Abstract
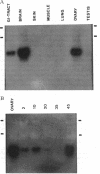
A cDNA encoding the precursor of a bombesinlike peptide was isolated from brain of Xenopus laevis. The predicted end product resembles neuromedin B, which was originally isolated from mammalian spinal cord. The mRNA for this precursor was also present in gastrointestinal tract and in ovaries. Moreover, it could be detected in early embryos (stage 2 and stage 10) of X. laevis. These findings suggest novel roles for peptides of the bombesin family in oocyte maturation and early amphibian development.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barra D., Falconieri Erspamer G., Simmaco M., Bossa F., Melchiorri P., Erspamer V. Rohdei-litorin: a new peptide from the skin of Phyllomedusa rohdei. FEBS Lett. 1985 Mar 11;182(1):53–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81152-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battey J. F., Way J. M., Corjay M. H., Shapira H., Kusano K., Harkins R., Wu J. M., Slattery T., Mann E., Feldman R. I. Molecular cloning of the bombesin/gastrin-releasing peptide receptor from Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):395–399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battey J., Wada E. Two distinct receptor subtypes for mammalian bombesin-like peptides. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Dec;14(12):524–528. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90005-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlon J. M., O'Harte F., Vaudry H. Primary structures of the bombesin-like neuropeptides in frog brain show that bombesin is not the amphibian gastrin-releasing peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jul 31;178(2):526–530. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90139-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuttitta F., Carney D. N., Mulshine J., Moody T. W., Fedorko J., Fischler A., Minna J. D. Bombesin-like peptides can function as autocrine growth factors in human small-cell lung cancer. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):823–826. doi: 10.1038/316823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erisman M. D., Linnoila R. I., Hernandez O., DiAugustine R. P., Lazarus L. H. Human lung small-cell carcinoma contains bombesin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2379–2383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erspamer V. Discovery, isolation, and characterization of bombesin-like peptides. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;547:3–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb23870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. B., Schonbrunn A. The bombesin receptor is coupled to a guanine nucleotide-binding protein which is insensitive to pertussis and cholera toxins. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2808–2816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson B. W., Poulter L., Williams D. H., Maggio J. E. Novel peptide fragments originating from PGLa and the caerulein and xenopsin precursors from Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5341–5349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korner J., Chun J., O'Bryan L., Axel R. Prohormone processing in Xenopus oocytes: characterization of cleavage signals and cleavage enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11393–11397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krane I. M., Naylor S. L., Helin-Davis D., Chin W. W., Spindel E. R. Molecular cloning of cDNAs encoding the human bombesin-like peptide neuromedin B. Chromosomal localization and comparison to cDNAs encoding its amphibian homolog ranatensin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13317–13323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. J., Jörnvall H., Nilsson G., Vagne M., Ghatei M., Bloom S. R., Mutt V. Characterization of a gastrin releasing peptide from porcine non-antral gastric tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 12;90(1):227–233. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91614-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Neuromedin B is a major bombesin-like peptide in rat brain: regional distribution of neuromedin B and neuromedin C in rat brain, pituitary and spinal cord. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 14;124(3):925–932. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Neuromedin B: a novel bombesin-like peptide identified in porcine spinal cord. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 29;114(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90814-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Neuromedin C: a bombesin-like peptide identified in porcine spinal cord. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 29;119(1):14–20. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91611-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody T. W., Pert C. B., Gazdar A. F., Carney D. N., Minna J. D. High levels of intracellular bombesin characterize human small-cell lung carcinoma. Science. 1981 Dec 11;214(4526):1246–1248. doi: 10.1126/science.6272398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Represa J. J., Miner C., Barbosa E., Giraldez F. Bombesin and other growth factors activate cell proliferation in chick embryo otic vesicles in culture. Development. 1988 May;103(1):87–96. doi: 10.1242/dev.103.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter K., Egger R., Kreil G. D-alanine in the frog skin peptide dermorphin is derived from L-alanine in the precursor. Science. 1987 Oct 9;238(4824):200–202. doi: 10.1126/science.3659910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter K., Egger R., Kreil G. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding the bombesin precursor in skin of Bombina variegata. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 26;262(2):353–355. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80227-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Sinnett-Smith J. Bombesin stimulation of DNA synthesis and cell division in cultures of Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2936–2940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindel E. R., Chin W. W., Price J., Rees L. H., Besser G. M., Habener J. F. Cloning and characterization of cDNAs encoding human gastrin-releasing peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5699–5703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindel E. R., Gibson B. W., Reeve J. R., Jr, Kelly M. Cloning of cDNAs encoding amphibian bombesin: evidence for the relationship between bombesin and gastrin-releasing peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9813–9817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindel E. R., Giladi E., Brehm P., Goodman R. H., Segerson T. P. Cloning and functional characterization of a complementary DNA encoding the murine fibroblast bombesin/gastrin-releasing peptide receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Dec;4(12):1956–1963. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-12-1956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindel E. R., Krane I. M. Molecular biology of bombesin-like peptides. Comparison of cDNAs encoding human gastrin-releasing peptide, human neuromedin B, and amphibian ranatensin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;547:10–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb23871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindel E. R., Sunday M. E., Hofler H., Wolfe H. J., Habener J. F., Chin W. W. Transient elevation of messenger RNA encoding gastrin-releasing peptide, a putative pulmonary growth factor in human fetal lung. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1172–1179. doi: 10.1172/JCI113176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. H., Lechago J., Wong H. C., Rosenquist G. L. Presence of ranatensin-like and bombesin-like peptides in amphibian brains. Regul Pept. 1982 Jan;3(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(82)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. H., Wong H. C., Dockray G. J. Bombesin-like peptides in mammals. Fed Proc. 1979 Aug;38(9):2315–2319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton J., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R., Ghatei M. A., Solcia E., Brown M. R., Pearse A. G. Bombesin-like immunoreactivity in the lung. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):769–770. doi: 10.1038/273769a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary I., Gil J., Lehmann W., Sinnett-Smith J., Rozengurt E. Bombesin, vasopressin, and endothelin rapidly stimulate tyrosine phosphorylation in intact Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4577–4581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary I., Woll P. J., Rozengurt E. A role for neuropeptides in the control of cell proliferation. Dev Biol. 1987 Dec;124(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90483-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]