Full text
PDF







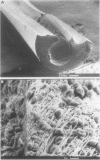
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnow P. M., Quimosing E. M., Beach M. Consequences of intravascular catheter sepsis. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Jun;16(6):778–784. doi: 10.1093/clind/16.6.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atela I., Coll P., Rello J., Quintana E., Barrio J., March F., Sanchez F., Barraquer P., Ballus J., Cotura A. Serial surveillance cultures of skin and catheter hub specimens from critically ill patients with central venous catheters: molecular epidemiology of infection and implications for clinical management and research. J Clin Microbiol. 1997 Jul;35(7):1784–1790. doi: 10.1128/jcm.35.7.1784-1790.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjornson H. S., Colley R., Bower R. H., Duty V. P., Schwartz-Fulton J. T., Fischer J. E. Association between microorganism growth at the catheter insertion site and colonization of the catheter in patients receiving total parenteral nutrition. Surgery. 1982 Oct;92(4):720–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capdevila J. A., Planes A. M., Palomar M., Gasser I., Almirante B., Pahissa A., Crespo E., Martínez-Vázquez J. M. Value of differential quantitative blood cultures in the diagnosis of catheter-related sepsis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992 May;11(5):403–407. doi: 10.1007/BF01961854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciresi D. L., Albrecht R. M., Volkers P. A., Scholten D. J. Failure of antiseptic bonding to prevent central venous catheter-related infection and sepsis. Am Surg. 1996 Aug;62(8):641–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleri D. J., Corrado M. L., Seligman S. J. Quantitative culture of intravenous catheters and other intravascular inserts. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jun;141(6):781–786. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.6.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. L., Hopkins C. C. Rapid diagnosis of intravascular catheter-associated infection by direct Gram staining of catheter segments. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 2;312(18):1142–1147. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505023121802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutlée F., Lemieux C., Paradis J. F. Value of direct catheter staining in the diagnosis of intravascular-catheter-related infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(6):1088–1090. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.6.1088-1090.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyna A. M., Hovenden J. L., Lehmann A., Rajaseker K., Kalia P. Routine replacement of central venous catheters: telephone survey of intensive care units in mainland Britain. BMJ. 1998 Jun 27;316(7149):1944–1945. doi: 10.1136/bmj.316.7149.1944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRUSKIN M. S., SIEGEL P. D. BACTERIAL CONTAMINATION OF INDWELLING INTRAVENOUS POLYETHYLENE CATHETERS. JAMA. 1963 Sep 21;185:966–968. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.03060120076031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn G. L., Burson G. G., Haynes J. R. Blood culture technique based on centrifugation: clinical evaluation. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Mar;3(3):258–263. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.3.258-263.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn G. L., Land G. A., Wilson G. E. Improved blood culture technique based on centrifugation: clinical evaluation. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):391–396. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.391-396.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T. S., Moss H. A., Tebbs S. E., Wilson I. C., Bonser R. S., Graham T. R., Burke L. P., Faroqui M. H. Novel approach to investigate a source of microbial contamination of central venous catheters. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1997 Mar;16(3):210–213. doi: 10.1007/BF01709583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan S. T., Teoh-Chan C. H., Lau K. F., Chu K. W., Kwan A. K., Wong K. K. Predictive value of surveillance skin and hub cultures in central venous catheters sepsis. J Hosp Infect. 1988 Oct;12(3):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(88)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faubion W. C., Wesley J. R., Khalidi N., Silva J. Total parenteral nutrition catheter sepsis: impact of the team approach. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1986 Nov-Dec;10(6):642–645. doi: 10.1177/0148607186010006642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabe N., Jakobsen C. J. Bacterial contamination of 'Venflon' intravenous cannulae with valved injection sideport. J Hosp Infect. 1983 Sep;4(3):291–295. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(83)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groeger J. S., Lucas A. B., Coit D., LaQuaglia M., Brown A. E., Turnbull A., Exelby P. A prospective, randomized evaluation of the effect of silver impregnated subcutaneous cuffs for preventing tunneled chronic venous access catheter infections in cancer patients. Ann Surg. 1993 Aug;218(2):206–210. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199308000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasaniya N. W., Angelis M., Brown M. R., Yu M. Efficacy of subcutaneous silver-impregnated cuffs in preventing central venous catheter infections. Chest. 