Abstract
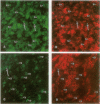
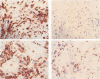
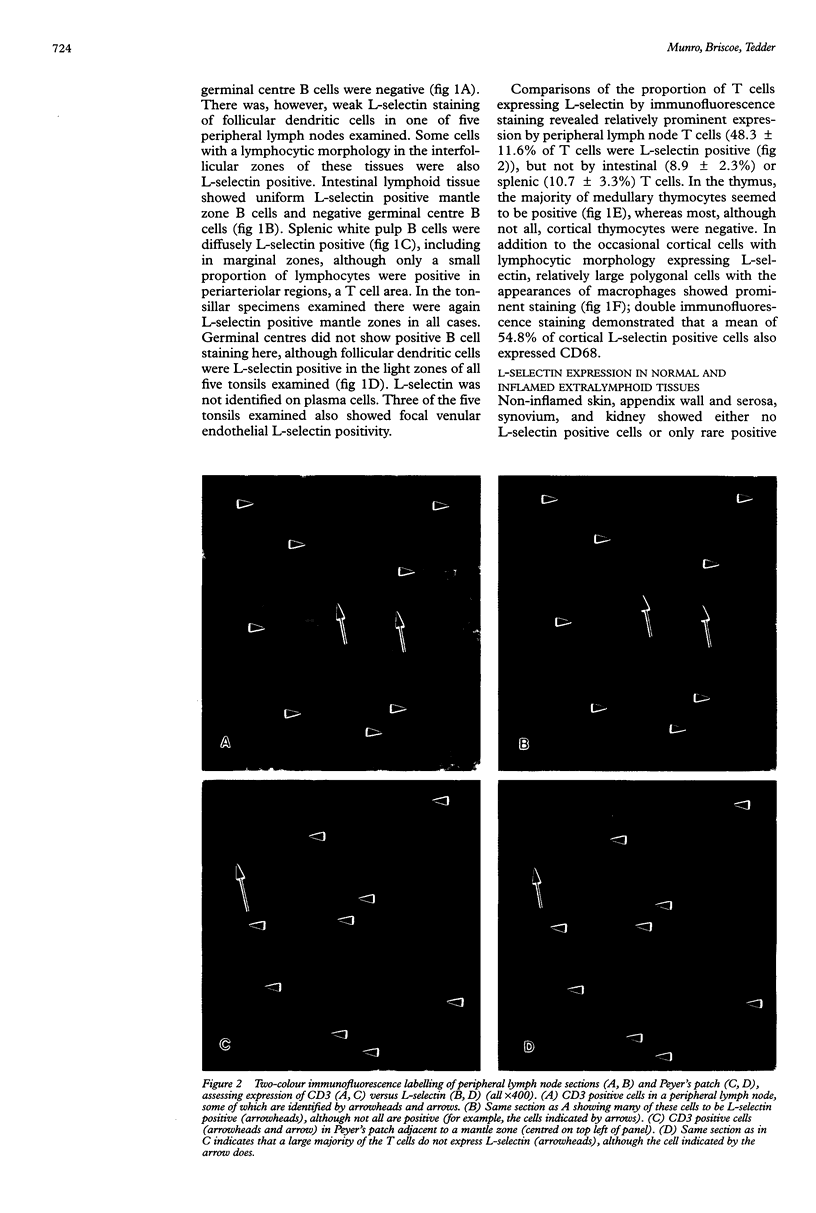
AIMS: To study tissue expression of L-selectin, a leucocyte cell surface molecule that is considered to be involved in adhesion to certain endothelia, particularly in peripheral lymph nodes and during inflammation, and is shed upon leucocyte activation. METHODS: Leucocytes were examined by immunohistochemistry and double immunofluorescence staining in various lymphoid sites and normal and inflamed extralymphoid tissues. RESULTS: L-selectin was present on mantle zone B lymphocytes in different lymphoid sites, including in intestinal lymphoid tissue, but was absent on germinal centre B cells. Splenic white pulp B cells also expressed L-selectin. The proportion of T lymphocytes expressing L-selectin depended on the site under study, being greatest in peripheral lymph nodes (mean 48% of T cells positive), and lower in mucosal lymphoid sites and spleen (9 and 11% positive, respectively). Non-lymphocytic L-selectin staining was observed on follicular dendritic cells in tonsils and on macrophages in thymus. L-selectin positive leucocytes were rare in normal extralymphoid tissues, and relatively few were seen in most inflammatory settings. However, in rejecting renal transplants, a higher proportion (30%) of leucocytes expressed L-selectin. CONCLUSIONS: Overall, the results indicate how the degree of L-selectin expression by leucocytes in particular tissues may reflect a requirement for L-selectin expression for entry into those tissues and the activation state of leucocytes once localised there.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbonés M. L., Ord D. C., Ley K., Ratech H., Maynard-Curry C., Otten G., Capon D. J., Tedder T. F. Lymphocyte homing and leukocyte rolling and migration are impaired in L-selectin-deficient mice. Immunity. 1994 Jul;1(4):247–260. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargatze R. F., Wu N. W., Weissman I. L., Butcher E. C. High endothelial venule binding as a predictor of the dissemination of passaged murine lymphomas. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):1125–1131. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumheter S., Singer M. S., Henzel W., Hemmerich S., Renz M., Rosen S. D., Lasky L. A. Binding of L-selectin to the vascular sialomucin CD34. Science. 1993 Oct 15;262(5132):436–438. doi: 10.1126/science.7692600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg E. L., McEvoy L. M., Berlin C., Bargatze R. F., Butcher E. C. L-selectin-mediated lymphocyte rolling on MAdCAM-1. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):695–698. doi: 10.1038/366695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabbi M., Tiso M., Gangemi R. M., Favre A., Demartini P., Bargellesi-Severi A. A novel 120-kDa antigen shared by immature human thymocytes and long-term-activated T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Jan;24(1):1–7. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallatin W. M., Weissman I. L., Butcher E. C. A cell-surface molecule involved in organ-specific homing of lymphocytes. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):30–34. doi: 10.1038/304030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. D., Spertini O., Ernst T. J., Belvin M. P., Levine H. B., Kanakura Y., Tedder T. F. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and other cytokines regulate surface expression of the leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 on human neutrophils, monocytes, and their precursors. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):576–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamann A., Jablonski-Westrich D., Jonas P., Thiele H. G. Homing receptors reexamined: mouse LECAM-1 (MEL-14 antigen) is involved in lymphocyte migration into gut-associated lymphoid tissue. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Dec;21(12):2925–2929. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzmann B., McIntyre B. W., Weissman I. L. Identification of a murine Peyer's patch--specific lymphocyte homing receptor as an integrin molecule with an alpha chain homologous to human VLA-4 alpha. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90981-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänninen A., Taylor C., Streeter P. R., Stark L. S., Sarte J. M., Shizuru J. A., Simell O., Michie S. A. Vascular addressins are induced on islet vessels during insulitis in nonobese diabetic mice and are involved in lymphoid cell binding to islet endothelium. J Clin Invest. 1993 Nov;92(5):2509–2515. doi: 10.1172/JCI116859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai Y., Lasky L. A., Rosen S. D. Sulphation requirement for GlyCAM-1, an endothelial ligand for L-selectin. Nature. 1993 Feb 11;361(6412):555–557. doi: 10.1038/361555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kansas G. S., Wood G. S., Fishwild D. M., Engleman E. G. Functional characterization of human T lymphocyte subsets distinguished by monoclonal anti-leu-8. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):2995–3002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. K., Jutila M. A., Berg E. L., Butcher E. C. Neutrophil Mac-1 and MEL-14 adhesion proteins inversely regulated by chemotactic factors. Science. 1989 Sep 15;245(4923):1238–1241. doi: 10.1126/science.2551036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraal G., Weissman I. L., Butcher E. C. Memory B cells express a phenotype consistent with migratory competence after secondary but not short-term primary immunization. Cell Immunol. 1988 Aug;115(1):78–87. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90163-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Singer M. S., Dowbenko D., Imai Y., Henzel W. J., Grimley C., Fennie C., Gillett N., Watson S. R., Rosen S. D. An endothelial ligand for L-selectin is a novel mucin-like molecule. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):927–938. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90612-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley K., Tedder T. F., Kansas G. S. L-selectin can mediate leukocyte rolling in untreated mesenteric venules in vivo independent of E- or P-selectin. Blood. 1993 Sep 1;82(5):1632–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro J. M. Endothelial-leukocyte adhesive interactions in inflammatory diseases. Eur Heart J. 1993 Dec;14 (Suppl K):72–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro J. M., Freedman A. S., Aster J. C., Gribben J. G., Lee N. C., Rhynhart K. K., Banchereau J., Nadler L. M. In vivo expression of the B7 costimulatory molecule by subsets of antigen-presenting cells and the malignant cells of Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1994 Feb 1;83(3):793–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro J. M., Lo S. K., Corless C., Robertson M. J., Lee N. C., Barnhill R. L., Weinberg D. S., Bevilacqua M. P. Expression of sialyl-Lewis X, an E-selectin ligand, in inflammation, immune processes, and lymphoid tissues. Am J Pathol. 1992 Dec;141(6):1397–1408. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwenhuis P., Ford W. L. Comparative migration of B- and T-Lymphocytes in the rat spleen and lymph nodes. Cell Immunol. 1976 May;23(2):254–267. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90191-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallesen G., Knudsen L. M. Leucocyte antigens in human post mortem tissues: their preservation and loss as demonstrated by monoclonal antibody immunohistological staining. Histopathology. 1985 Aug;9(8):791–804. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1985.tb02867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleiffenbaum B., Spertini O., Tedder T. F. Soluble L-selectin is present in human plasma at high levels and retains functional activity. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(1):229–238. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.1.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelman M. H., van de Rijn M., Weissman I. L. Mouse lymph node homing receptor cDNA clone encodes a glycoprotein revealing tandem interaction domains. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1165–1172. doi: 10.1126/science.2646713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spertini O., Freedman A. S., Belvin M. P., Penta A. C., Griffin J. D., Tedder T. F. Regulation of leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (TQ1, Leu-8) expression and shedding by normal and malignant cells. Leukemia. 1991 Apr;5(4):300–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spertini O., Kansas G. S., Munro J. M., Griffin J. D., Tedder T. F. Regulation of leukocyte migration by activation of the leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (LAM-1) selectin. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):691–694. doi: 10.1038/349691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spertini O., Kansas G. S., Reimann K. A., Mackay C. R., Tedder T. F. Function and evolutionary conservation of distinct epitopes on the leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (TQ-1, Leu-8) that regulate leukocyte migration. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 1;147(3):942–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spertini O., Luscinskas F. W., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Tedder T. F. Monocyte attachment to activated human vascular endothelium in vitro is mediated by leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (L-selectin) under nonstatic conditions. J Exp Med. 1992 Jun 1;175(6):1789–1792. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.6.1789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spertini O., Luscinskas F. W., Kansas G. S., Munro J. M., Griffin J. D., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Tedder T. F. Leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (LAM-1, L-selectin) interacts with an inducible endothelial cell ligand to support leukocyte adhesion. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 15;147(8):2565–2573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Traffic signals for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: the multistep paradigm. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamper H. B., Jr, Woodruff J. J. Lymphocyte homing into lymph nodes: in vitro demonstration of the selective affinity of recirculating lymphocytes for high-endothelial venules. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):828–833. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder T. F., Isaacs C. M., Ernst T. J., Demetri G. D., Adler D. A., Disteche C. M. Isolation and chromosomal localization of cDNAs encoding a novel human lymphocyte cell surface molecule, LAM-1. Homology with the mouse lymphocyte homing receptor and other human adhesion proteins. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):123–133. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder T. F., Penta A. C., Levine H. B., Freedman A. S. Expression of the human leukocyte adhesion molecule, LAM1. Identity with the TQ1 and Leu-8 differentiation antigens. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):532–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. R., Fennie C., Lasky L. A. Neutrophil influx into an inflammatory site inhibited by a soluble homing receptor-IgG chimaera. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):164–167. doi: 10.1038/349164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X. D., Karin N., Tisch R., Steinman L., McDevitt H. O. Inhibition of insulitis and prevention of diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice by blocking L-selectin and very late antigen 4 adhesion receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10494–10498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]