Significance
This study explores whether archaeologically detectable declines in resilience precede the onset of large-scale human population collapses. Our case study is the European Neolithic: a period that began approximately 9,000 y ago when the introduction of agricultural technologies initiated phases of rapid population growth that were in many cases followed by demographic instability and dramatic collapse. Our study finds evidence that statistical signatures of decreasing resilience can be detected long before population decline begins. To our knowledge, this study is the first to find early warning signals of demographic regime shift among human populations. The results suggest that archaeological information can potentially be used to monitor social and ecological vulnerability in human societies at large spatial and temporal scales.
Keywords: archaeology, early warning signs, human paleodemography, Neolithic Europe, resilience
Abstract
Ecosystems on the verge of major reorganization—regime shift—may exhibit declining resilience, which can be detected using a collection of generic statistical tests known as early warning signals (EWSs). This study explores whether EWSs anticipated human population collapse during the European Neolithic. It analyzes recent reconstructions of European Neolithic (8–4 kya) population trends that reveal regime shifts from a period of rapid growth following the introduction of agriculture to a period of instability and collapse. We find statistical support for EWSs in advance of population collapse. Seven of nine regional datasets exhibit increasing autocorrelation and variance leading up to collapse, suggesting that these societies began to recover from perturbation more slowly as resilience declined. We derive EWS statistics from a prehistoric population proxy based on summed archaeological radiocarbon date probability densities. We use simulation to validate our methods and show that sampling biases, atmospheric effects, radiocarbon calibration error, and taphonomic processes are unlikely to explain the observed EWS patterns. The implications of these results for understanding the dynamics of Neolithic ecosystems are discussed, and we present a general framework for analyzing societal regime shifts using EWS at large spatial and temporal scales. We suggest that our findings are consistent with an adaptive cycling model that highlights both the vulnerability and resilience of early European populations. We close by discussing the implications of the detection of EWS in human systems for archaeology and sustainability science.
A 2012 Special Issue in PNAS debates how analysis of historical collapse in ancient societies can contribute to sustainability science (1). Key themes include accounting for complexity and multicausality in instances of collapse, modeling, and predicting both short- and long-term environmental change and the importance of historical and archaeological case studies. Although significant progress has been made in measuring ecosystem resilience and predicting collapse (2), quantifying the resilience of human societies presents a major challenge for social science research (3, 4). Further, the use of archaeological data and EWS methods to predict known periods of collapse in ancient human societies (i.e., retrodiction) (5) remains largely unexplored. Resilience as we use the concept here is defined as the ability of a system to absorb change and recover from disturbance while maintaining relationships between populations or state variables (6). Recent developments in ecology point to a promising new direction that follows from the observation that ecosystem resilience tends to decrease in advance of regime shifts—major transitions among qualitatively distinct ecosystem states (7). Theoretical and empirical studies of nonhuman systems reveal that decreasing resilience is detectable via time series statistics termed early warning signals (EWSs) (8). Although regime shifts are well documented in human-dominated ecosystems (9–13), the degree to which EWSs anticipate them remains largely unexamined due to data limitations at requisite spatial and temporal scales. However, recent advances in the integration of large-scale archaeological data (14–16) are narrowing the gap between theory and data. This study presents what we believe to be the first statistical evidence for EWSs of regime shifts in human population dynamics.
Our case studies include 2,378 archaeological sites from nine regions of Neolithic Europe, ca. 8–4 kya. Previous research has observed evidence of major demographic regime shifts in the form of large-scale boom-bust dynamics among many of these Neolithic cases (17). Estimated population declines range from 20% to 60% in as little as a century. The population proxies that revealed these boom-bust dynamics are based on the temporal frequencies of radiocarbon-dated archaeological sites, which are represented as summed probability densities (SPDs). This site-based population proxy assumes that the temporal frequencies of occupied human settlements in a given region index relative human population size. Use of SPD-based approaches to inferring population change has been debated in the literature (18–26). Critics have raised concerns about confounding factors including atmospheric effects, sampling biases, taphonomic processes, or calibration error; however, the methods used here and elsewhere (20) attempt to control for these sources of error by (i) correcting systematic biases in the data and (ii) comparing the corrected empirical patterns to null SPD models that simulate exogenous processes. Thus, current SPD methods reflect a significantly more conservative version of the approach that Rick (27) originally proposed.
We analyze archaeological SPDs for two classes of EWSs: critical slowing down (CSD) and flickering. CSD describes a general increase in the time it takes a system to recover from external shocks such as population loss due to disease, warfare, or crop failure. Flickering describes increasing directional bias in a system’s response rate to such perturbations, such as a society stuck in a socio-ecological trap where strong reinforcing behavior and a lack of innovation prevents adaptation (28–30). Here, flickering would suggest increasing recovery time from population decline events relative to growth events before major collapse. Because a number of nonhuman biological populations exhibit critical slowing down and flickering in advance of regime shifts (31–38), we consider the possibility that these EWS indicators could also be detected in long-term human population dynamics as viewed through archaeological proxies.
Results
CSD Detection with a Simulated Demographic Regime Shift and an Archaeological Deposition Process Model.
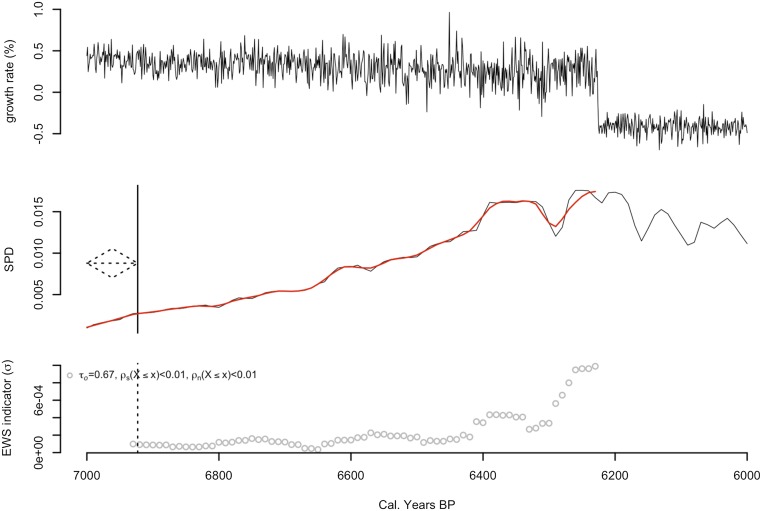
Fig. 1 illustrates how CSD can be detected in a model system that transitions from a high growth regime to low growth. In the model, slowly decreasing human population growth rates and increasing variance precedes the transition to the low growth regime. These simulated growth rates are used to simulate an archaeological SPD including deposition processes, taphonomic decay, atmospheric effects, radiocarbon calibration, and isotopic counting error processes (Materials and Methods). The SPD is then evaluated for EWSs using the same statistical procedures we use in the empirical analysis. Declining resilience is indicated in the bottom panel by the increasing EWS indicator values up to the point of collapse. The EWS indicator increase is statistically significant using the individual tau observations () and with a robust statistical test (). Empirically, any of a number of drivers such as changing climate, declining environmental productivity, disease, warfare, or some combination thereof could produce these results.
Fig. 1.
A regime shift model of population growth rate variability, radiocarbon date calibration, and EWSs that demonstrates CSD in growth rates can be recovered from simulated SPDs.
Results for All European Neolithic Regions.
Qualitative EWS trends are evident in many cases (Table S1 and Dataset S1), leading us to perform quantitative tests (see Fig. S1 and SI Text, Early Warning Signals of Collapse in Neolithic Paris Basin for an illustrative example). Table 1 presents the results of for the three EWS metrics, including their associated statistical strengths (). All but 2 of the 27 tests produced statistically significant results (), indicating that statistical effects are unlikely to account for the observed EWSs. However, these standard probability tests for do not distinguish between EWSs produced by Neolithic demographic processes and those produced by the confounding factors, so we next compare the empirical tau values to a simulated null model. This comparison shows that in seven of nine regions, both AR (1) and σ exhibit increases that are significantly different from those produced by the null model (). Conversely, produces only one result of nine that is significantly different from the tau values produced by the null model. We conclude that confounding factors (i) are unlikely to account for the majority of CSD patterns in the empirical data but (ii) can account for the majority of skewness patterns in the data.
Table S1.
