Abstract
AIMS--To present a non-isotopic procedure for the analysis of the different apolipoprotein E genotypes in normal subjects and patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. METHODS--Apolipoprotein E genotypes were detected following polymerase chain reaction and miniaturised sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) (PhastSystem Pharmacia). RESULTS--The time taken from extraction of DNA from 6 microliters whole blood to the final result was eight hours. The allele frequencies in patients with diabetes mellitus in our series were similar to those found in the control subjects. CONCLUSIONS--SDS-PAGE is rapid, reliable and safe with few drawbacks, can be used as a routine procedure and may easily replace apolipoprotein E phenotyping.
Full text
PDF

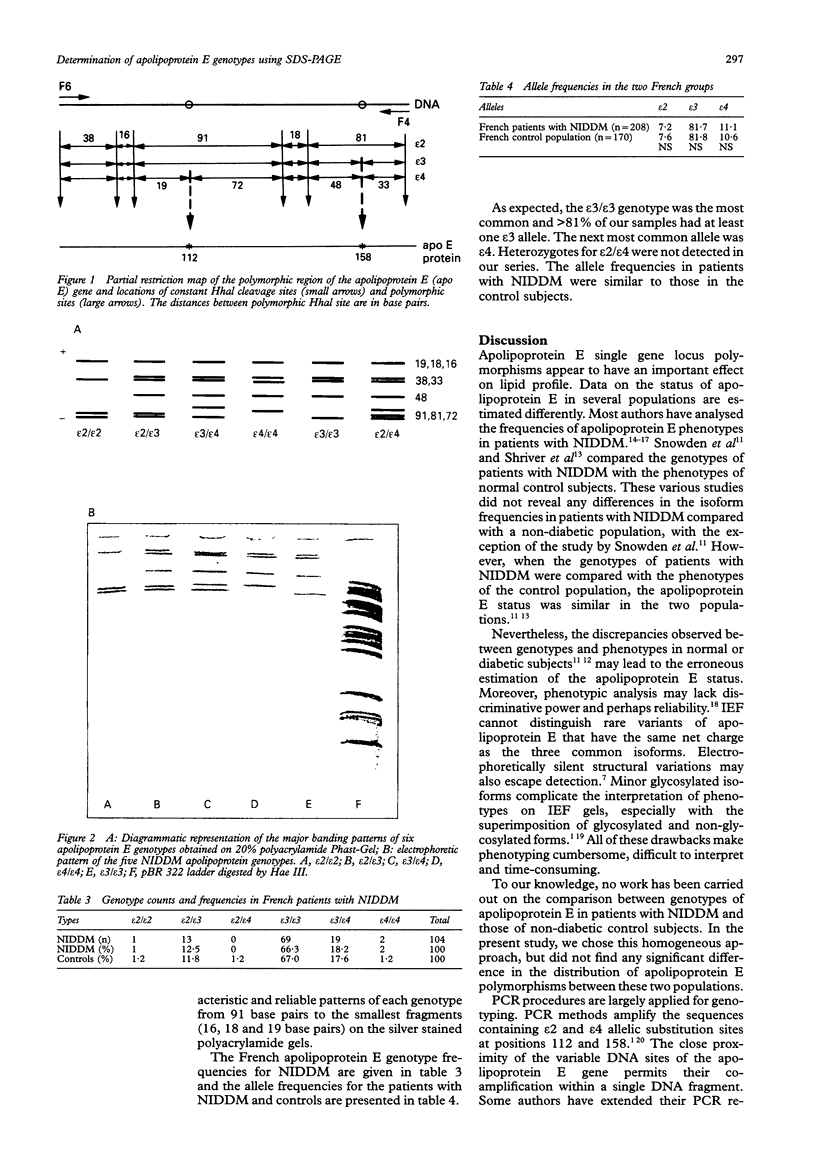


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cormier-Daire V., Clavel C., Polette M., Doco M., Boutterin M. C., Binninger I., Birembaut P. Non radioactive single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) analysis of exon 11 of the CFTR gene using the Pharmacia PhastSystem. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1993 Oct;41(8):713–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davignon J., Gregg R. E., Sing C. F. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis. 1988 Jan-Feb;8(1):1–21. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.8.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emi M., Wu L. L., Robertson M. A., Myers R. L., Hegele R. A., Williams R. R., White R., Lalouel J. M. Genotyping and sequence analysis of apolipoprotein E isoforms. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):373–379. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eto M., Watanabe K., Iwashima Y., Morikawa A., Oshima E., Sekiguchi M., Ishii K. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and hyperlipemia in type II diabetics. Diabetes. 1986 Dec;35(12):1374–1382. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.12.1374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. K., Bain S. C., Day P. J., Barnett A. H., Charleson F., Jones A. F., Walker M. R. Detection of human apolipoprotein E3, E2, and E4 genotypes by an allele-specific oligonucleotide-primed polymerase chain reaction assay: development and validation. Clin Chem. 1991 Jul;37(7):1263–1268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hixson J. E., Vernier D. T. Restriction isotyping of human apolipoprotein E by gene amplification and cleavage with HhaI. J Lipid Res. 1990 Mar;31(3):545–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imari Y., Koga S., Ibayashi H. Phenotypes of apolipoprotein E and abnormalities in lipid metabolism in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 1988 Dec;37(12):1134–1138. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(88)90189-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James R. W., Voliotis C., Grab B., Pometta D. Phénotypes de l'apoprotéine E (apo E) et lipides sériques des diabétiques. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1987 Dec 12;117(50):2021–2023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontula K., Aalto-Setälä K., Kuusi T., Hämäläinen L., Syvänen A. C. