Abstract
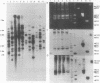
AIMS--To evaluate the usefulness of two IS6110 based typing methods, an amplityping assay and restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis, for fingerprinting respiratory isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. METHODS--For amplityping, a pair of primers which amplify the intervening sequence between the repetitive insertion sequence IS6110 was used to generate a banding pattern which was confirmed by hybridisation. This assay was compared with conventional chromosomal DNA RFLP typing in the evaluation of 110 epidemiologically diverse isolates. RESULTS--Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplityping generated a single pattern in Hong Kong Chinese strains, but two and four diverse patterns in Filipino and Vietnamese strains, respectively, and could be completed within four days. When compared with chromosomal DNA RFLP typing, which took three weeks to complete, four different RFLP patterns could be seen among the Chinese strains, while seven patterns were found in the Filipino and Vietnamese strains. No change in amplityping or RFLP patterns was found in 36 sequential isolates from the same patients after anti-tuberculosis treatment for up to 12 months, despite the emergence of resistance in three of these strains. No specific amplityping or RFLP pattern could be related to different patterns of drug susceptibility. CONCLUSION--PCR amplityping could be used initially as a rapid typing method to distinguish strains originating from different localities. This could be important for investigation of outbreaks of tuberculosis--for example, in refugee camps.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bose M., Chander A., Das R. H. A rapid and gentle method for the isolation of genomic DNA from mycobacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 25;21(10):2529–2530. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.10.2529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevrel-Dellagi D., Abderrahman A., Haltiti R., Koubaji H., Gicquel B., Dellagi K. Large-scale DNA fingerprinting of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains as a tool for epidemiological studies of tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Sep;31(9):2446–2450. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.9.2446-2450.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daley C. L., Small P. M., Schecter G. F., Schoolnik G. K., McAdam R. A., Jacobs W. R., Jr, Hopewell P. C. An outbreak of tuberculosis with accelerated progression among persons infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. An analysis using restriction-fragment-length polymorphisms. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jan 23;326(4):231–235. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199201233260404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das S., Chan S. L., Allen B. W., Mitchison D. A., Lowrie D. B. Application of DNA fingerprinting with IS986 to sequential mycobacterial isolates obtained from pulmonary tuberculosis patients in Hong Kong before, during and after short-course chemotherapy. Tuber Lung Dis. 1993 Feb;74(1):47–51. doi: 10.1016/0962-8479(93)90068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenach K. D., Cave M. D., Bates J. H., Crawford J. T. Polymerase chain reaction amplification of a repetitive DNA sequence specific for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):977–981. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey-Faussett P., Stoker N. G. Aspects of tuberculosis in Africa. 3. Genetic 'fingerprinting' for clues to the pathogenesis of tuberculosis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Sep-Oct;86(5):472–475. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(92)90072-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas W. H., Butler W. R., Woodley C. L., Crawford J. T. Mixed-linker polymerase chain reaction: a new method for rapid fingerprinting of isolates of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 May;31(5):1293–1298. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.5.1293-1298.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffner S. E., Svenson S. B., Norberg R., Dias F., Ghebremichael S., Källenius G. Biochemical heterogeneity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex isolates in Guinea-Bissau. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Aug;31(8):2215–2217. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.8.2215-2217.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jereb J. A., Burwen D. R., Dooley S. W., Haas W. H., Crawford J. T., Geiter L. J., Edmond M. B., Dowling J. N., Shapiro R., Pasculle A. W. Nosocomial outbreak of tuberculosis in a renal transplant unit: application of a new technique for restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates. J Infect Dis. 1993 Nov;168(5):1219–1224. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.5.1219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan C. M., Elarth A. M., Barr H., Saeed A. M., Risser D. R. An outbreak of tuberculosis in a shelter for homeless men. A description of its evolution and control. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Feb;143(2):257–261. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/143.2.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palittapongarnpim P., Chomyc S., Fanning A., Kunimoto D. DNA fingerprinting of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates by ligation-mediated polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 11;21(3):761–762. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palittapongarnpim P., Chomyc S., Fanning A., Kunimoto D. DNA fragment length polymorphism analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates by arbitrarily primed polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 1993 Apr;167(4):975–978. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.4.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plikaytis B. B., Crawford J. T., Woodley C. L., Butler W. R., Eisenach K. D., Cave M. D., Shinnick T. M. Rapid, amplification-based fingerprinting of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1993 Jul;139(7):1537–1542. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-7-1537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross B. C., Dwyer B. Rapid, simple method for typing isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by using the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Feb;31(2):329–334. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.2.329-334.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross B. C., Raios K., Jackson K., Sievers A., Dwyer B. Differentiation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains by use of a nonradioactive Southern blot hybridization method. J Infect Dis. 1991 Apr;163(4):904–907. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.4.904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small P. M., McClenny N. B., Singh S. P., Schoolnik G. K., Tompkins L. S., Mickelsen P. A. Molecular strain typing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to confirm cross-contamination in the mycobacteriology laboratory and modification of procedures to minimize occurrence of false-positive cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jul;31(7):1677–1682. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.7.1677-1682.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry D., Cave M. D., Eisenach K. D., Crawford J. T., Bates J. H., Gicquel B., Guesdon J. L. IS6110, an IS-like element of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):188–188. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiid I. J., Werely C., Beyers N., Donald P., van Helden P. D. Oligonucleotide (GTG)5 as a marker for Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain identification. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 May;32(5):1318–1321. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.5.1318-1321.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen K. Y., Chan K. S., Chan C. M., Ho B. S., Dai L. K., Chau P. Y., Ng M. H. Use of PCR in routine diagnosis of treated and untreated pulmonary tuberculosis. J Clin Pathol. 1993 Apr;46(4):318–322. doi: 10.1136/jcp.46.4.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Soolingen D., Hermans P. W., de Haas P. E., Soll D. R., van Embden J. D. Occurrence and stability of insertion sequences in Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains: evaluation of an insertion sequence-dependent DNA polymorphism as a tool in the epidemiology of tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2578–2586. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2578-2586.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Soolingen D., de Haas P. E., Hermans P. W., Groenen P. M., van Embden J. D. Comparison of various repetitive DNA elements as genetic markers for strain differentiation and epidemiology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Aug;31(8):1987–1995. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.8.1987-1995.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]