44v6 expression in human gastric intestinal and diffuse type cancers for metastatic lymphogenic spreading. J Mol Med (Berl) 1995 Aug;73(8):395–401. doi: 10.1007/BF00240138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox S. B., Fawcett J., Jackson D. G., Collins I., Gatter K. C., Harris A. L., Gearing A., Simmons D. L. Normal human tissues, in addition to some tumors, express multiple different CD44 isoforms. Cancer Res. 1994 Aug 15;54(16):4539–4546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günthert U., Hofmann M., Rudy W., Reber S., Zöller M., Haussmann I., Matzku S., Wenzel A., Ponta H., Herrlich P. A new variant of glycoprotein CD44 confers metastatic potential to rat carcinoma cells. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):13–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90403-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heider K. H., Dämmrich J., Skroch-Angel P., Müller-Hermelink H. K., Vollmers H. P., Herrlich P., Ponta H. Differential expression of CD44 splice variants in intestinal- and diffuse-type human gastric carcinomas and normal gastric mucosa. Cancer Res. 1993 Sep 15;53(18):4197–4203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrlich P., Zöller M., Pals S. T., Ponta H. CD44 splice variants: metastases meet lymphocytes. Immunol Today. 1993 Aug;14(8):395–399. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann M., Rudy W., Zöller M., Tölg C., Ponta H., Herrlich P., Günthert U. CD44 splice variants confer metastatic behavior in rats: homologous sequences are expressed in human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1991 Oct 1;51(19):5292–5297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann M., Heider K. H., Sinn H. P., von Minckwitz G., Ponta H., Herrlich P. CD44 variant exon epitopes in primary breast cancer and length of survival. Lancet. 1995 Mar 11;345(8950):615–619. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)90521-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesley J., Hyman R., Kincade P. W. CD44 and its interaction with extracellular matrix. Adv Immunol. 1993;54:271–335. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60537-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B., Jauch K. W., Günthert U., Figdor C. G., Schildberg F. W., Funke I., Johnson J. P. De-novo expression of CD44 and survival in gastric cancer. Lancet. 1993 Oct 23;342(8878):1019–1022. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92879-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder J. W., Kruyt P. M., Sewnath M., Oosting J., Seldenrijk C. A., Weidema W. F., Offerhaus G. J., Pals S. T. Colorectal cancer prognosis and expression of exon-v6-containing CD44 proteins. Lancet. 1994 Nov 26;344(8935):1470–1472. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90290-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picker L. J., Nakache M., Butcher E. C. Monoclonal antibodies to human lymphocyte homing receptors define a novel class of adhesion molecules on diverse cell types. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):927–937. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristamäki R., Joensuu H., Söderström K. O., Jalkanen S. CD44v6 expression in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: an association with low histological grade and poor prognosis. J Pathol. 1995 Jul;176(3):259–267. doi: 10.1002/path.1711760308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington K., Gottfried M. R., Telen M. J. Expression of the cell adhesion molecule CD44 in gastric adenocarcinomas. Hum Pathol. 1994 Oct;25(10):1043–1049. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wielenga V. J., Heider K. H., Offerhaus G. J., Adolf G. R., van den Berg F. M., Ponta H., Herrlich P., Pals S. T. Expression of CD44 variant proteins in human colorectal cancer is related to tumor progression. Cancer Res. 1993 Oct 15;53(20):4754–4756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodland D. L., Smith H. P., Surman S., Le P., Wen R., Blackman M. A. Major histocompatibility complex-specific recognition of Mls-1 is mediated by multiple elements of the T cell receptor. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):433–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]