Abstract
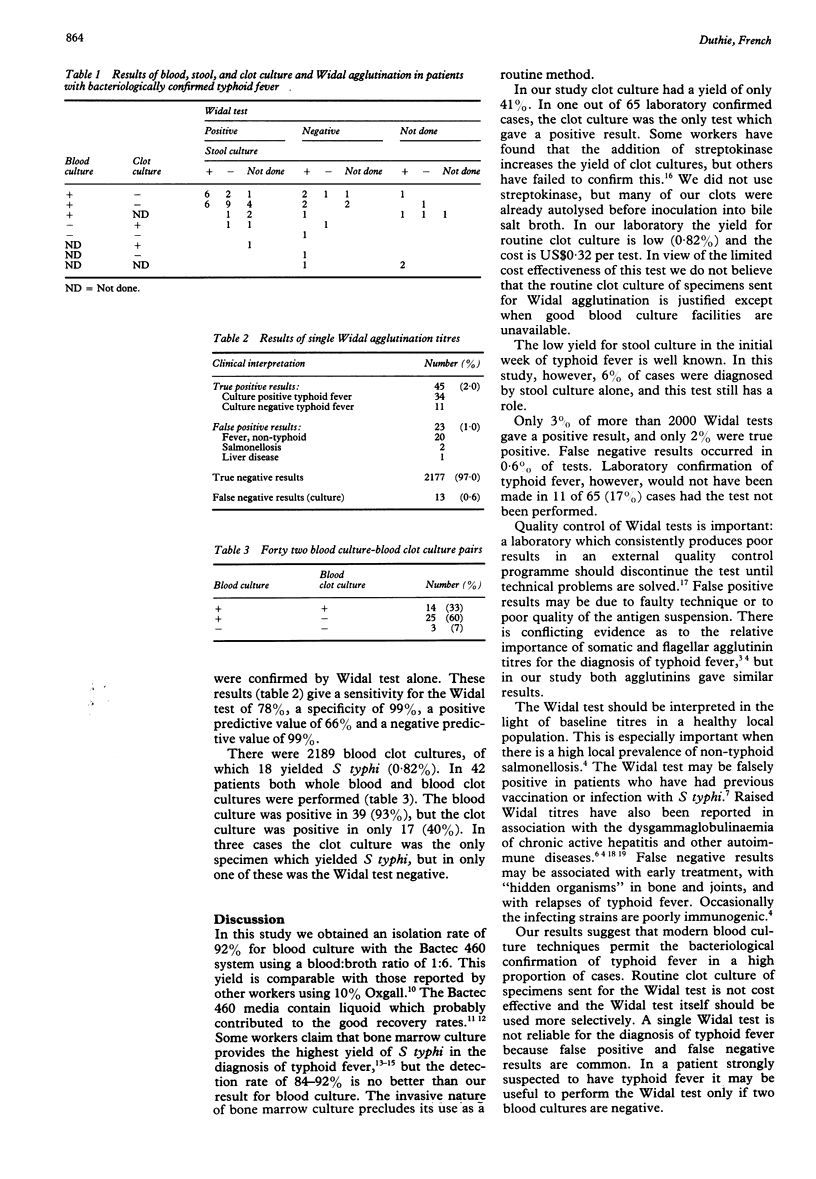
Over five years the Bactec radiometric blood culture method yielded Salmonella typhi in 41 of 45 confirmed cases of typhoid fever, 90% of which were from the first culture set taken. Blood clot culture was positive in 18 (41%) of 44 confirmed cases and stool culture in 24 (59%) of 41. The yield from 2189 Widal clot cultures was only 0.03%. There were 68 positive results in 2258 unpaired Widal tests: 23 of them were falsely positive and 13 falsely negative, but in 11 out of 68 cases the Widal was the only positive laboratory test. It is concluded that routine clot culture is not cost effective if a sensitive blood culture method is used, and that the Widal test is useful only in selected patients.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brodie J. Antibodies and the Aberdeen typhoid outbreak of 1964. I. The Widal reaction. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Oct;79(2):161–180. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400052979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster W. D. Letter: Laboratory diagnosis of typhoid fever. Lancet. 1975 Jul 12;2(7924):80–80. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90527-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman S. L., Edman D. C., Punjabi N. H., Lesmana M., Cholid A., Sundah S., Harahap J. Bone marrow aspirate culture superior to streptokinase clot culture and 8 ml 1:10 blood-to-broth ratio blood culture for diagnosis of typhoid fever. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Jul;35(4):836–839. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang T., Puthucheary S. D. Significance and value of the Widal test in the diagnosis of typhoid fever in an endemic area. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Apr;36(4):471–475. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.4.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Protell R. L., Soloway R. D., Martin W. J., Schoenfield L. J., Summerskill W. H. Anti-Salmonella agglutinins in chronic active liver disease. Lancet. 1971 Aug 14;2(7720):330–332. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pu S. J., Huang H. S. Diagnostic value of a single Widal test. Zhonghua Min Guo Wei Sheng Wu Ji Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 1985 Nov;18(4):256–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senewiratne B., Senewiratne K. Reassessment of the Widal test in the diagnosis of typhoid. Gastroenterology. 1977 Aug;73(2):233–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shehabi A. A. The value of a single Widal test in the diagnosis of acute typhoid fever. Trop Geogr Med. 1981 Jun;33(2):113–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simanjuntak C. H., Hoffman S. L., Darmowigoto R., Lesmana M., Soeprawoto, Edman D. C. Streptokinase clot culture compared with whole blood culture for isolation of Salmonella typhi and S. paratyphi A from patients with enteric fever. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1988;82(2):340–341. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(88)90471-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallenas C., Hernandez H., Kay B., Black R., Gotuzzo E. Efficacy of bone marrow, blood, stool and duodenal contents cultures for bacteriologic confirmation of typhoid fever in children. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1985 Sep-Oct;4(5):496–498. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198509000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON K. C. The fate of S. typhi in blood clot in relation to the problem of isolation. J Clin Pathol. 1955 Feb;8(1):52–54. doi: 10.1136/jcp.8.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson K. C. Laboratory and clinical investigation of recovery of Salmonella typhi from blood. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):122–126. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.122-126.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


