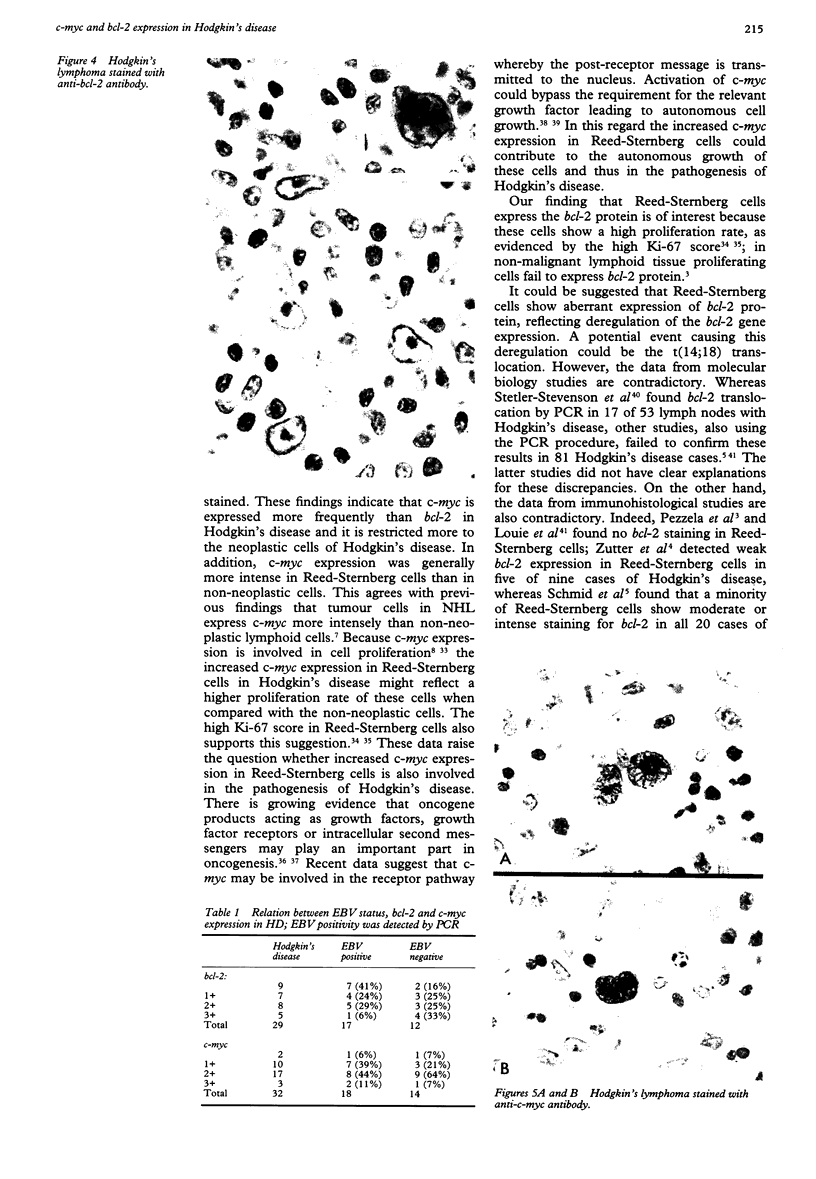
Abstract
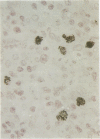
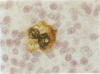
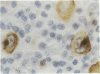
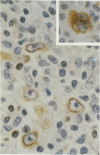
AIMS: To evaluate the expression of c-myc and bcl-2 oncogene products in Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease, especially in relation to Epstein-Barr virus infection and expression of EBV encoded latent membrane protein (LMP). METHODS: Tissues from 33 cases of Hodgkin's disease were studied for the presence of EBV DNA by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and DNA in situ hybridisation (DISH), for the presence of EBER-1 and EBER-2 EBV RNA by RNA in situ hybridisation (RISH); and for the presence of LMP, bcl-2, and c-myc proteins by immunohistochemical staining. RESULTS: A substantial number of Reed-Sternberg cells expressed bcl-2 in 20 of 29 (69%) and c-myc in 30 of 32 (94%) Hodgkin's disease samples. In 18 of the 25 (72%) cases Reed-Sternberg cells expressed both oncogene products. Of these 18 cases, 10 (56%) were EBV-PCR positive; eight (44%) were EBV-PCR negative. CONCLUSIONS: Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease frequently express both bcl-2 and c-myc oncogene products, suggesting that these oncogenes may act in concert in the pathogenesis of the disease. Moreover, the expression of c-myc and bcl-2 proteins in Reed-Sternberg cells is independent of EBV and LMP status.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfieri C., Birkenbach M., Kieff E. Early events in Epstein-Barr virus infection of human B lymphocytes. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):595–608. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90893-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Algara P., Martinez P., Sanchez L., Villuendas R., Orradre J. L., Oliva H., Piris M. A. Lymphocyte predominance Hodgkin's disease (nodular paragranuloma)--a bcl-2 negative germinal centre lymphoma. Histopathology. 1991 Jul;19(1):69–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1991.tb00896.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armelin H. A., Armelin M. C., Kelly K., Stewart T., Leder P., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D. Functional role for c-myc in mitogenic response to platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):655–660. doi: 10.1038/310655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balk S. D., Riley T. M., Gunther H. S., Morisi A. Heparin-treated, v-myc-transformed chicken heart mesenchymal cells assume a normal morphology but are hypersensitive to epidermal growth factor (EGF) and brain fibroblast growth factor (bFGF); cells transformed by the v-Ha-ras oncogene are refractory to EGF and bFGF but are hypersensitive to insulin-like growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5781–5785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Bregni M., Erikson J., Patterson D., Gallo R. C., Croce C. M. Human c-myc onc gene is located on the region of chromosome 8 that is translocated in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7824–7827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jong D., Voetdijk B. M., Beverstock G. C., van Ommen G. J., Willemze R., Kluin P. M. Activation of the c-myc oncogene in a precursor-B-cell blast crisis of follicular lymphoma, presenting as composite lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 26;318(21):1373–1378. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805263182106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman R. N., Tachibana C. Y., Abrams H. D., Hann S. R. V-myc- and c-myc-encoded proteins are associated with the nuclear matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):114–126. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falini B., Stein H., Pileri S., Canino S., Farabbi R., Martelli M. F., Grignani F., Fagioli M., Minelli O., Ciani C. Expression of lymphoid-associated antigens on Hodgkin's and Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease. An immunocytochemical study on lymph node cytospins using monoclonal antibodies. Histopathology. 