Abstract
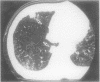
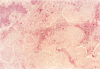
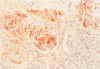
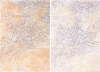
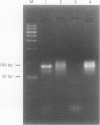
AIMS: To investigate the relation between localised amyloidosis and immunocytic dyscrasia. METHODS: Open lung biopsy specimens from a 72 year old man with multiple nodules in the right middle and lower lung were stained with haematoxylin-eosin, Congo red, and antibodies against IgG, IgA, IgM, and kappa and lambda light chains. Semi-nested PCR amplification for the immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) gene was performed using consensus primers for the VDJ region of the IgH gene, FR3A, LJH, and VLJH. RESULTS: The biopsy specimens contained eosinophilic amorphous material stained with Congro red and anti-kappa light chain, and surrounded by inflammatory cells intermingled with plasma cells. Plasma cells in the adjacent amorphous material showed cytoplasmic staining with anti-kappa. Polymerase chain reaction revealed a discrete amplified band of apparently uniform size with background smear. CONCLUSIONS: Primary AL type localised amyloidosis involves local accumulation of monoclonal plasma cells and their secreted products, as in nodular cutaneous amyloidosis. Localised AL type nodular amyloidosis is a separate entity in amyloidosis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brisco M. J., Tan L. W., Orsborn A. M., Morley A. A. Development of a highly sensitive assay, based on the polymerase chain reaction, for rare B-lymphocyte clones in a polyclonal population. Br J Haematol. 1990 Jun;75(2):163–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb02643.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deans G. T., Hale R. J., McMahon R. F., Brough W. A. Amyloid tumour of the colon. J Clin Pathol. 1995 Jun;48(6):592–593. doi: 10.1136/jcp.48.6.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk R. H., Comenzo R. L., Skinner M. The systemic amyloidoses. N Engl J Med. 1997 Sep 25;337(13):898–909. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199709253371306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grünewald K., Sepp N., Weyrer K., Lhotta K., Feichtinger H., Konwalinka G., Breathnach S. M., Hintner H. Gene rearrangement studies in the diagnosis of primary systemic and nodular primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Oct;97(4):693–696. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12484004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagari Y., Mihara M., Hagari S. Nodular localized cutaneous amyloidosis: detection of monoclonality of infiltrating plasma cells by polymerase chain reaction. Br J Dermatol. 1996 Oct;135(4):630–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagari Y., Mihara M., Konohana I., Ueki H., Yamamoto O., Koizumi H. Nodular localized cutaneous amyloidosis: further demonstration of monoclonality of infiltrating plasma cells in four additional Japanese patients. Br J Dermatol. 1998 Apr;138(4):652–654. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.1998.02179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui A. N., Koss M. N., Hochholzer L., Wehunt W. D. Amyloidosis presenting in the lower respiratory tract. Clinicopathologic, radiologic, immunohistochemical, and histochemical studies on 48 cases. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986 Mar;110(3):212–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaworski A., Goldberg S. K., Walkenstein M. D., Wilson B., Lippmann M. L. Utility of immediate postlobectomy fiberoptic bronchoscopy in preventing atelectasis. Chest. 1988 Jul;94(1):38–43. doi: 10.1378/chest.94.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyle R. A., Gertz M. A. Primary systemic amyloidosis: clinical and laboratory features in 474 cases. Semin Hematol. 1995 Jan;32(1):45–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laeng R. H., Altermatt H. J., Scheithauer B. W., Zimmermann D. R. Amyloidomas of the nervous system: a monoclonal B-cell disorder with monotypic amyloid light chain lambda amyloid production. Cancer. 1998 Jan 15;82(2):362–374. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0142(19980115)82:2<375::aid-cncr18>3.0.co;2-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mata J. M., Cáceres J., Senac J. P., Giron J., Alegret X. General case of the day. Nodular amyloidosis of the lung. Radiographics. 1991 Jul;11(4):716–718. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.11.4.1887124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura K., Shirasawa H. Lambda III subgroup immunoglobulin light chains are precursor proteins of nodular pulmonary amyloidosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1993 Nov;100(5):561–566. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/100.5.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipe J. D. Amyloidosis. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1994;31(4):325–354. doi: 10.3109/10408369409084679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trainor K. J., Brisco M. J., Story C. J., Morley A. A. Monoclonality in B-lymphoproliferative disorders detected at the DNA level. Blood. 1990 Jun 1;75(11):2220–2222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utz J. P., Swensen S. J., Gertz M. A. Pulmonary amyloidosis. The Mayo Clinic experience from 1980 to 1993. Ann Intern Med. 1996 Feb 15;124(4):407–413. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-124-4-199602150-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan J. H., Trainor K. J., Brisco M. J., Morley A. A. Monoclonality in B cell lymphoma detected in paraffin wax embedded sections using the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Pathol. 1990 Nov;43(11):888–890. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.11.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]