1996 Apr;109(4):1030–1032. doi: 10.1378/chest.109.4.1030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiselman D. Nosocomial bloodstream infections in the critically ill. JAMA. 1994 Dec 21;272(23):1819–1820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herwaldt L. A., Geiss M., Kao C., Pfaller M. A. The positive predictive value of isolating coagulase-negative staphylococci from blood cultures. Clin Infect Dis. 1996 Jan;22(1):14–20. doi: 10.1093/clinids/22.1.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kite P., Dobbins B. M., Wilcox M. H., Fawley W. N., Kindon A. J., Thomas D., Tighe M. J., McMahon M. J. Evaluation of a novel endoluminal brush method for in situ diagnosis of catheter related sepsis. J Clin Pathol. 1997 Apr;50(4):278–282. doi: 10.1136/jcp.50.4.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristinsson K. G., Burnett I. A., Spencer R. C. Evaluation of three methods for culturing long intravascular catheters. J Hosp Infect. 1989 Oct;14(3):183–191. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(89)90034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livesley M. A., Tebbs S. E., Moss H. A., Faroqui M. H., Lambert P. A., Elliott T. S. Use of pulsed field gel electrophoresis to determine the source of microbial contamination of central venous catheters. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1998 Feb;17(2):108–112. doi: 10.1007/BF01682166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logghe C., Van Ossel C., D'Hoore W., Ezzedine H., Wauters G., Haxhe J. J. Evaluation of chlorhexidine and silver-sulfadiazine impregnated central venous catheters for the prevention of bloodstream infection in leukaemic patients: a randomized controlled trial. J Hosp Infect. 1997 Oct;37(2):145–156. doi: 10.1016/s0195-6701(97)90184-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki D. G., Cobb L., Garman J. K., Shapiro J. M., Ringer M., Helgerson R. B. An attachable silver-impregnated cuff for prevention of infection with central venous catheters: a prospective randomized multicenter trial. Am J Med. 1988 Sep;85(3):307–314. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90579-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki D. G., Cobb L., Garman J. K., Shapiro J. M., Ringer M., Helgerson R. B. An attachable silver-impregnated cuff for prevention of infection with central venous catheters: a prospective randomized multicenter trial. Am J Med. 1988 Sep;85(3):307–314. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90579-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki D. G., Stolz S. M., Wheeler S., Mermel L. A. Prevention of central venous catheter-related bloodstream infection by use of an antiseptic-impregnated catheter. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1997 Aug 15;127(4):257–266. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-127-4-199708150-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki D. G., Weise C. E., Sarafin H. W. A semiquantitative culture method for identifying intravenous-catheter-related infection. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jun 9;296(23):1305–1309. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197706092962301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel L., McMichan J. C., Bachy J. L. Microbial colonization of indwelling central venous catheters: statistical evaluation of potential contaminating factors. Am J Surg. 1979 Jun;137(6):745–748. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(79)90085-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padberg F. T., Jr, Ruggiero J., Blackburn G. L., Bistrian B. R. Central venous catheterization for parenteral nutrition. Ann Surg. 1981 Mar;193(3):264–270. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198103000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson M. L., Abrutyn E. Reducing the risk for catheter-related infections: a new strategy. Ann Intern Med. 1997 Aug 15;127(4):304–306. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-127-4-199708150-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson M. L. Guideline for prevention of intravascular device-related infections. Hospital Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1996 Jul;17(7):438–473. doi: 10.1086/647338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton L. B., Ross V., Cuddy P., Kremer H., Fessler T., McGurk E. No difference in catheter sepsis between standard and antiseptic central venous catheters. A prospective randomized trial. Arch Surg. 1996 Sep;131(9):986–989. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1996.01430210084018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittet D., Tarara D., Wenzel R. P. Nosocomial bloodstream infection in critically ill patients. Excess length of stay, extra costs, and attributable mortality. JAMA. 1994 May 25;271(20):1598–1601. doi: 10.1001/jama.271.20.1598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell C., Kudsk K. A., Kulich P. A., Mandelbaum J. A., Fabri P. J. Effect of frequent guidewire changes on triple-lumen catheter sepsis. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1988 Sep-Oct;12(5):462–464. doi: 10.1177/0148607188012005462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prager R. L., Silva J., Jr Colonization of central venous catheters. South Med J. 1984 Apr;77(4):458–461. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198404000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raad I., Costerton W., Sabharwal U., Sacilowski M., Anaissie E., Bodey G. P. Ultrastructural analysis of indwelling vascular catheters: a quantitative relationship between luminal colonization and duration of placement. J Infect Dis. 1993 Aug;168(2):400–407. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.2.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raad I., Darouiche R., Dupuis J., Abi-Said D., Gabrielli A., Hachem R., Wall M., Harris R., Jones J., Buzaid A. Central venous catheters coated with minocycline and rifampin for the prevention of catheter-related colonization and bloodstream infections. A randomized, double-blind trial. The Texas Medical Center Catheter Study Group. Ann Intern Med. 1997 Aug 15;127(4):267–274. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-127-4-199708150-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raad I. Intravascular-catheter-related infections. Lancet. 1998 Mar 21;351(9106):893–898. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)10006-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raucher H. S., Hyatt A. C., Barzilai A., Harris M. B., Weiner M. A., LeLeiko N. S., Hodes D. S. Quantitative blood cultures in the evaluation of septicemia in children with Broviac catheters. J Pediatr. 1984 Jan;104(1):29–33. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80584-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushforth J. A., Hoy C. M., Kite P., Puntis J. W. Rapid diagnosis of central venous catheter sepsis. Lancet. 1993 Aug 14;342(8868):402–403. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92815-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. A., Jr, Abel R. M., Abbott W. M., Hopkins C. C., Chesney T. M., Colley R., Phillips K., Fischer J. E. Catheter complications in total parenteral nutrition. A prospective study of 200 consecutive patients. N Engl J Med. 1974 Apr 4;290(14):757–761. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197404042901401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman M. B., Isenberg H. D., Shapiro J. F., Lipsitz P. J., Rubin L. G. A prospective study of the catheter hub as the portal of entry for microorganisms causing catheter-related sepsis in neonates. J Infect Dis. 1993 Feb;167(2):487–490. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.2.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segura M., Alvarez-Lerma F., Tellado J. M., Jiménez-Ferreres J., Oms L., Rello J., Baró T., Sánchez R., Morera A., Mariscal D. A clinical trial on the prevention of catheter-related sepsis using a new hub model. Ann Surg. 1996 Apr;223(4):363–369. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199604000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherertz R. J., Heard S. O., Raad I. I. Diagnosis of triple-lumen catheter infection: comparison of roll plate, sonication, and flushing methodologies. J Clin Microbiol. 1997 Mar;35(3):641–646. doi: 10.1128/jcm.35.3.641-646.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitges-Serra A., Linares J., Garau J. Catheter sepsis: the clue is the hub. Surgery. 1985 Mar;97(3):355–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitges-Serra A., Liñares J. Limitations of semiquantitative method for catheter culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):1074–1076. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.1074-1076.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souvenir D., Anderson D. E., Jr, Palpant S., Mroch H., Askin S., Anderson J., Claridge J., Eiland J., Malone C., Garrison M. W. Blood cultures positive for coagulase-negative staphylococci: antisepsis, pseudobacteremia, and therapy of patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1998 Jul;36(7):1923–1926. doi: 10.1128/jcm.36.7.1923-1926.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tighe M. J., Kite P., Fawley W. N., Thomas D., McMahon M. J. An endoluminal brush to detect the infected central venous catheter in situ: a pilot study. BMJ. 1996 Dec 14;313(7071):1528–1529. doi: 10.1136/bmj.313.7071.1528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tighe M. J., Kite P., Thomas D., Fawley W. N., McMahon M. J. Rapid diagnosis of catheter-related sepsis using the acridine orange leukocyte cytospin test and an endoluminal brush. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1996 May-Jun;20(3):215–218. doi: 10.1177/0148607196020003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilton R. C. The laboratory approach to the detection of bacteremia. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:467–493. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer A. F., Nettleman M., Flint K., Wenzel R. P. The clinical impact of culturing central venous catheters. A prospective study. Arch Intern Med. 1992 Jun;152(6):1299–1302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox M., Kite P., Dobbins B. Antimicrobial intravascular catheters--which surface to coat? J Hosp Infect. 1998 Apr;38(4):322–324. doi: 10.1016/s0195-6701(98)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagupsky P., Nolte F. S. Quantitative aspects of septicemia. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jul;3(3):269–279. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.3.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]