1987 Dec;11(12):1229–1242. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1987.tb01869.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J., Van Baarlen J., Pileri S., Schwarting R., Van Unnik J. A., Stein H. Tumor cell growth fraction in Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1987 Sep;128(3):390–393. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyette M., Petropoulos C. J., Shank P. R., Fausto N. Expression of a cellular oncogene during liver regeneration. Science. 1983 Feb 4;219(4584):510–512. doi: 10.1126/science.6297003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Growth factors: mechanism of action and relation to oncogenes. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90296-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S., Rowe M., Gregory C., Croom-Carter D., Wang F., Longnecker R., Kieff E., Rickinson A. Induction of bcl-2 expression by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 protects infected B cells from programmed cell death. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1107–1115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90007-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst H., Niedobitek G., Kneba M., Hummel M., Finn T., Anagnostopoulos I., Bergholz M., Krieger G., Stein H. High incidence of Epstein-Barr virus genomes in Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jul;137(1):13–18. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockenbery D., Nuñez G., Milliman C., Schreiber R. D., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):334–336. doi: 10.1038/348334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack A. S., Kerr I. B., Evan G., Lee F. D. The distribution of the c-myc oncogene product in malignant lymphomas and various normal tissues as demonstrated by immunocytochemistry. Br J Cancer. 1986 Jun;53(6):713–719. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1986.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. J., Ghosh A. K., Moore M., Schofield P. F. A critical appraisal of the immunohistochemical detection of the c-myc oncogene product in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 1987 Dec;56(6):779–783. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louie D. C., Kant J. A., Brooks J. J., Reed J. C. Absence of t(14;18) major and minor breakpoints and of Bcl-2 protein overproduction in Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1991 Dec;139(6):1231–1237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinet Y., Bitterman P. B., Mornex J. F., Grotendorst G. R., Martin G. R., Crystal R. G. Activated human monocytes express the c-sis proto-oncogene and release a mediator showing PDGF-like activity. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):158–160. doi: 10.1038/319158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell T. J., Korsmeyer S. J. Progression from lymphoid hyperplasia to high-grade malignant lymphoma in mice transgenic for the t(14; 18). Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):254–256. doi: 10.1038/349254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeithan T. W. Molecular biology of non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Semin Oncol. 1990 Feb;17(1):30–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitani S., Sugawara I., Shiku H., Mori S. Expression of c-myc oncogene product and ras family oncogene products in various human malignant lymphomas defined by immunohistochemical techniques. Cancer. 1988 Nov 15;62(10):2085–2093. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19881115)62:10<2085::aid-cncr2820621003>3.0.co;2-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullink H., Vos W., Jiwa M., Horstman A., van der Valk P., Walboomers J. M., Meijer C. J. Application and comparison of silver intensification methods for the diaminobenzidine and diaminobenzidine-nickel endproduct of the peroxidation reaction in immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Apr;40(4):495–504. doi: 10.1177/40.4.1532404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel B. G., Jhanwar S. C., Chaganti R. S., Hayward W. S. Two human c-onc genes are located on the long arm of chromosome 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7842–7846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallesen G., Hamilton-Dutoit S. J., Rowe M., Young L. S. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene products in tumour cells of Hodgkin's disease. Lancet. 1991 Feb 9;337(8737):320–322. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90943-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzella F., Tse A. G., Cordell J. L., Pulford K. A., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. Expression of the bcl-2 oncogene protein is not specific for the 14;18 chromosomal translocation. Am J Pathol. 1990 Aug;137(2):225–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C., Pan L., Diss T., Isaacson P. G. Expression of B-cell antigens by Hodgkin's and Reed-Sternberg cells. Am J Pathol. 1991 Oct;139(4):701–707. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler-Stevenson M., Crush-Stanton S., Cossman J. Involvement of the bcl-2 gene in Hodgkin's disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 May 16;82(10):855–858. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.10.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasser A., Harris A. W., Bath M. L., Cory S. Novel primitive lymphoid tumours induced in transgenic mice by cooperation between myc and bcl-2. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):331–333. doi: 10.1038/348331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J. L. Epstein-Barr virus and lymphoproliferative disorders. Semin Hematol. 1988 Jul;25(3):269–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R., Kirsch I., Morton C., Lenoir G., Swan D., Tronick S., Aaronson S., Leder P. Translocation of the c-myc gene into the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in human Burkitt lymphoma and murine plasmacytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7837–7841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Gorham J., Cossman J., Jaffe E., Croce C. M. The t(14;18) chromosome translocations involved in B-cell neoplasms result from mistakes in VDJ joining. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1390–1393. doi: 10.1126/science.3929382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L., Cory S., Adams J. M. Bcl-2 gene promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to immortalize pre-B cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):440–442. doi: 10.1038/335440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Movahed L. A., Warnke R. A., Sklar J. Detection of Epstein-Barr viral genomes in Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 23;320(8):502–506. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902233200806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Warnke R. A., Sklar J., Cleary M. L. Molecular analysis of the t(14;18) chromosomal translocation in malignant lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 1987 Nov 5;317(19):1185–1189. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198711053171904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. E., Frierson H. F., Jr, Tabbarah S., Ennis P. S. Fine-needle aspiration of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Southern blot analysis for antigen receptor, bcl-2, and c-myc gene rearrangements. Am J Clin Pathol. 1990 Jun;93(6):754–759. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/93.6.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynford-Thomas D. Oncogenes and anti-oncogenes; the molecular basis of tumour behaviour. J Pathol. 1991 Nov;165(3):187–201. doi: 10.1002/path.1711650302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zutter M., Hockenbery D., Silverman G. A., Korsmeyer S. J. Immunolocalization of the Bcl-2 protein within hematopoietic neoplasms. Blood. 1991 Aug 15;78(4):1062–1068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]