Qualitative classification of EWS trends in all regions
| Region | EWS trend | Summary | ||
| AR (1) | σ | |||
| Expectation | + | + | − | AR (1) and σ are expected to increase and is expected to decrease in advance of a regime shift to lower population levels. |
| Southern Germany | + | + | − | Long period of stability between 7 and 6 kya followed by increasing AR (1) and σ between ∼6.4–5.6 kya and long-term decreasing trend in . |
| Eastern Switzerland | + | . | − | Increase in AR (1) beginning ∼6 kya, and σ also increases around 6 kya but then declines ∼5.8 kya against expectation. begins to decline just after 6 kya. |
| England and Wales (without Wessex and Sussex) | + | + | − | Increasing AR (1) beginning slightly after 5.8 kya and σ begins increasing at 5.7 kya. Decreasing beginning ∼5.8 kya. |
| Ireland | + | + | − | AR (1) begins increasing slightly after 5.8 kya, and σ begins increasing at 5.7 kya. There is a weak long-term decreasing trend in . |
| Paris Basin | + | + | − | Increasing trend in AR (1) beginning ∼6.8 kya and increasing σ ∼6.3 kya. There is a weak long-term decreasing trend in . |
| Rhone-Languedoc | + | + | − | Some indication of increasing trends in AR (1) and σ beginning around 6.4 kya. begins weak decreasing trend after increase around 6.3 kya. |
| Scotland | + | + | . | AR (1) increase beginning around 5.8 kya, and σ increase beginning around 5.7 kya with no clear trend. |
| Southern England (Wessex and Sussex) | . | + | − | No clear trend in AR (1), but clear and strong increasing trend in σ beginning around ∼6 kya. Very slight long-term decrease in . |
| Western France | + | + | . | Long-term increasing AR (1) beginning ∼6.4 kya, and strong long-term increasing σ trend. Equivocal, or increasing trend in against expectation. |
Here we subjectively classify each EWS trend as increasing (+), decreasing (−), or equivocal (.) and describe the overall pattern including the relationship to interesting events in the underlying SPD.
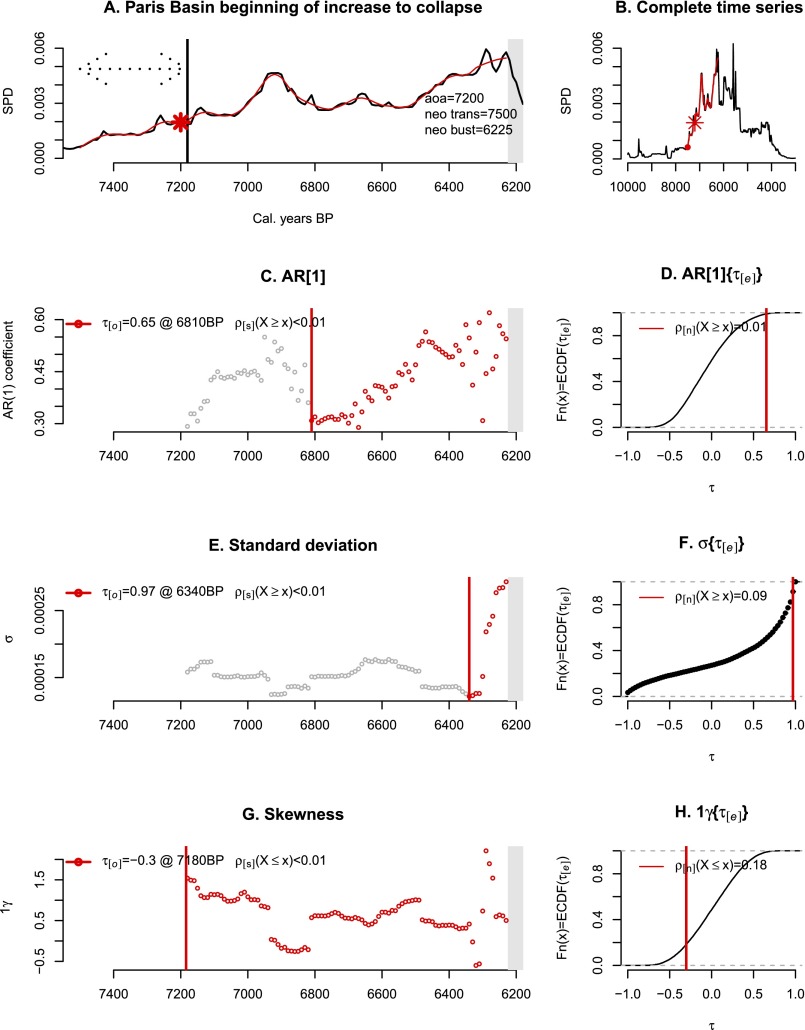
Fig. S1.
EWS analysis of Neolithic Paris Basin showing statistical support for CSD in advance of population collapse ∼6.2 kya. (B) Overall population trajectory used in EWS analysis. (A) Region of the curve before collapse that is analyzed for EWS. (C, E, and G) Three EWS metrics and associated values with probabilities. (D, F, and H) Comparison of empirical EWS results to simulated values given a null model defined by confounding factors. Overall, these results identify CSD in advance of collapse in Neolithic Paris Basin but it does not provide evidence for flickering.
Table 1.
EWS analysis results of summed probability distributions of nine European regions
| Region | AR (1) | σ | |||||||
| Southern Germany | 0.54 | 0.00*** | 0.04** | 0.89 | 0.00*** | 0.32 | −0.78 | 0.00*** | 0.04** |
| Eastern Switzerland | 0.59 | 0.00*** | 0.05** | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.47 | −0.47 | 0.00*** | 0.14 |
| England and Wales (without Wessex and Sussex) | 0.49 | 0.00*** | 0.04** | 0.96 | 0.00*** | 0.01*** | −0.51 | 0.00*** | 0.14 |
| Ireland | 0.70 | 0.00*** | 0.01*** | 0.96 | 0.00*** | 0.03** | −0.37 | 0.00*** | 0.27 |
| Paris Basin | 0.65 | 0.00*** | 0.01*** | 0.97 | 0.00*** | 0.09* | −0.30 | 0.00*** | 0.18 |
| Rhone-Languedoc | 0.65 | 0.00*** | 0.09* | 0.95 | 0.00*** | 0.04** | −0.79 | 0.00*** | 0.27 |
| Scotland | 0.49 | 0.00*** | 0.03** | 0.95 | 0.00*** | 0.02** | −0.09 | 0.31 | 0.42 |
| Southern England (Wessex and Sussex) | 0.42 | 0.04** | 0.17 | 0.68 | 0.00*** | 0.06* | −0.44 | 0.00*** | 0.13 |
| Western France | 0.48 | 0.02** | 0.14 | 0.62 | 0.00*** | 0.04** | −0.36 | 0.02** | 0.37 |
Significance levels: *P = 0.10; **P = 0.05; ***P = 0.01.
Table 2 considers whether the multiple statistically significant results could be obtained by chance given values that are uniformly distributed between 0 and 1. For each set of nine outcomes for AR (1), σ, and , Fisher’s exact tests for AR (1) (7:2) and σ (7:2) show that the empirical results are unlikely to be explained by sampling effects (), whereas (1:8) can be explained by sampling effects (). In sum, the data from all regions reveal evidence of CSD but flickering does not appear to be a useful indicator of population collapse.
Table 2.
Fisher’s exact tests for multiple analyses
| Tau () | EWS | Pass† | Fail† | CI low | CI high | P‡ |
| Sample () | AR (1) | 9 | 0 | 6.67 | Infinity | 0.00*** |
| σ | 8 | 1 | 3.54 | 4,053.00 | 0.00*** | |
| 8 | 1 | 3.54 | 4,053.00 | 0.00*** | ||
| Null model () | AR (1) | 7 | 2 | 2.20 | 1,854.15 | 0.00*** |
| σ | 7 | 2 | 2.20 | 1,854.15 | 0.00*** | |
| 1 | 8 | 0.02 | 117.49 | 1.00 |
Significance level: ***P = 0.01. CI, confidence interval.
Pass/fail at P < 0.1.
Expected ratio used in Fisher test is 1:8, pass:fail.
