Abstract
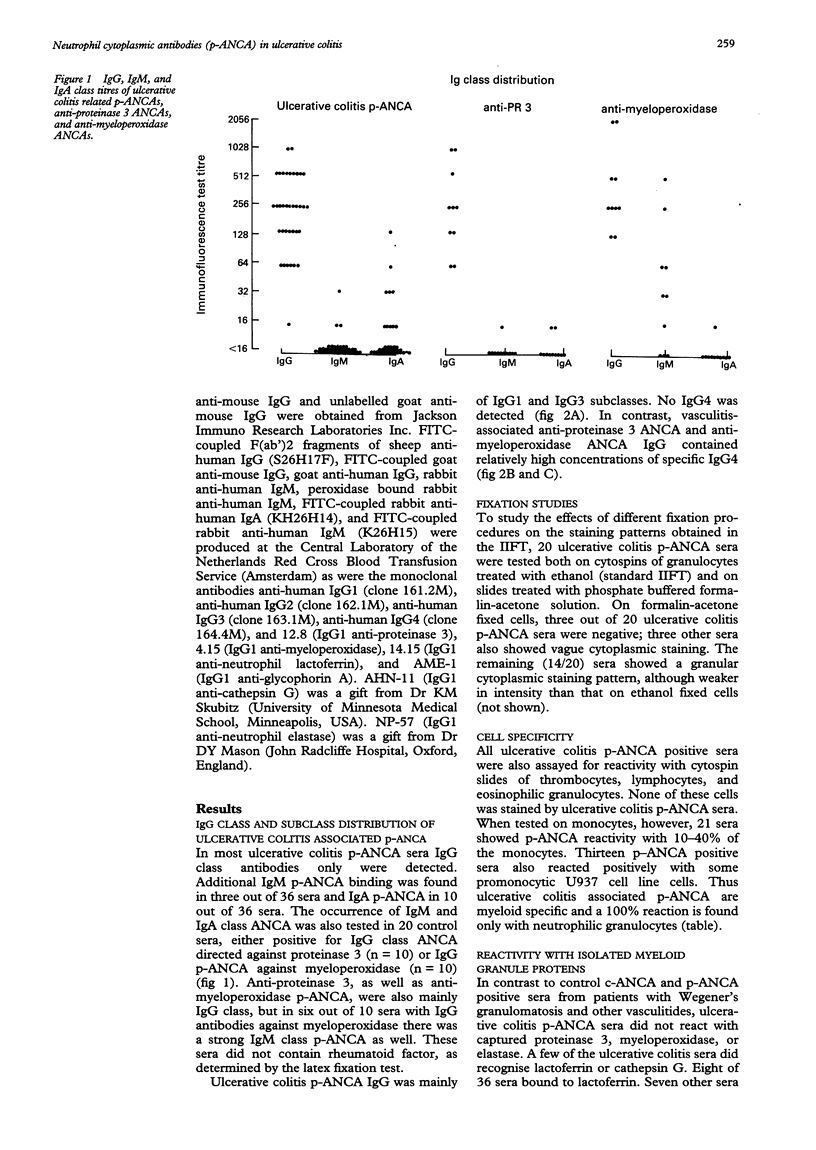
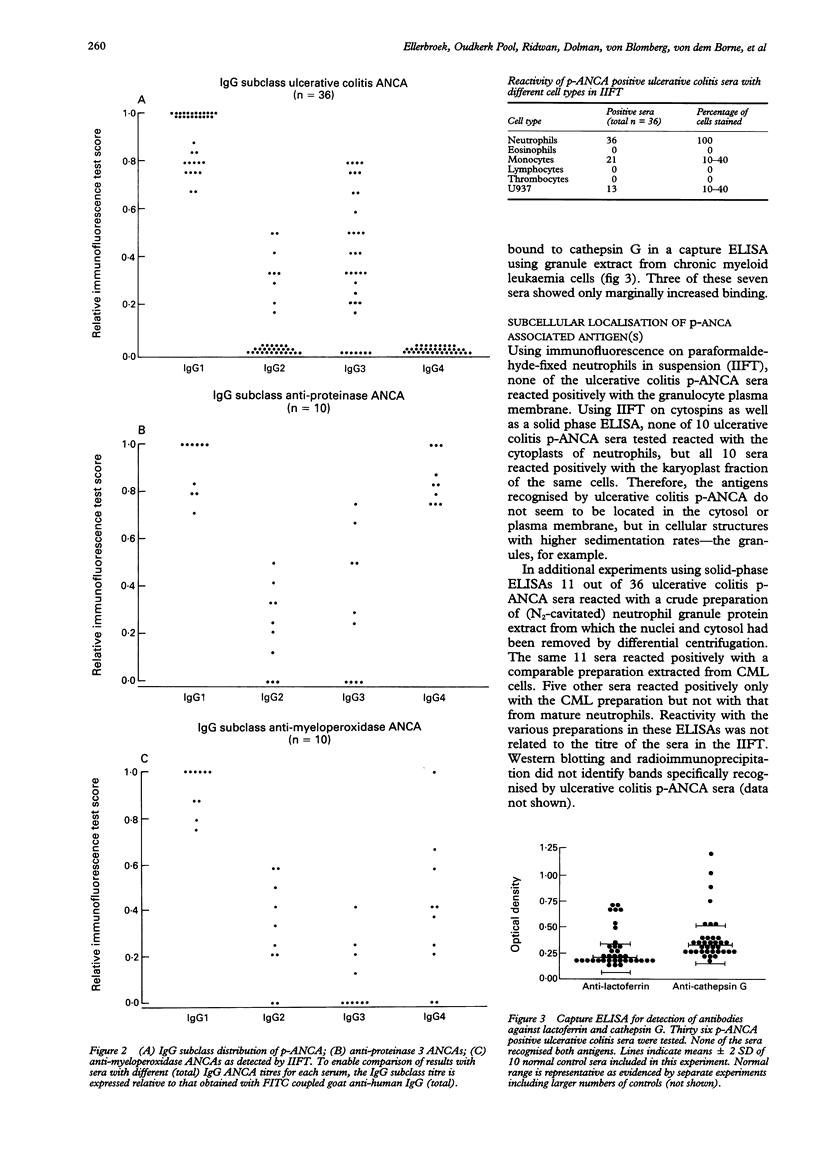
AIMS--To study ulcerative colitis associated neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (p-ANCA) in respect of class and subclass distribution, antigen specificity, and (sub)cellular localisation of the antigen(s) to which these antibodies are directed. METHODS--p-ANCA positivity was determined using the standard indirect immunofluorescence test (IIFT). The immunoglobulin (Ig) subclass distribution of p-ANCA was investigated using monoclonal antibodies directed against IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4. Intracellular antigen localisation studies were performed on (fractionated) neutrophils using antigen-specific antibodies. RESULTS--In contrast to vasculitis associated ANCA, ulcerative colitis p-ANCA are mainly of IgG1 and IgG3 subclass and lack IgG4. Ulcerative colitis p-ANCA are myeloid specific. IIFT data indicate that the related antigen(s) seem(s) to be located not in the cytosol, but in the granules (most likely the azurophil granules) of the neutrophil. CONCLUSIONS--p-ANCA in ulcerative colitis have a different immunoglobulin subclass distribution than the ANCA of systemic necrotising vasculitis and necrotising and crescentic glomerulonephritis. This may point to differences in immune regulation between these diseases. Both cathepsin G and lactoferrin are recognised by a subpopulation of ulcerative colitis p-ANCA. In our series, eight out of 36 (22%) of ulcerative colitis associated p-ANCA react with lactoferrin and seven (19.5%) other sera with cathepsin G. None of them recognised both antigens. The main target antigen(s) of ulcerative colitis p-ANCA still remain(s) to be identified.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borregaard N., Heiple J. M., Simons E. R., Clark R. A. Subcellular localization of the b-cytochrome component of the human neutrophil microbicidal oxidase: translocation during activation. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):52–61. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouwer E., Tervaert J. W., Horst G., Huitema M. G., van der Giessen M., Limburg P. C., Kallenberg C. G. Predominance of IgG1 and IgG4 subclasses of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies (ANCA) in patients with Wegener's granulomatosis and clinically related disorders. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Mar;83(3):379–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05647.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell E. J., Cury J. D., Shapiro S. D., Goldberg G. I., Welgus H. G. Neutral proteinases of human mononuclear phagocytes. Cellular differentiation markedly alters cell phenotype for serine proteinases, metalloproteinases, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1286–1293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duerr R. H., Targan S. R., Landers C. J., LaRusso N. F., Lindsay K. L., Wiesner R. H., Shanahan F. Neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies: a link between primary sclerosing cholangitis and ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1991 May;100(5 Pt 1):1385–1391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk R. J., Hogan S. L., Wilkman A. S., Terrell R. S., Lauritzen S., Charles L. A., Jennette J. C. Myeloperoxidase specific anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies (MPO-ANCA). Neth J Med. 1990 Apr;36(3-4):121–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk R. J., Jennette J. C. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies with specificity for myeloperoxidase in patients with systemic vasculitis and idiopathic necrotizing and crescentic glomerulonephritis. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 23;318(25):1651–1657. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806233182504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk R. J., Terrell R. S., Charles L. A., Jennette J. C. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies induce neutrophils to degranulate and produce oxygen radicals in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4115–4119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmeding R., van der Schoot C. E., ten Bokkel Huinink D., Hack C. E., van den Ende M. E., Kallenberg C. G., von dem Borne A. E. Wegener's granulomatosis autoantibodies identify a novel diisopropylfluorophosphate-binding protein in the lysosomes of normal human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1577–1587. doi: 10.1172/JCI114335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross W. L., Schmitt W. H., Csernok E. ANCA and associated diseases: immunodiagnostic and pathogenetic aspects. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Jan;91(1):1–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb03345.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbwachs-Mecarelli L., Nusbaum P., Noël L. H., Reumaux D., Erlinger S., Grünfeld J. P., Lesavre P. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA) directed against cathepsin G in ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease and primary sclerosing cholangitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Oct;90(1):79–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb05835.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao R. C., Wehner N. G., Skubitz K. M., Gray B. H., Hoidal J. R. Proteinase 3. A distinct human polymorphonuclear leukocyte proteinase that produces emphysema in hamsters. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):1963–1973. doi: 10.1172/JCI113816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. S., Adu D., Thompson R. A. Anti-myeloperoxidase antibodies in systemic vasculitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Jan;79(1):41–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05124.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüdemann J., Utecht B., Gross W. L. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibodies in Wegener's granulomatosis recognize an elastinolytic enzyme. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):357–362. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen H., Wiik A., Elmgreen J. Granulocyte specific antinuclear antibodies in ulcerative colitis. Aid in differential diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1983 Feb;91(1):23–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll H. Characterization of macromolecules by constant velocity sedimentation. Nature. 1967 Jul 22;215(5099):360–363. doi: 10.1038/215360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudkerk Pool M., Ellerbroek P. M., Ridwan B. U., Goldschmeding R., von Blomberg B. M., Peña A. S., Dolman K. M., Bril H., Dekker W., Nauta J. J. Serum antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies in inflammatory bowel disease are mainly associated with ulcerative colitis. A correlation study between perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies and clinical parameters, medical, and surgical treatment. Gut. 1993 Jan;34(1):46–50. