Abstract
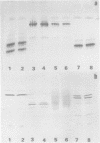
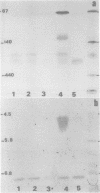
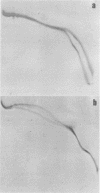
AIM--To identify a physico-chemical criterion, or set of criteria, explaining and possibly predicting the nephrotoxic behaviour of Bence-Jones proteins (BJP). METHODS--The electrophoretic mobility and isoelectric point (pI) of 92 BJP isolates were determined using various electrophoresis procedures on polyacrylamide gel. The proportions of monomers and dimers were determined using sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS PAGE) in 58 cases. PAGE data for 10 BJP isolates were used to construct Ferguson plots and titration curves. RESULTS--The distribution of electrophoretic mobility and pI values was bimodal and showed a positive correlation when the pI was above 6. The values of these two parameters in 22 patients with renal impairment were not significantly different from those in the patients without renal impairment, and the statistical analysis showed no predictive value for the onset of renal impairment. However, patients excreting the lambda light chain isotype had a 2.8-fold higher risk of developing renal impairment compared with the other patients. Studies of the charge variation of the protein with pH indicated three types of behaviour, suggesting that the charge of BJP is highly variable at physiological pH. CONCLUSION--It is important to study not only the positivity or negativity of the BJP charge at a given pH, but also its intensity. The study of the BJP titration curves in patients with renal impairment suggests that a low charge at physiological urinary pH could predict renal impairment.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexanian R., Haut A., Khan A. U., Lane M., McKelvey E. M., Migliore P. J., Stuckey W. J., Jr, Wilson H. E. Treatment for multiple myeloma. Combination chemotherapy with different melphalan dose regimens. JAMA. 1969 Jun 2;208(9):1680–1685. doi: 10.1001/jama.208.9.1680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNIER G. M., PUTNAM F. W. POLYMERISM, POLYMORPHISM, AND IMPURITIES IN BENCE-JONES PROTEINS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 11;86:295–308. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaufils M., Morel-Maroger L. Pathogenesis of renal disease in monoclonal gammopathies: current concepts. Nephron. 1978;20(3):125–131. doi: 10.1159/000181210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berggård I., Peterson P. A. Polymeric forms of free normal kappa and lambda chains of human immunoglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4299–4307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clyne D. H., Pesce A. J., Thompson R. E. Nephrotoxicity of Bence Jones proteins in the rat: importance of protein isoelectric point. Kidney Int. 1979 Sep;16(3):345–352. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coward R. A., Delamore I. W., Mallick N. P., Robinson E. L. The importance of urinary immunoglobulin light chain isoelectric point (pI) in nephrotoxicity in multiple myeloma. Clin Sci (Lond) 1984 Feb;66(2):229–232. doi: 10.1042/cs0660229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Cooke C. R., Wright J. R., Humphrey R. L. Renal function in patients with multiple myeloma. Medicine (Baltimore) 1978 Mar;57(2):151–166. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197803000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deegan M. J. Bence jones proteins: nature, metabolism, detection and significance. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1976 Jan-Feb;6(1):38–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defronzo R. A., Humphrey R. L., Wright J. R., Cooke C. R. Acute renal failure in multiple myeloma. Medicine (Baltimore) 1975 May;54(3):209–223. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197505000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang L. S. Light-chain nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1985 Mar;27(3):582–592. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb M. F. Two-dimensional electrophoretic analysis of immunoglobulin patterns in monoclonal gammopathies. Electrophoresis. 1992 Jul;13(7):440–444. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150130191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill G. S., Morel-Maroger L., Méry J. P., Brouet J. C., Mignon F. Renal lesions in multiple myeloma: their relationship to associated protein abnormalities. Am J Kidney Dis. 1983 Jan;2(4):423–438. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(83)80075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P. J., Sampson C. J., Cooper E. H., Heney D., Brocklebank J. T. Analysis of proteinuria using a commercial system for automated electrophoresis and isoelectric focusing. Ann Clin Biochem. 