Abstract
AIMS: To determine levels of expression of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1) in benign and malignant tissues harbouring EBV in relation to EBNA1 promoter usage. METHODS: Expression of EBNA1 was investigated by means of immunohistochemistry using a mixture of two EBNA1 specific monoclonal antibodies, 1H4-1 and 2B4-1. The presence of EBV was detected by EBER1/2 RNA in situ hybridisation. Detection of promoter specific EBNA1 transcripts was by RT-PCR analysis. RESULTS: EBNA1 positive cells were detected in all 20 EBV associated B cell lymphomas, 18 of which had arisen in immunocompromised patients; in eight of nine EBV associated T cell lymphomas; in 11 of 27 EBV positive cases of Hodgkin's disease; and in reactive lymphoid tissue harbouring EBV, including four cases of infectious mononucleosis. A diffuse EBNA1 staining pattern was observed in most of the EBV associated B cell lymphomas and was comparable with the EBER1/2 staining pattern. In the T cell lymphomas the number of EBNA1 positive cells was usually considerably less than the number of EBER1/2 positive ones. RT-PCR analysis revealed that in tumours with restricted EBNA1 expression-that is, T cell lymphomas and Hodgkin's disease lesions, EBNA1 transcripts were usually generated only by the F/Q promoter, whereas in B cell lymphomas EBNA1 transcripts were usually generated by both the C/W and F/Q promoters. CONCLUSIONS: EBNA1 is expressed in all types of tissue harbouring EBV, but the level of expression varies greatly. This may be the result of differential promoter usage.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bijl J., van Oostveen J. W., Kreike M., Rieger E., van der Raaij-Helmer L. M., Walboomers J. M., Corte G., Boncinelli E., van den Brule A. J., Meijer C. J. Expression of HOXC4, HOXC5, and HOXC6 in human lymphoid cell lines, leukemias, and benign and malignant lymphoid tissue. Blood. 1996 Mar 1;87(5):1737–1745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobrow M. N., Shaughnessy K. J., Litt G. J. Catalyzed reporter deposition, a novel method of signal amplification. II. Application to membrane immunoassays. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Mar 1;137(1):103–112. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90399-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks L. A., Lear A. L., Young L. S., Rickinson A. B. Transcripts from the Epstein-Barr virus BamHI A fragment are detectable in all three forms of virus latency. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3182–3190. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3182-3190.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks L., Yao Q. Y., Rickinson A. B., Young L. S. Epstein-Barr virus latent gene transcription in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells: coexpression of EBNA1, LMP1, and LMP2 transcripts. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2689–2697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2689-2697.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. L., Sadler R. H., Walling D. M., Su I. J., Hsieh H. C., Raab-Traub N. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) gene expression in EBV-positive peripheral T-cell lymphomas. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):6303–6308. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.6303-6308.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen F., Zou J. Z., di Renzo L., Winberg G., Hu L. F., Klein E., Klein G., Ernberg I. A subpopulation of normal B cells latently infected with Epstein-Barr virus resembles Burkitt lymphoma cells in expressing EBNA-1 but not EBNA-2 or LMP1. J Virol. 1995 Jun;69(6):3752–3758. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.6.3752-3758.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bruin P. C., Jiwa N. M., Van der Valk P., Van Heerde P., Gordijn R., Ossenkoppele G. J., Walboomers J. M., Meijer C. J. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus nucleic acid sequences and protein in nodal T-cell lymphomas: relation between latent membrane protein-1 positivity and clinical course. Histopathology. 1993 Dec;23(6):509–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1993.tb01236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deacon E. M., Pallesen G., Niedobitek G., Crocker J., Brooks L., Rickinson A. B., Young L. S. Epstein-Barr virus and Hodgkin's disease: transcriptional analysis of virus latency in the malignant cells. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):339–349. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzera G., Hanto D. W., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Rosai J., McKenna R. W., Sibley R. K., Holahan K. P., Lindquist L. L. Polymorphic diffuse B-cell hyperplasias and lymphomas in renal transplant recipients. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4262–4279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratama J. W., Zutter M. M., Minarovits J., Oosterveer M. A., Thomas E. D., Klein G., Ernberg I. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded growth-transformation-associated proteins in lymphoproliferations of bone-marrow transplant recipients. Int J Cancer. 1991 Jan 21;47(2):188–192. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910470205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grässer F. A., Murray P. G., Kremmer E., Klein K., Remberger K., Feiden W., Reynolds G., Niedobitek G., Young L. S., Mueller-Lantzsch N. Monoclonal antibodies directed against the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1): immunohistologic detection of EBNA1 in the malignant cells of Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1994 Dec 1;84(11):3792–3798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Dutoit S. J., Pallesen G. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus small RNAs in routine paraffin sections using non-isotopic RNA/RNA in situ hybridization. Histopathology. 1994 Aug;25(2):101–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1994.tb01565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Dutoit S. J., Pallesen G., Franzmann M. B., Karkov J., Black F., Skinhøj P., Pedersen C. AIDS-related lymphoma. Histopathology, immunophenotype, and association with Epstein-Barr virus as demonstrated by in situ nucleic acid hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):149–163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris N. L., Jaffe E. S., Stein H., Banks P. M., Chan J. K., Cleary M. L., Delsol G., De Wolf-Peeters C., Falini B., Gatter K. C. A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: a proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood. 1994 Sep 1;84(5):1361–1392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst H., Dallenbach F., Hummel M., Niedobitek G., Pileri S., Müller-Lantzsch N., Stein H. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein expression in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4766–4770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. G., Steitz J. A. Localization of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNAs by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9006–9010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummel M., Anagnostopoulos I., Korbjuhn P., Stein H. Epstein-Barr virus in B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas: unexpected infection patterns and different infection incidence in low- and high-grade types. J Pathol. 1995 Mar;175(3):263–271. doi: 10.1002/path.1711750303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiwa N. M., Kanavaros P., De Bruin P. C., van der Valk P., Horstman A., Vos W., Mullink H., Walboomers J. M., Meijer C. J. Presence of Epstein-Barr virus harbouring small and intermediate-sized cells in Hodgkin's disease. Is there a relationship with Reed-Sternberg cells? J Pathol. 1993 Jun;170(2):129–136. doi: 10.1002/path.1711700206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
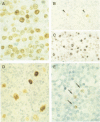
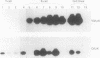
- Jiwa N. M., Oudejans J. J., Dukers D. F., Vos W., Horstman A., van der Valk P., Middledorp J. M., Walboomers J. M., Meijer C. J. Immunohistochemical demonstration of different latent membrane protein-1 epitopes of Epstein-Barr virus in lymphoproliferative diseases. J Clin Pathol. 1995 May;48(5):438–442. doi: 10.1136/jcp.48.5.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan L. D., Shiramizu B., Herndier B., Hahn J., Meeker T. C., Ng V., Volberding P. A., McGrath M. S. Influence of molecular characteristics on clinical outcome in human immunodeficiency virus-associated non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: identification of a subgroup with favorable clinical outcome. Blood. 1995 Apr 1;85(7):1727–1735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye K. M., Izumi K. M., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 is essential for B-lymphocyte growth transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):9150–9154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.9150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan G., Naase M. A. Down-regulation of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 in Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease. J Clin Pathol. 1995 Sep;48(9):845–848. doi: 10.1136/jcp.48.9.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles D. M., Cesarman E., Chadburn A., Frizzera G., Chen J., Rose E. A., Michler R. E. Correlative morphologic and molecular genetic analysis demonstrates three distinct categories of posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorders. Blood. 1995 Jan 15;85(2):552–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korbjuhn P., Anagnostopoulos I., Hummel M., Tiemann M., Dallenbach F., Parwaresch M. R., Stein H. Frequent latent Epstein-Barr virus infection of neoplastic T cells and bystander B cells in human immunodeficiency virus-negative European peripheral pleomorphic T-cell lymphomas. Blood. 