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism determined by restriction enzyme analysis of DNA amplified by polymerase chain reaction: convenient alternative to phenotyping by isoelectric focusing. Clin Chem. 1990 Dec;36(12):2087–2092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontula K., Koivisto U. M., Miettinen H. The use of PCR in diagnosing lipoprotein disorders. Ann Med. 1992 Jun;24(3):195–199. doi: 10.3109/07853899209147821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):622–630. doi: 10.1126/science.3283935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mailly F., Moll P., Kottke B. A., Kamboh M. I., Humphries S. E., Ferrell R. E. Estimation of the frequency of isoform-genotype discrepancies at the apolipoprotein E locus in heterozygotes for the isoforms. Genet Epidemiol. 1992;9(4):239–248. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370090403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Knott T. J., Shaw D. J., Brook J. D. Localization of genes encoding apolipoproteins CI, CII, and E to the p13----cen region of human chromosome 19. Hum Genet. 1985;71(2):144–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00283370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shriver M. D., Boerwinkle E., Hewett-Emmett D., Hanis C. L. Frequency and effects of apolipoprotein E polymorphism in Mexican-American NIDDM subjects. Diabetes. 1991 Mar;40(3):334–337. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.3.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeets B., Poddighe J., Brunner H., Ropers H. H., Wieringa B. Tight linkage between myotonic dystrophy and apolipoprotein E genes revealed with allele-specific oligonucleotides. Hum Genet. 1988 Sep;80(1):49–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00451455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snowden C., Houlston R. S., Arif M. H., Laker M. F., Humphries S. E., Alberti K. G. Disparity between apolipoprotein E phenotypes and genotypes (as determined by polymerase chain reaction and oligonucleotide probes) in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Clin Chim Acta. 1991 Jan 31;196(1):49–57. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(91)90207-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Saunders A. M., Schmechel D., Pericak-Vance M., Enghild J., Salvesen G. S., Roses A. D. Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1977–1981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism in health and disease. Am Heart J. 1987 Feb;113(2 Pt 2):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(87)90610-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenham P. R., Newton C. R., Price W. H. Analysis of apolipoprotein E genotypes by the Amplification Refractory Mutation System. Clin Chem. 1991 Feb;37(2):241–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenham P. R., Price W. H., Blandell G. Apolipoprotein E genotyping by one-stage PCR. Lancet. 1991 May 11;337(8750):1158–1159. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92823-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenham P. R., Sedky A., Spooner R. J. Apolipoprotein E phenotyping: a word of caution. Ann Clin Biochem. 1991 Nov;28(Pt 6):599–605. doi: 10.1177/000456329102800610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Human very low density lipoprotein apolipoprotein E isoprotein polymorphism is explained by genetic variation and posttranslational modification. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):1033–1041. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