Discussion
It is unsurprising that societies on the verge of collapse may exhibit warnings signs; yet it is difficult to demonstrate such phenomena empirically. Our results support the hypothesis that CSD was present in Neolithic Europe demographics, detectable in archaeological SPD curves, and that the EWSs are not artifacts of sampling or confounding effects. This surprising finding encourages us to explore systemic relationships between human paleodemography and CSD and to consider the implications for human ecosystem monitoring (see also SI Text, Theoretical Considerations Related to SPD-Based EWSs Among Human Societies).
Regime Shifts in Human Societies.
Human population dynamics are known to exhibit multidimensional and nonlinear processes; therefore, regime shifts and EWSs should also be expected. Equilibrium, multiple stable population points, and chaotic regimes are all known to emerge from even the simplest demographic models (39). When density-dependent population feedbacks, or Allee affects, interact with logistic growth and environmental perturbations, critical transitions may ensue (6, 40). Allee effects and logistic growth processes have been observed or suspected in many biological populations including yeast, plants, shellfish, and humans (41–43). Moreover, human systems involve cross-generational effects of past environments on the population levels of later generations (44, 45). For example, dramatic environmental change, warfare, disease, or complex interactions among these mechanisms may lead to population collapse. Regime shifts and CSD should therefore be expected in at least some human population dynamics.
A Framework for Interpreting EWSs Among Human Populations at Large Spatial and Temporal Scales.
Following a recent theoretical synthesis on resilience in socio-ecological systems (46), we consider the following three generic mechanisms that may offer insights into the general mechanisms of regime shifts in human systems over large spatial and temporal scales: (MI) a slowly changing driver to tipping point, (MII) interaction of fast and slow cycles, and (MIII) large but infrequent changes in external drivers.
MI entails an external driver that slowly forces a system across a tipping point to a qualitatively different state. Such critical transitions entail feedback loops that create the context for nonlinear responses to linear changes in the external driver (37). As noted above, Allee effects can trigger critical transitions, and several authors (37, 47) propose that Neolithic population collapse in the US Southwest and among human societies more generally can be understood as critical transitions [see also (48)]. As resource availability steadily declines, sunk-cost effects can generate adaptive feedback loops that artificially lock humans into maladaptive strategies such as remaining in established settlements until the exogenous driver eventually forces the system across a tipping point into an alternative adaptive regime. Continuing on such unsustainable courses in the face of steady resource decline ultimately leads to catastrophic failure. More recently, Lade et al. (49) show that common-pool resource management systems can create a context for critical transitions in human societies when external drivers slowly force systems to alternative states.
In MI systems, the timing of regime shifts can be predicted at the point when variance and autocorrelation reach infinity, known technically as a bifurcation point (or tipping point). However, reaching a bifurcation point would only happen under stringent conditions, and stochasticity in real-world systems will tend to trigger regime shifts before the theoretical transition; for example, in early agricultural societies (Fig. S2). Regardless, CSD should precede the regime shift (46). Of the three mechanisms discussed here, only MI causes true critical transitions with bifurcations. As a result, reducing or reversing the driver variable after a bifurcation will not return the system to the previous regime without resetting other system parameters (i.e., hysteresis). The other two mechanisms also cause regime shifts, but because recovery is possible and the changes are not permanent, these are not considered critical transitions (46).
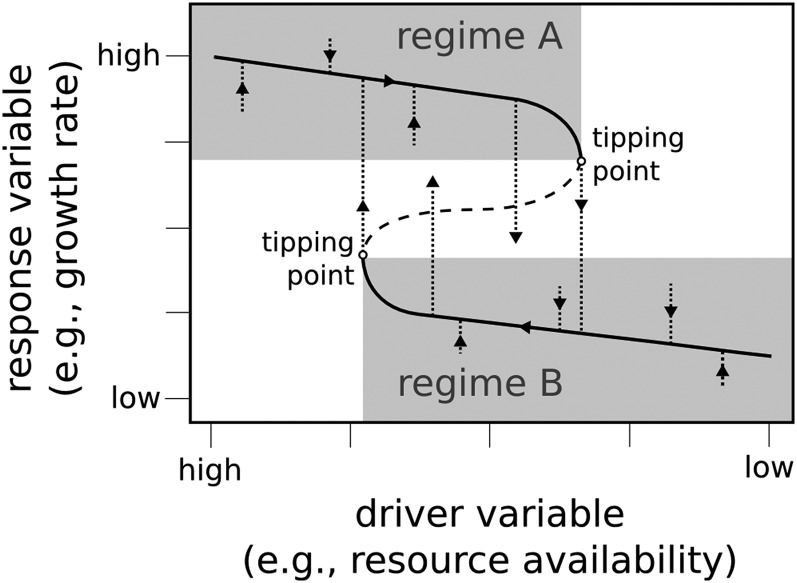
Fig. S2.
Conceptual fold bifurcation model for human population collapse. We consider that bifurcation acts on population growth rates. Reading the graphic from left to right, early agricultural societies have initially high growth rates. Land degradation slowly drives the growth rates down, whereas agricultural surpluses and cultural mechanisms maintain the growth rates at artificially high levels within growth regime A. As the system approaches the tipping point, it becomes increasingly unstable and susceptible to shifts into the low growth-rate regime (regime B). The system exhibits hysteresis insofar as the recovery of agricultural productivity does not necessarily result in recovery of the higher regime A growth rates.
MII describes interaction between slow and fast cycles that can cause dramatic regime shifts without bifurcation. For example, annual cultivation cycles in agricultural systems that involve forest clearing (i.e., swidden or slash-and-burn) are highly constrained by soil fertility and biomass recovery dynamics occurring over decades. Repeated and intensive forest cultivation can cause local resources to become depleted and ultimately trigger the abandonment of settlements, but eventually forests and soils can recover and abandoned settlements may be reoccupied. Many types of environmental and human cycling exist that could lead to interactions and regime shifts, including environmental overexploitation and recovery (45, 50), biogeochemical cycling (51), land surface change (2), climate cycling (52), epidemiology (53), human demography (13), and episodes of human violence (54, 55). These dynamics are predicted to exhibit the statistical signatures of CSD (46).
In MIII systems, a large but infrequent change in external conditions forces a system into another state. For example, catastrophic population losses could result from unusual natural disasters (56, 57), the emergence of genetically novel disease transmission vectors [e.g., airborne transmission of Yersinia pestis (58) and the Black Death (59)], social conflict at novel scales of severity (e.g., World War I), or extreme and rare climatic events such as volcanic eruptions (e.g., Pompeii). However, the demographic system itself is not trapped at low levels and may eventually recover. EWSs are not expected in such cases (46).
Implications for Understanding the Causes of Collapse During the European Neolithic.