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peen E., Almer S., Bodemar G., Rydén B. O., Sjölin C., Tejle K., Skogh T. Anti-lactoferrin antibodies and other types of ANCA in ulcerative colitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and Crohn's disease. Gut. 1993 Jan;34(1):56–62. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos D., Voetman A. A., Meerhof L. J. Functional activity of enucleated human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):368–377. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos D., de Boer M. Purification and cryopreservation of phagocytes from human blood. Methods Enzymol. 1986;132:225–243. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(86)32010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savige J. A., Gallicchio M., Georgiou T., Davies D. J. Diverse target antigens recognized by circulating antibodies in anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated renal vasculitides. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Nov;82(2):238–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05433.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxon A., Shanahan F., Landers C., Ganz T., Targan S. A distinct subset of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies is associated with inflammatory bowel disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990 Aug;86(2):202–210. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(05)80067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schur P. H. IgG subclasses--a review. Ann Allergy. 1987 Feb;58(2):89-96, 99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaper-Cortenbach I. C., Admiraal L. G., Kerr J. M., van Leeuwen E. F., von dem Borne A. E., Tetteroo P. A. Flow-cytometric detection of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase and other intracellular antigens in combination with membrane antigens in acute lymphatic leukemias. Blood. 1988 Nov;72(5):1639–1644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snook J. A., Chapman R. W., Fleming K., Jewell D. P. Anti-neutrophil nuclear antibody in ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease and primary sclerosing cholangitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Apr;76(1):30–33. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. A., Lee S. S. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies. Lancet. 1989 Mar 25;1(8639):670–671. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheugt F. W., von dem Borne A. E., Décary F., Engelfriet C. P. The detection of granulocyte alloantibodies with an indirect immunofluorescence test. Br J Haematol. 1977 Aug;36(4):533–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb00994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiik A. Delineation of a standard procedure for indirect immunofluorescence detection of ANCA. APMIS Suppl. 1989;6:12–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiik A. Granulocyte-specific antinuclear antibodies. Possible significance for the pathogenesis, clinical features and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Allergy. 1980 Jun;35(4):263–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1980.tb01768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