1993 Jul 1;82(1):217–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lear A. L., Rowe M., Kurilla M. G., Lee S., Henderson S., Kieff E., Rickinson A. B. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 1 BamHI F promoter is activated on entry of EBV-transformed B cells into the lytic cycle. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7461–7468. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7461-7468.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton T., Gahn T. A., Martin J. M., Sugden B. Immortalizing genes of Epstein-Barr virus. Adv Virus Res. 1991;40:19–55. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60276-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudejans J. J., Jiwa M., van den Brule A. J., Grässer F. A., Horstman A., Vos W., Kluin P. M., van der Valk P., Walboomers J. M., Meijer C. J. Detection of heterogeneous Epstein-Barr virus gene expression patterns within individual post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorders. Am J Pathol. 1995 Oct;147(4):923–933. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudejans J. J., van den Brule A. J., Jiwa N. M., de Bruin P. C., Ossenkoppele G. J., van der Valk P., Walboomers J. M., Meijer C. J. BHRF1, the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) homologue of the BCL-2 protooncogene, is transcribed in EBV-associated B-cell lymphomas and in reactive lymphocytes. Blood. 1995 Sep 1;86(5):1893–1902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab-Traub N. Epstein-Barr virus and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol. 1992 Oct;3(5):297–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea D., Fourcade C., Leblond V., Rowe M., Joab I., Edelman L., Bitker M. O., Gandjbakhch I., Suberbielle C., Farcet J. P. Patterns of Epstein-Barr virus latent and replicative gene expression in Epstein-Barr virus B cell lymphoproliferative disorders after organ transplantation. Transplantation. 1994 Aug 15;58(3):317–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Brooks L., Sample C., Young L., Rowe M., Gregory C., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Restricted Epstein-Barr virus protein expression in Burkitt lymphoma is due to a different Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 transcriptional initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6343–6347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer B. C., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. The Epstein-Barr virus BamHI F promoter is an early lytic promoter: lack of correlation with EBNA 1 gene transcription in group 1 Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines. J Virol. 1995 Aug;69(8):5039–5047. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.8.5039-5047.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivas S. K., Sixbey J. W. Epstein-Barr virus induction of recombinase-activating genes RAG1 and RAG2. J Virol. 1995 Dec;69(12):8155–8158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.12.8155-8158.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stansfeld A. G., Diebold J., Noel H., Kapanci Y., Rilke F., Kelényi G., Sundstrom C., Lennert K., van Unnik J. A., Mioduszewska O. Updated Kiel classification for lymphomas. Lancet. 1988 Feb 6;1(8580):292–293. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90367-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Hotchin N. A., Allday M. J., Amlot P., Rose M., Yacoub M., Crawford D. H. Immunohistology of Epstein-Barr virus-associated antigens in B cell disorders from immunocompromised individuals. Transplantation. 1990 May;49(5):944–953. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199005000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tierney R. J., Steven N., Young L. S., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus latency in blood mononuclear cells: analysis of viral gene transcription during primary infection and in the carrier state. J Virol. 1994 Nov;68(11):7374–7385. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.11.7374-7385.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Jaffe E. S., Liu X. F., Chen Y. Y., Shibata D., Medeiros L. J. Detection and localization of Epstein-Barr viral genomes in angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy and angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy-like lymphoma. Blood. 1992 Apr 1;79(7):1789–1795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Movahed L. A., Warnke R. A., Sklar J. Detection of Epstein-Barr viral genomes in Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 23;320(8):502–506. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902233200806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin P. C., Jiwa M., Oudejans J. J., van der Valk P., van Heerde P., Sabourin J. C., Csanaky G., Gaulard P., Noorduyn A. L., Willemze R. Presence of Epstein-Barr virus in extranodal T-cell lymphomas: differences in relation to site. Blood. 1994 Mar 15;83(6):1612–1618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]