1988 May;25(Pt 3):319–324. doi: 10.1177/000456328802500322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns E. A., Turner R., Cooper E. H., Maclennan I. C. Isoelectric points of urinary light chains in myelomatosis: analysis in relation to nephrotoxicity. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Aug;39(8):833–837. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.8.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyle R. A. Multiple myeloma: review of 869 cases. Mayo Clin Proc. 1975 Jan;50(1):29–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenert P., Drazen F., Tepavcević P., Pejin D., Curić S., Ilić V., Uzurov V., Popowić S., Zupunski A., Djisalov M. Influence of Bence-Jones proteins, hyperviscosity, hypercalcemia, hyperuricemia and dehydration on development of renal changes in plasma cell dyscrasias. Przegl Lek. 1985;42(4):384–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melcion C., Mougenot B., Baudouin B., Ronco P., Moulonguet-Doleris L., Vanhille P., Beaufils M., Morel-Maroger L., Verroust P., Richet G. Renal failure in myeloma: relationship with isoelectric point of immunoglobulin light chains. Clin Nephrol. 1984 Sep;22(3):138–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden A. G., Flynn F. V., Fulcher L. M., Richards J. D. Renal impairment in myeloma: negative association with isoelectric point of excreted Bence-Jones protein. J Clin Pathol. 1989 Jan;42(1):59–62. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palant C. E., Bonitati J., Bartholomew W. R., Brentjens J. R., Walshe J. J., Bentzel C. J. Nodular glomerulosclerosis associated with multiple myeloma. Role of light chain isoelectric point. Am J Med. 1986 Jan;80(1):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders P. W., Booker B. B., Bishop J. B., Cheung H. C. Mechanisms of intranephronal proteinaceous cast formation by low molecular weight proteins. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):570–576. doi: 10.1172/JCI114474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders P. W., Booker B. B. Pathobiology of cast nephropathy from human Bence Jones proteins. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):630–639. doi: 10.1172/JCI115629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders P. W., Herrera G. A., Chen A., Booker B. B., Galla J. H. Differential nephrotoxicity of low molecular weight proteins including Bence Jones proteins in the perfused rat nephron in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):2086–2096. doi: 10.1172/JCI113830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders P. W., Herrera G. A., Galla J. H. Human Bence Jones protein toxicity in rat proximal tubule epithelium in vivo. Kidney Int. 1987 Dec;32(6):851–861. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolens P., Barnes J. L., Kreisberg R. Hypercalcemia can potentiate the nephrotoxicity of Bence Jones proteins. J Lab Clin Med. 1987 Oct;110(4):460–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolens P., Barnes J. L., Stein J. H. Effect of chronic administration of different Bence Jones proteins on rat kidney. Kidney Int. 1986 Dec;30(6):874–882. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolens P., Venkatachalam M., Stein J. H. Myeloma kidney cast nephropathy in a rat model of multiple myeloma. Kidney Int. 1983 Aug;24(2):192–204. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon A. Bence-Jones proteins and light chains of immunoglobulins (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Jan 1;294(1):17–23. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197601012940105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon A. Clinical implications of monoclonal light chains. Semin Oncol. 1986 Sep;13(3):341–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens F. J., Westholm F. A., Solomon A., Schiffer M. Self-association of human immunoglobulin kappa I light chains: role of the third hypervariable region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1144–1148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill B. C., Tucker F. L., Bolton W. K. Immunoglobulin light chain nephropathies. Pathol Annu. 1987;22(Pt 2):133–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sølling K., Sølling J., Lanng Nielsen J. Polymeric Bence Jones proteins in serum in myeloma patients with renal insufficiency. Acta Med Scand. 1984;216(5):495–502. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1984.tb05037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan M., Epstein W. Polymer formation during the degradation of human light chain and Bence-Jones proteins by an extrct of the lysosomal fraction of normal human kidney. Immunochemistry. 1972 Jan;9(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90278-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. H., Williams R. H., Galla J. H., Gottschall J. L., Rees E. D., Bhathena D., Luke R. G. Pathophysiology of acute Bence-Jones protein nephrotoxicity in the rat. Kidney Int. 1981 Aug;20(2):198–210. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]