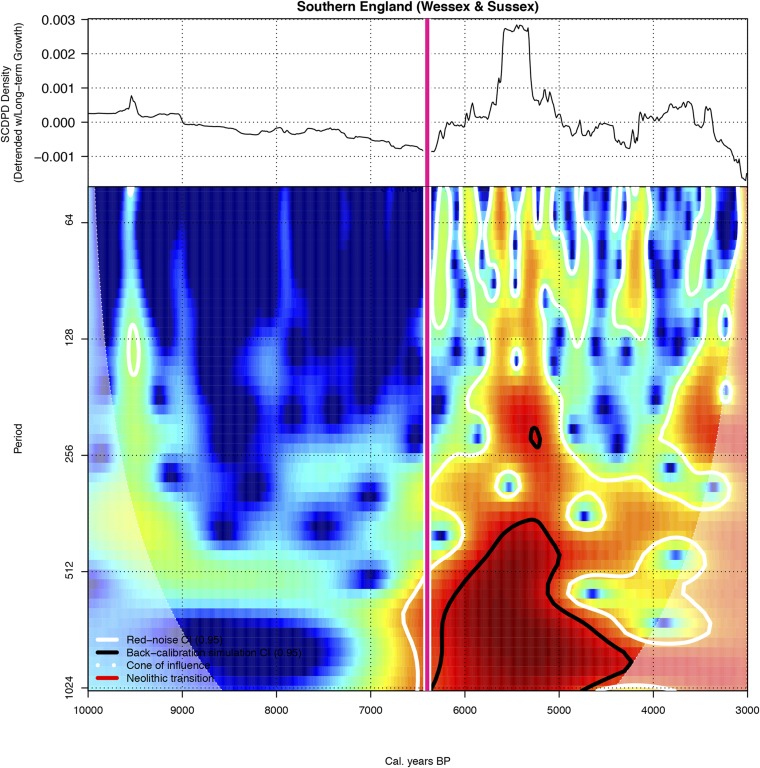
The EWS analysis of Neolithic Europe population dynamics tends to exhibit EWSs in AR (1) and σ, suggesting that MI and MII are plausible and that MIII is unsupported. However, determining which of the two potential regime shift mechanisms is the more plausible explanation for a pattern of collapse occurring independently at different times and in different regions throughout Europe cannot be determined from the EWS analysis alone. Instead, we use wavelet analysis to test the expectation of an MII slow-fast cycling mechanism (SI Materials and Methods). For example, the Wessex-Sussex region of England exhibits statistically significant cycling patterns in the SPDs (Fig. 2). In this case, the standard Gaussian white-noise filter identifies significant cycles at high frequencies that are probably associated with the radiocarbon date calibration process. However, when we use a noise filter based on the SPD null model distribution, the main statistically significant cycles remaining are around 5.5 kya with a frequency of between 400 and 1,000 y. The pattern holds for each of the nine regions (Dataset S1), and we find it to be in line with predictions from human demographic modeling (13). A possible explanation is that interactions between fast human demographic cycles and slower ecosystem recovery cycles may explain the observed pattern of demographic collapse in Neolithic Europe. Similar cycling patterns have been observed among prehistoric agrarian populations in the US Southwest (54, 55), and the hypothesis is consistent with recent paleoenvironmental research that finds correlations between deforestation and human population growth during the European Neolithic (60–62). Using the framework introduced in the previous section, this deforestation hypothesis would suggest that MII cycle interactions between rapidly increasing human population levels and environmental dynamics during the early Neolithic may have contributed to the observed demographic collapses.
Fig. 2.
Wavelet analysis of Southern England showing Neolithic transition date (red line), periods of significant cycling and frequency using a Gaussian noise (white highlight), and the SPD null model (black highlight).
Importantly, fast–slow cycle interactions in human societies are more consistent with adaptive cycles (3, 45) than Lotka–Volterra interactions. In contrast to the latter, adaptive cycling emphasizes collapse and reorganization that may or may not reproduce previous ecological states. Instead, each collapse is generally followed by a level of recovery that sometimes exceeded precollapse levels and was often accompanied by distinct socioeconomic structure (e.g., Bronze Age systems). Recovery may be understood as the outcome of adaptive reorganization on fundamentally altered cultural and natural landscapes. Such reorganization is generally expected among human populations with cumulative culture. In some cases, endogenous expansion-growth dynamics may have temporarily increased societal resilience to changing rates of climate variability (e.g., during Linear Pottery Culture) (63). Therefore, on one hand, some societies tended to experience quantifiable loss of resilience that led to dramatic declines in population levels; on the other hand, other societies recovered to generate larger and presumably more resilient populations. Where recovery did not occur, other societies with new adaptations moved in, as ancient DNA studies are beginning to show (64). As such, our results highlight both the vulnerability and the resilience of early European societies.
SI Materials and Methods
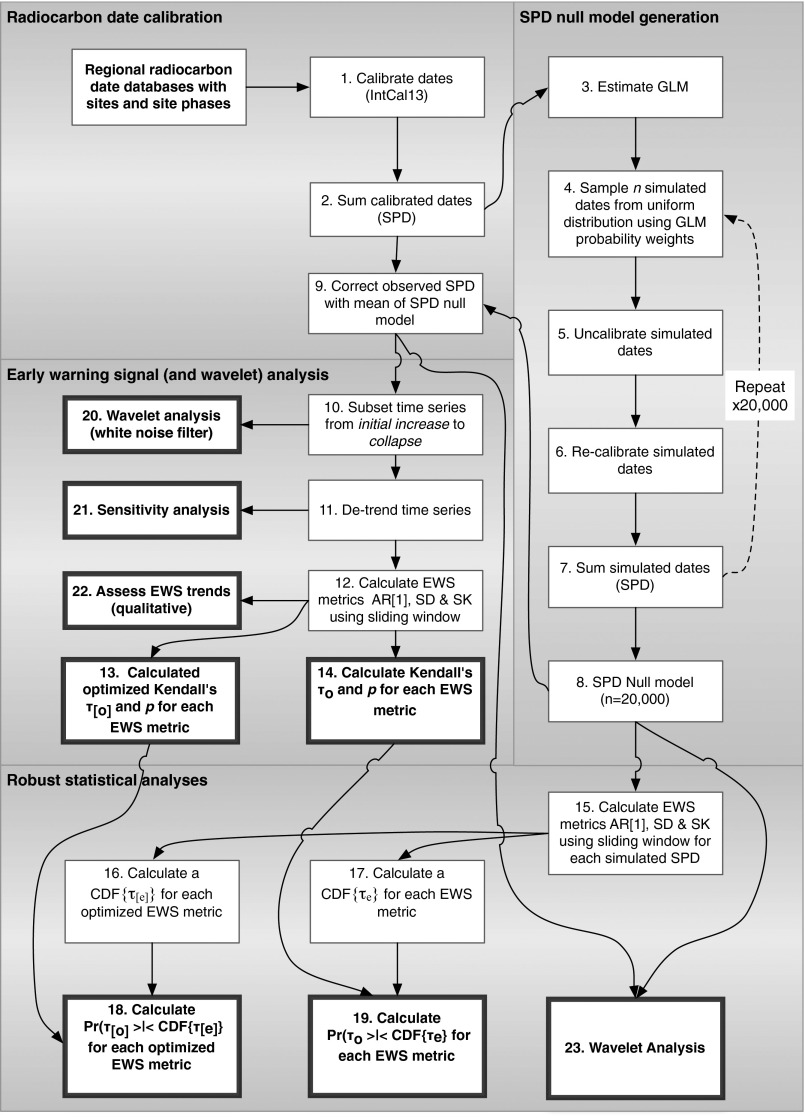
We present the complete methods in five parts. First, we describe the archaeological proxy data and the generation of an SPD. Second, we describe the method for generating an SPD null model of the confounding factors: sampling error, taphonomic bias, and radiocarbon calibration effects. These procedures have been presented in previous publications (17, 20, 26), so we only briefly outline them here. Third, we describe the methods for calculating EWS metrics for the empirical data of each region, including the workflow for generating expected EWS results for each region given a null model. Fig. S4 outlines the method and each step is cross-referenced in the text with curly braces (e.g., {1}). Fourth, we describe the simulation model used in Fig. 1. Fifth, we describe the method for the wavelet analysis. All analyses are performed using R (73). Code is available on request.
Fig. S4.
EWS method flowchart.
Archaeological Radiocarbon Database.
The publicly available dataset includes more than 13,658 archaeological radiocarbon dates comprising 2,759 sites for Mesolithic and Neolithic Europe, ca. 10–3.5 kya (65). Each site is assigned to a geographic region based on physiography, perceived spatial clustering, and prior knowledge of prehistoric cultural regions. Problematic dates including outliers and those with ambiguous stratigraphic associations are discarded. We select a subset of nine regions (Table S2) for the EWS analysis because they provide the clearest qualitative and quantitative shifts from high to low growth regimes–that is, population booms and busts (17), raising the possibility of EWSs leading up to the bust events.
Table S2.
Summary of 14C samples and Neolithic events for the European cases examined in this study
| Region | Collapse date (cal. BP)* | Neolithic transition (cal. BP) | Neolithic bust (cal. BP) | Duration (y) | Complete time series | EWS analysis | ||||
| Uncalibrated dates | Site-phases | Sites | Uncalibrated dates | Site-phases | Sites | |||||
| Southern Germany | 7,400 | 7,600 | 5,600 | 2,000 | 391 | 119 | 80 | 185 | 51 | 35 |
| Eastern Switzerland | 6,500 | 6,500 | 5,650 | 850 | 275 | 89 | 48 | 47 | 13 | 9 |
| England and Wales (without Wessex and Sussex) | 6,000 | 6,100 | 5,600 | 500 | 1,188 | 782 | 509 | 45 | 38 | 34 |
| Ireland | 6,000 | 6,100 | 5,600 | 500 | 1,721 | 1,007 | 607 | 71 | 39 | 30 |
| Paris Basin | 7,200 | 7,500 | 6,225 | 1,275 | 570 | 300 | 176 | 90 | 57 | 51 |
| Rhone-Languedoc | 7,800 | 7,800 | 5,800 | 2,000 | 978 | 568 | 359 | 316 | 178 | 124 |
| Scotland | 6,000 | 6,000 | 5,600 | 400 | 579 | 326 | 210 | 58 | 32 | 29 |
| Southern England (Wessex and Sussex) | 6,000 | 6,400 | 5,400 | 1,000 | 581 | 286 | 176 | 25 | 20 | 16 |
| Western France | 7,000 | 7,000 | 5,940 | 1,060 | 494 | 298 | 213 | 73 | 51 | 40 |
| Totals | 6,777 | 3,775 | 2378 | 910 | 479 | 368 | ||||
Collapse dates from ref. 17.
