Abstract
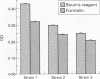
Methodological modifications, particularly the use of different fixatives, may account for discrepancies between studies of the relation between virulence and biofilm production in vitro by isolates of coagulase negative staphylococci. The efficacy of formalin and Bouin's reagent for fixing coagulase negative staphylococcal biofilms in a microtitre tray assay was compared. The optical density of stained adherent growth by three strains was reduced by an average of 20% following fixation with 10% formaldehyde compared with Bouin's reagent. This difference seemed to be mainly because of increased background staining and blackening of the biofilm when Bouin's reagent was used. Formalin fixation was also effective at identifying early and late biofilm production in adherence growth kinetic experiments with 10 coagulase negative staphylococcal clinical isolates.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander W., Rimland D. Lack of correlation of slime production with pathogenicity in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis peritonitis caused by coagulase negative staphylococci. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1987 Dec;8(4):215–220. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(87)90052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddour L. M., Smalley D. L., Kraus A. P., Jr, Lamoreaux W. J., Christensen G. D. Comparison of microbiologic characteristics of pathogenic and saprophytic coagulase-negative staphylococci from patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1986 Sep;5(3):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(86)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldassarri L., Simpson W. A., Donelli G., Christensen G. D. Variable fixation of staphylococcal slime by different histochemical fixatives. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1993 Nov;12(11):866–868. doi: 10.1007/BF02000411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Younger J. J., Baddour L. M., Barrett F. F., Melton D. M., Beachey E. H. Adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to plastic tissue culture plates: a quantitative model for the adherence of staphylococci to medical devices. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):996–1006. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.996-1006.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deighton M. A., Balkau B. Adherence measured by microtiter assay as a virulence marker for Staphylococcus epidermidis infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Nov;28(11):2442–2447. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.11.2442-2447.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch R. G., Edwards R., Filik R., Wilcox M. H. Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) peritonitis: the effect of antibiotic on the adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to silicone rubber catheter material. Perit Dial Int. 1989;9(2):103–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain M., Wilcox M. H., White P. J. The slime of coagulase-negative staphylococci: biochemistry and relation to adherence. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1993 Apr;10(3-4):191–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb05867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox M. H., Finch R. G., Smith D. G., Williams P., Denyer S. P. Effects of carbon dioxide and sub-lethal levels of antibiotics on adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to polystyrene and silicone rubber. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 May;27(5):577–587. doi: 10.1093/jac/27.5.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox M. H., Schumacher-Perdreau F. Lack of evidence for increased adherent growth in broth or human serum of clinically significant coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Hosp Infect. 1994 Apr;26(4):239–250. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(94)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Younger J. J., Christensen G. D., Bartley D. L., Simmons J. C., Barrett F. F. Coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from cerebrospinal fluid shunts: importance of slime production, species identification, and shunt removal to clinical outcome. J Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;156(4):548–554. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.4.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]