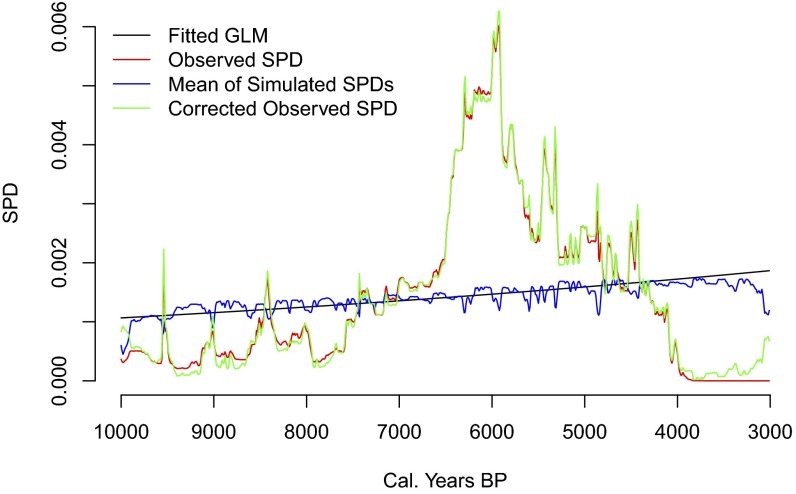
To minimize the effects of radiocarbon sampling bias within and among sites, we use the following phase-based summing procedure (22–24). Each date for a given site is assigned to a temporal site-phase and multiple phases are defined at a site when the minimum pairwise distances among all radiocarbon dates exceed 20014C y. One 14C assay is then randomly selected from each site phase and calibrated {1} using the Bchron R package (67) and IntCal13 atmospheric correction curve (68). The resultant probability distributions are summed to unity. This procedure is repeated 20,000 times and each SPD is averaged {2}. The resultant SPDs are binned in 10-y periods. As a final step, we correct each probability density curve for radiocarbon calibration effects (66) and taphonomic bias (21) by estimating a null model using a Monte Carlo routine and subtracting it from the observed curve to generate a corrected SPD curve {9}.
SPD Null Model Generation.
To explore the possibility of observing EWSs when they did not actually exist in the systemic context (type I error), we construct a null model that simulates monotonic population growth, archaeological sampling, atmospheric effects on radiocarbon proxies, and taphonomic decay of radiocarbon proxies (Fig. S3). We first fit a generalized linear model (GLM) to the empirical SPD {3}. This simultaneously models exponential growth of populations and decay of archaeological carbon (17). Second, to model sampling, we randomly draw a probabilistic sample from a uniform distribution using the fitted GLM for probability weights and a sample size equivalent to the empirical sample size {4}. Third, to model the effects of the radiocarbon calibration process, we “un-calibrate” each simulated date by passing it backward through the IntCal13 radiocarbon calibration curve {5}. We then calibrate the uncalibrated values using them as 14C means with SE values sampled without replacement from the SE values in the empirical sample {6} and sum the results {7}. This procedure is iterated 20,000 times and all calibrated probability distributions are summed to unity to produce a null SPD model {8}.
Fig. S3.
Example of a corrected site density distribution analyzed for EWSs.
Calculating EWS Metrics Using SPD.
The methods for calculating EWS statistics generally follow those outlined in ref. 69. For each of the nine population trajectories, we isolate a subset of the time series from the beginning of the population boom to the end, or the collapse date {10}. The beginning date takes into account both qualitative evidence of growth as observed in the SPDs and the estimated date of earliest local archaeological evidence for agriculture. The date of collapse in each region is determined qualitatively by inspecting the SPD plots. The SPD curves may include edge effects due to decreased sampling in later periods, however the collapse dates are earlier in time so this does not affect the EWS analysis results. Next, we detrend the time series to remove linear structure in the time series by fitting a LOESS model and calculating residuals. The LOESS fitting procedure uses local regression to predict SPD values along the x axis ( ), and residuals are calculated as the difference between the predicted and observed SPD values. We then calculate autocorrelation [AR (1)], variance (σ), and skewness (1λ) values for the detrended data using a sliding time-window {12}. The first window includes the first 25% of points in the time series and then iteratively slides forward one decade at a time until reaching the defined collapse date. The size of this sliding window follows the recommendation of (69) and considers the scale of human demographic processes. Additionally, we conduct a sensitivity analysis (Dataset S1) for each region to evaluate the effect of sliding window size and the length of the time series on the significance of the EWS statistics (70). Autocorrelation within the sliding window is one of the simplest measurements of critical slowing down. AR (1) measures the degree of correlation between pairs of temporally adjacent measurements of state variable values (i.e., and ). As the sliding window approaches the collapse point, increasing AR (1) values indicate the SPD values are becoming increasingly similar, which is an EWS for decreasing system resilience. This measurement is made here by fitting a lag-1 [AR (1)] ordinary least-squares regression model to each window of data and estimating the autoregression coefficient. More precisely, temporal autocorrelation is found as follows: where α is an autoregressive coefficient and is Gaussian white noise. Variance, reported here as a SD (σ), quantifies the spread of values, which may indicate a system is approaching a regime shift. σ is found as follows: , where z is SPD density. Skewness () measures directional bias in the data as the standardized third moment around the mean of a distribution, or (69). The shape of the distribution of system indicator variables can change in systems that are undergoing CSD because as the system slows down, it will hover around a critical transition point. These values can also include ones that indicate alternative system states, a process sometimes called flickering (32). This ambivalence in the system trajectory can yield increasingly skewed distributions with significant skewness statistics in either the positive or negative direction, depending on whether a system is moving toward larger or smaller values.
Once the summary statistics are calculated for each time increment, we qualitatively assess the data trends for EWSs (Table S1); if a given system exhibits EWSs of a regime shift (collapse), theory predicts increasing autocorrelation and variance and decreasing skewness. Next, we assess these predictions for each region statistically using the Kendall’s tau () rank correlation test for the entire time series subset. The τ statistic indicates the direction of the EWS statistic as either increasing () or decreasing (). We also calculate an optimized tau value () by finding the maximum (or minimum) τ value from time series of varying durations that iteratively extend back from the collapse date beyond a minimum temporal window of 100 y before the collapse. This optimization routine is necessary for two reasons. First, we do not know a priori when resilience began to decline in these systems. The time series data under consideration may be much longer than the period of declining resilience. Second, the EWS:noise ratio is expected to be low and may preferentially obscure signals that are necessarily weaker earlier in time. Optimized tau values are calculated separately for each EWS statistic because we currently have no reason to expect different EWS metrics to change at proportionate rates and thus emerge through background noise at the same point in time. Rather, once a system begins to experience declining resilience, different EWS may change at different rates and thus emerge through background noise at different points in time. The EWS results for the Neolithic Paris Basin illustrate a situation in which (i) the quantitative method as applied to the full range of data are unable to capture qualitatively distinct AR (1) and σ EWS leading up to collapse, and (ii) AR (1) and σ trends indicate differential sensitivities to the empirical SPD. Conversely, the optimization routine identifies these trends, and, therefore, we report the in Fig. 2 and Table 1. We follow standard approaches and report the probability values associated with {13} and {14} using single-tailed tests, and , respectively {13, 14}. For completeness, we report in Table S3 and both and in Dataset S1.
Table S3.
EWS analysis results of summed probability distributions of nine European regions using the complete (nonoptimized) subset
| Region | AR (1) | σ | |||||||
| Southern Germany | −0.20 | 1.00 | 0.52 | −0.01 | 0.60 | 0.57 | −0.61 | 0.00*** | 0.03** |
| Eastern Switzerland | 0.05 | 0.28 | 0.50 | 0.07 | 0.21 | 0.35 | −0.07 | 0.21 | 0.46 |
| England and Wales (without Wessex and Sussex) | −0.27 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.34 | 0.00*** | 0.18 | −0.15 | 0.10* | 0.25 |
| Ireland | −0.08 | 0.76 | 0.81 | 0.32 | 0.00*** | 0.18 | −0.25 | 0.01*** | 0.18 |
| Paris Basin | 0.33 | 0.00*** | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.34 | 0.52 | −0.30 | 0.00*** | 0.18 |
| Rhone-Languedoc | −0.12 | 0.99 | 0.52 | 0.67 | 0.00*** | 0.01*** | 0.26 | 1.00 | 0.73 |
| Scotland | 0.08 | 0.28 | 0.36 | 0.00 | 0.51 | 0.41 | 0.17 | 0.91 | 0.79 |
| Southern England (Wessex and Sussex) | 0.15 | 0.03** | 0.34 | 0.68 | 0.00*** | 0.06* | −0.15 | 0.02 | 0.31 |
| Western France | −0.19 | 0.99 | 0.55 | 0.61 | 0.00*** | 0.04** | 0.43 | 1.00 | 0.91 |
Significance levels: *P = 0.10; **P = 0.05; ***P = 0.01.
Recognizing the potential for spurious results given the complexity of these archaeological cases, we develop a rigorous statistical test to examine the effects of confounding factors. To do this, we analyze the SPD null model. We calculate EWS statistics for each of the 20,000 simulated density curves and combine them into distributions represented as and {15}. Cumulative density functions (CDFs) are computed {16, 17}, and the probabilities of and are determined for each EWS statistic, given a null model of exogenous processes {18, 19}. Thus, we define two “robust” probability values using single-sided tests, and as , where is the CDF for and , respectively.
Last, we examine the probability of obtaining the observed ratio of statistically significant:insignificant results. We apply a Fisher exact test, which involves classifying the probability values for each EWS statistic of each region as either passing or failing given a one-tailed probability test to determine the likelihood that the significant EWS statistics and could have occurred by chance. Given the sample size of nine cases, we use a 0.1 significance level in this classification. The number of observed cases of nine that pass or fail a given EWS test is given using an expected pass:fail ratio of 1:8. We report Fisher exact test results for and in Table 2 and for and in Table S4.
Table S4.
Fisher’s exact tests for multiple analyses using the complete (nonoptimized) subset
| Data subset | Test | EWS | Pass† | Fail† | CI low | CI high | P‡ |
| Tau for all data () | Sampling () | AR (1) | 2 | 7 | 0.13 | 201.64 | 0.55 |
| σ | 5 | 4 | 0.94 | 703.78 | 0.05** | ||
| 5 | 4 | 0.94 | 703.78 | 0.05** | |||
| Null model () | AR (1) | 0 | 9 | 0.00 | 51.96 | 1.00 | |
| σ | 3 | 6 | 0.32 | 313.65 | 0.27 | ||
| 1 | 8 | 0.02 | 117.49 | 1.00 |
Significance level: **P = 0.10. CI, confidence interval.
Pass/fail at P < 0.1.
Expected ratio used in Fisher test is 1:8, pass:fail.
A Regime-Shift Model for Human Settlement Densities at Large Spatial and Temporal Scales.
The model shown in Fig. 1 uses a simple step function with a high value step decreasing from 0.4% to 0.2% and a low value step at −0.4% growth. The upper limit of 0.4% growth reflects the upper end of expected annual population growth rates in early agricultural populations (12). To simulate increasing variance leading up to collapse, a randomization function is applied to the upper step values in which the mean is zero and the SD increases from 0.1% to 0.2%. The variance in the lower step is set to be constant at 0.2%. The growth rate model is then used to simulate an SPD curve by assuming a starting population of 500 individuals and iteratively increasing the population size by the modeled growth rate value at a given time step. We model the effects of the radiocarbon date calibration process, including atmospheric effects and isotopic counting error, by back-calibrating a uniform sample of dates 7–5.5 kya (n = 1,000), adding error sampled from a Poisson distribution , and calibrating these simulated dates using the IntCal13 calibration curve (68). To model the effects of archaeological sampling, a random sample of 1,000 dates is drawn from the simulated population. The modified population curve is finally summed by the same binning procedure used on the empirical data. The result is a simulated SPD that results from a theoretical fold bifurcation in population growth rates, and we calculate the variance EWS metric on the SPD data assuming a collapse date at 6,225 cal. BP. We use a 77-y sliding window (∼10% of the 775-y duration; see ref. 69). Finally, we calculate and test its significance using and . We note that this model is developed to illustrate that EWSs are detectable in archaeological SPDs despite the potentially confounding factors discussed in the main text. The model explores a number of interactions, although it is not exhaustive. Other interactions, such as the relative strength of EWSs that would be required for detecting EWSs at varying points in the calibration curve or the possibility of CSD due to biological population growth may require additional investigation.
Wavelet Analysis.
A univariate continuous wavelet transform analysis (71) is run using the R biwavelet package (72). For each region, we analyze a corrected and detrended SPD and plot two 95% significance contour intervals (Dataset S1). The significance contour plotted in white uses the built-in time-averaged filters. Plotting the second significance contour involves performing univariate wavelet transforms and calculating the 95% quantile on the distribution of power matrices from the simulated SPDs from the null model. The power matrix from the observed SPD is then divided by the quantiles from the SPD null simulations, and the resulting 95% significance contour is plotted in black.
Conclusion: Prospects and Contributions to Archaeology and Sustainability Science
During the Neolithic revolution new agricultural technologies initiated rapid demographic growth, followed by periods of devastating societal instability that we are only now beginning to understand. It remains unclear whether modern technological innovation can continue to outpace demand, and it is important for sustainability scientists to consider the possibility that generic mechanisms can contribute to demographic collapse in human societies, as well as to develop ways to detect declining resilience. Here we present evidence that early warning signals preceded large-scale population collapse in the European Neolithic Period. To encourage further study of human ecodynamics, we include a framework for interpreting societal regime shift at large spatial and temporal scales that links three generic mechanisms that are known for causing social and ecological regime shifts with social processes such as growth and collapse, climate change, resource degradation, disease, and warfare. We suggest that complex interactions among social and natural factors, and emergent patterns such as Allee and sunk-cost effects, may slow the recovery of human societies during periods of decreased resilience. Further, distinct statistical signatures of declining resilience due to these processes are detectable despite the complex depositional processes that confound archaeological proxy data. We suggest that the detection of EWSs in human settlement patterns is a general finding that points to a need for EWS analyses of other types of archaeological data and other historical datasets. We believe our framework can provide a way to analyze complex dynamics in human ecosystems, and perhaps ultimately to monitor and prevent catastrophic consequences of societal regime shifts.
Materials and Methods
Archaeological Radiocarbon Database.
The complete dataset includes archaeological radiocarbon dates comprising 2,759 sites for Mesolithic and Neolithic Europe, ca. 10–3.5 kya (65). Nine regions were selected for the EWS analysis because they provide the clearest qualitative and quantitative shifts from high to low growth regimes (Table S2).
Statistical Methods and SPD Modeling.
To minimize the effects of sampling bias, radiocarbon calibration effects (66) and taphonomic bias (21), we use the Bchron R package (67), IntCal13 (68), and Monte Carlo simulation to generate a corrected SPD curve (Fig. S3). The EWS analysis involves isolating subsets from each time series from the Neolithic transition to the point of collapse, detrending the resulting time series, and calculating three EWS statistics including autocorrelation, variance, and skewness following ref. 69. EWS patterns are assessed qualitatively (Table S1), and statistically using the Kendall’s tau rank correlation test with both an optimized tau value (Table 1) and the complete time series (Table S3). The procedures for generating a null model follow ref. 17 and the rigorous statistical test for examining the effects of confounding archaeological factors on the EWS analysis involves computing cumulative density functions from the null model and calculating the probabilities of each observed EWS statistic using single-tailed tests. Fisher’s exact tests are used to determine the probability of the significant EWS statistics and for the optimized time series (Table 2) and for the full time series (Table S4). A sensitivity analysis evaluates the effect of sliding window size and the length of the time series on the significance of the EWS statistics (70) (Dataset S1). These EWS methods (Fig. S4), the simulation shown in Fig. 1, and the wavelet analysis (71, 72) are described in further detail in the SI Materials and Methods. All analyses are performed using R (73). Code is available on request.
SI Text
Early Warning Signals of Collapse in Neolithic Paris Basin.
Here we briefly step through a sample case to illustrate the procedure and interpretation of results. Fig. S1 illustrates how EWSs are detected in the Neolithic Paris Basin. Fig. S1B shows the complete SPD curve including the region of the time series isolated for EWS analysis. The SPD curve serves as a temporal proxy for population change throughout the Paris Basin Neolithic period. Following previous studies (17, 20, 26), we assign a regime-shift date, or “bust” point, at which time the system shifted from population growth to decline. For the Paris Basin example, the bust point was previously identified at 6,225 cal. BP. We then qualitatively define a point-of-beginning for the Neolithic boom. In most cases, this is simply the point at which agriculture is thought to have entered the region. However, if the SPD exhibits growth before the currently accepted agricultural start date, we assign an earlier point-of-beginning. This decision is justifiable given that archaeological estimates of agricultural origins reflect minimum possible dates due to sample limitations. For the Paris Basin, we assign the beginning of the population boom to 7,500 cal. BP, which precedes the currently accepted agricultural origins date by 300 y. Thus, the Paris Basin population boom isolated for EWS analysis ranges from 7,500 to 6,225 cal. BP.
Fig. S1A shows the extracted time series, the time-series trend model, and a schematic representation of the EWS sliding window, all of which are used in the derivation of EWS metrics. Fig. S1 C, E, and G shows the results of the EWS analysis for the three statistical indicators considered here, including lag-1 autocorrelation [AR (1)], SD (σ), and skewness (). AR (1) and σ are expected to increase (+), whereas skewness is expected to decrease (−) in advance of regime shift (37). In the case of Neolithic Paris Basin, qualitative increases in AR (1) (+) and σ (+) are apparent after 6,800 and 6,300 cal. BP, respectively. In contrast, does not exhibit clear directionality, although some decrease may be present. Kendall’s tau () statistics are used to quantify directionality and to assess statistical significance. The statistics support the qualitative observations at . That is, AR (1), σ, and exhibit significant departures from zero.
These statistics tentatively support the presence of CSD in the empirical data, but they cannot distinguish CSD due to systemic changes in human demography from CSD due to exogenous factors such as sampling error, atmospheric effects on radiocarbon, and taphonomic biases. Fig. S1 D, F, and H shows the cumulative density distributions [] for trend statistics generated from a null model simulating the effects of these confounding factors and the probability of obtaining the empirical values given the null model (Materials and Methods). The probability values for the trend statistics for AR (1) and σ reveal significant departures from the null model (), whereas does not. Therefore, the CSD trends are more likely to reflect demographic processes rather than exogenous factors. We conclude that CSD preceded the Neolithic Paris Basin collapse that occurred around 6,225 cal. BP. In contrast, the skewness results are inconclusive.
Theoretical Considerations Related to SPD-Based EWSs Among Human Societies.
Although regime shifts and CSD may be expected, direct observation of such dynamics at requisite spatial and temporal scales is difficult. Archaeological data provide us with long-term, spatially extensive proxies for human demography (4). The SPD method in this study does not directly measure human population levels but rather approximates the number of inhabited settlements in a given spatiotemporal unit, which is taken to index human population levels after applying appropriate corrections. Thus, SPDs directly measure how settlement densities changed through time, but they do not directly measure population change. However, recent work has shown strong correlation between SPDs and a more direct demographic proxy based on skeletal measurements known as the juvenility index; this study also compared settlement plans and ethnographic censuses from contemporary farmers and foragers and found that differential settlement densities do not obscure demographic reconstruction using SPDs (26).
Because CSD is predicted to occur in human populations, a theoretical question that arises is how CSD should manifest in human settlement change, which may involve distinct dynamics. To explain how human settlement dynamics could come to reflect CSD in human populations, we hypothesize the relationships between archaeological settlement patterns in high and low growth regimes. In a high growth regime, such as occurred immediately after the introduction of agriculture in Neolithic Europe, there would have been a mix of young and old villages with new settlements forming from parent villages and rapid overall regional growth. In this regime, any abandoned settlements would have been rapidly repopulated because of high regional growth rates and high demand for resources. In a low growth regime, settlements would have been older on average with fewer new settlements appearing. Demographic variance and system shocks such as warfare, conflict, disease, or stochastic environmental effects would have had significant impacts, and failed settlements would have rarely repopulated because of the low overall demand for resources.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Anthropology Department, the College of Behavioral and Social Sciences at the University of Maryland, and European Research Council Advanced Grant 249390 (to S.J.S.).
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission. T.A.K. is a Guest Editor invited by the Editorial Board.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1602504113/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Butzer KW, Endfield GH. Critical perspectives on historical collapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109(10):3628–3631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1114772109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Streeter R, Dugmore AJ. Anticipating land surface change. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(15):5779–5784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1220161110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Allen CR, Angeler DG, Garmestani AS, Gunderson LH, Holling CS. Panarchy: Theory and application. Ecosystems (N Y) 2014;17(4):578–589. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Redman CL. Resilience theory in archaeology. Am Anthropol. 2005;107(1):70–77. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Noble IR. 1996. Global change and terrestrial ecosystems. International Geosphere-Biosphere Programme Book Series, eds Walker B, Steffan B, No. 2 (Cambridge Univ Press, Cambridge, UK) pp. 173–183.
- 6.Holling CS. Resilience and stability of ecological systems. Annu Rev Ecol Syst. 1973;4:1–23. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Scheffer M, Carpenter S, Foley JA, Folke C, Walker B. Catastrophic shifts in ecosystems. Nature. 2001;413(6856):591–596. doi: 10.1038/35098000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Scheffer M, Carpenter SR, Dakos V, Nes Ev. Generic indicators of ecological resilience: Inferring the chance of a critical transition. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst. 2015;46(1):145–167. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tainter JA. The Collapse of Complex Societies. Cambridge Univ Press; New York: 1988. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Diamond JM. Collapse: How Societies Choose to Fail or Succeed. Viking; New York: 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 11.May RM, Levin SA, Sugihara G. Complex systems: Ecology for bankers. Nature. 2008;451(7181):893–895. doi: 10.1038/451893a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bocquet-Appel J-P. When the world’s population took off: The springboard of the Neolithic Demographic Transition. Science. 2011;333(6042):560–561. doi: 10.1126/science.1208880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Turchin P. Long-term population cycles in human societies. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009;1162:1–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kintigh KW, et al. Grand challenges for archaeology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111(3):879–880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1324000111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.van der Leeuw S, et al. Toward an integrated history to guide the future. Ecol Soc. 2011;16(4):2. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dearing JA, Braimoh AK, Reenberg A, Turner BL, van der Leeuw S. Complex land systems: The need for long time perspectives to assess their future. Ecol Soc. 2010;15(4):21. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Shennan S, et al. Regional population collapse followed initial agriculture booms in mid-Holocene Europe. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2486. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Williams AN. The use of summed radiocarbon probability distributions in archaeology: A review of methods. J Archaeol Sci. 2012;39(3):578–589. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Collard M, Edinborough K, Shennan S, Thomas MG. Radiocarbon evidence indicates that migrants introduced farming to Britain. J Archaeol Sci. 2010;37(4):866–870. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Timpson A, et al. Reconstructing regional population fluctuations in the European Neolithic using radiocarbon dates: A new case-study using an improved method. J Archaeol Sci. 2014;52:549–557. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Surovell TA, Byrd Finley J, Smith GM, Brantingham PJ, Kelly R. Correcting temporal frequency distributions for taphonomic bias. J Archaeol Sci. 2009;36(8):1715–1724. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ballenger JAM, Mabry JB. Temporal frequency distributions of alluvium in the American Southwest: Taphonomic, paleohydraulic, and demographic implications. J Archaeol Sci. 2011;38(6):1314–1325. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Torfing T. Neolithic population and summed probability distribution of 14C-dates. J Archaeol Sci. 2015;63:193–198. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Timpson A, Manning K, Shennan S. Inferential mistakes in population proxies: A response to Torfing’s “Neolithic population and summed probability distribution of 14C-dates”. J Archaeol Sci. 2015;63:199–202. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zahid HJ, Robinson E, Kelly RL. Agriculture, population growth, and statistical analysis of the radiocarbon record. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113(4):931–935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1517650112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Downey SS, Bocaege E, Kerig T, Edinborough K, Shennan S. The neolithic demographic transition in Europe: Correlation with juvenility index supports interpretation of the summed calibrated radiocarbon date probability distribution (SCDPD) as a valid demographic proxy. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e105730. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Rick JW. Dates as data: An examination of the Peruvian Preceramic radiocarbon record. Am Antiq. 1987;52(1):55–73. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Boonstra WJ, de Boer FW. The historical dynamics of social-ecological traps. Ambio. 2014;43(3):260–274. doi: 10.1007/s13280-013-0419-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Carpenter SR, Brock WA. Adaptive capacity and traps. Ecol Soc. 2008;13:40. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tschakert P, Shaffer LJ. Social-Ecological Systems in Transition. Springer; New York: 2014. pp. 139–156. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Carstensen J, Telford RJ, Birks HJB. Diatom flickering prior to regime shift. Nature. 2013;498(7455):E11–E12. doi: 10.1038/nature12272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dakos V, van Nes EH, Scheffer M. Flickering as an early warning signal. Theor Ecol. 2013;6(3):309–317. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wang R, et al. Flickering gives early warning signals of a critical transition to a eutrophic lake state. Nature. 2012;492(7429):419–422. doi: 10.1038/nature11655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bailey RM. Spatial and temporal signatures of fragility and threshold proximity in modelled semi-arid vegetation. Proc Biol Sci. 2011;278(1708):1064–1071. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2010.1750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Drake JM, Griffen BD. Early warning signals of extinction in deteriorating environments. Nature. 2010;467(7314):456–459. doi: 10.1038/nature09389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Scheffer M, et al. Early-warning signals for critical transitions. Nature. 2009;461(7260):53–59. doi: 10.1038/nature08227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Scheffer M. Critical Transitions in Nature and Society. Princeton Univ Press; Princeton: 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hefley TJ, Tyre AJ, Blankenship EE. Statistical indicators and state–space population models predict extinction in a population of bobwhite quail. Theor Ecol. 2013;6(3):319–331. [Google Scholar]
- 39.May RM. Simple mathematical models with very complicated dynamics. Nature. 1976;261(5560):459–467. doi: 10.1038/261459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dai L, Vorselen D, Korolev KS, Gore J. Generic indicators for loss of resilience before a tipping point leading to population collapse. Science. 2012;336(6085):1175–1177. doi: 10.1126/science.1219805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Taylor CM, Hastings A. Allee effects in biological invasions. Ecol Lett. 2005;8(8):895–908. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Steele J. Radiocarbon dates as data: Quantitative strategies for estimating colonization front speeds and event densities. J Archaeol Sci. 2010;37(8):2017–2030. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Steele J. Human dispersals: Mathematical models and the archaeological record. Hum Biol. 2009;81(2-3):121–140. doi: 10.3378/027.081.0302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Benton TG, Plaistow SJ, Coulson TN. Complex population dynamics and complex causation: Devils, details and demography. Proc Biol Sci. 2006;273(1591):1173–1181. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2006.3495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Gunderson LH, Holling CS, editors. Panarchy: Understanding Transformations in Human and Natural Systems. Island Press; Washington, DC: 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 46. Dakos, V, Carpenter, S. R, Nes, E. H. v, Scheffer M. (2015) Resilience indicators: prospects and limitations for early warnings of regime shifts. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 370:20130263.
- 47.Janssen MA, Kohler TA, Scheffer M. Sunk-cost effects and vulnerability to collapse in ancient societies. Curr Anthropol. 2003;44(5):722–728. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hegmon M, et al. Social transformation and its human costs in the prehispanic U.S. Southwest. Am Anthropol. 2008;110(3):313–324. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lade SJ, Tavoni A, Levin SA, Schlüter M. Regime shifts in a social-ecological system. Theor Ecol. 2013;6(3):359–372. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Lee CT, Tuljapurkar S. Population and prehistory I: Food-dependent population growth in constant environments. Theor Popul Biol. 2008;73(4):473–482. doi: 10.1016/j.tpb.2008.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Folke C, et al. Regime shifts, resilience, and biodiversity in ecosystem management. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst. 2004;35:557–581. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Chavez FP, Ryan J, Lluch-Cota SE, Niquen C M. From anchovies to sardines and back: Multidecadal change in the Pacific Ocean. Science. 2003;299(5604):217–221. doi: 10.1126/science.1075880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Althouse BM, Hébert-Dufresne L. Epidemic cycles driven by host behaviour. J R Soc Interface. 2014;11(99):11. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2014.0575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Turchin P, Korotayev A. Population dynamics and internal warfare: A reconsideration. Social Evol History. 2006;5(2):112–147. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kohler TA, Cole S, Ciupe S. In: Pattern and Process in Cultural Evolution. Shennan S, editor. Univ of California Press; Berkeley: 2009. pp. 277–295. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Firestone RB, et al. Evidence for an extraterrestrial impact 12,900 years ago that contributed to the megafaunal extinctions and the Younger Dryas cooling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104(41):16016–16021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706977104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kuijt I. Reconsidering the cause of cultural collapse in the Lillooet area of British Columbia, Canada: A geoarchaeological perspective. Am Antiq. 2001;66(4):692–703. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Rasmussen S, et al. Early divergent strains of Yersinia pestis in Eurasia 5,000 years ago. Cell. 2015;163(3):571–582. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.10.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Benedictow OJ. The Black Death 1346-1353: The Complete History. 1st Ed Boydell Press; Suffolk, UK: 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Fyfe RM, Woodbridge J, Roberts N. From forest to farmland: Pollen-inferred land cover change across Europe using the pseudobiomization approach. Glob Change Biol. 2015;21(3):1197–1212. doi: 10.1111/gcb.12776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Woodbridge J, et al. The impact of the Neolithic agricultural transition in Britain: A comparison of pollen-based land-cover and archaeological 14C date-inferred population change. J Archaeol Sci. 2014;51:216–224. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Lechterbeck J, et al. Is Neolithic land use correlated with demography? An evaluation of pollen-derived land cover and radiocarbon-inferred demographic change from central Europe. Holocene. 2014;24(10):1297–1307. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Gronenborn D, Strien H-C, Dietrich S, Sirocko F. ‘Adaptive cycles’ and climate fluctuations: A case study from Linear Pottery Culture in western Central Europe. J Archaeol Sci. 2014;51:73–83. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Haak W, et al. Massive migration from the steppe was a source for Indo-European languages in Europe. Nature. 2015;522(7555):207–211. doi: 10.1038/nature14317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Manning K, Colledge S, Crema E, Shennan S, Timpson A. 2016. The cultural evolution of Neolithic Europe. EUROEVOL dataset 1: Sites, phases and radiocarbon data. J Open Archaeol Data 5:e2.
- 66.Brown WA. Through a filter, darkly: Population size estimation, systematic error, and random error in radiocarbon-supported demographic temporal frequency analysis. J Archaeol Sci. 2015;53:133–147. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Parnell A. 2015 Bchron: Radiocarbon dating, age-depth modelling, relative sea-level rate estimation, and non-parametric phase modelling (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna), R package version 4.1.2. Available at https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=Bchron.
- 68.Reimer P. IntCal13 and Marine13 radiocarbon age calibration curves 0-50,000 years cal BP. Radiocarbon. 2013;55(4):1869–1887. [Google Scholar]
- 69.Dakos V, et al. Methods for detecting early warnings of critical transitions in time series illustrated using simulated ecological data. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41010. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Best D, Gipps P. Algorithm as 71: The upper tail probabilities of Kendall’s tau. Appl Stat. 1974;23(1):98–100. [Google Scholar]
- 71.Torrence C, Compo GP. A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull Am Meteorol Soc. 1998;79(1):61–78. [Google Scholar]
- 72.Gouhier T. 2014. biwavelet: Conduct Univariate and Bivariate Wavelet Analyses, Version 0.17.4. Available at https://github.com/tgouhier/biwavelet.
- 73.R Core Team . R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing; Vienna: 2015. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.