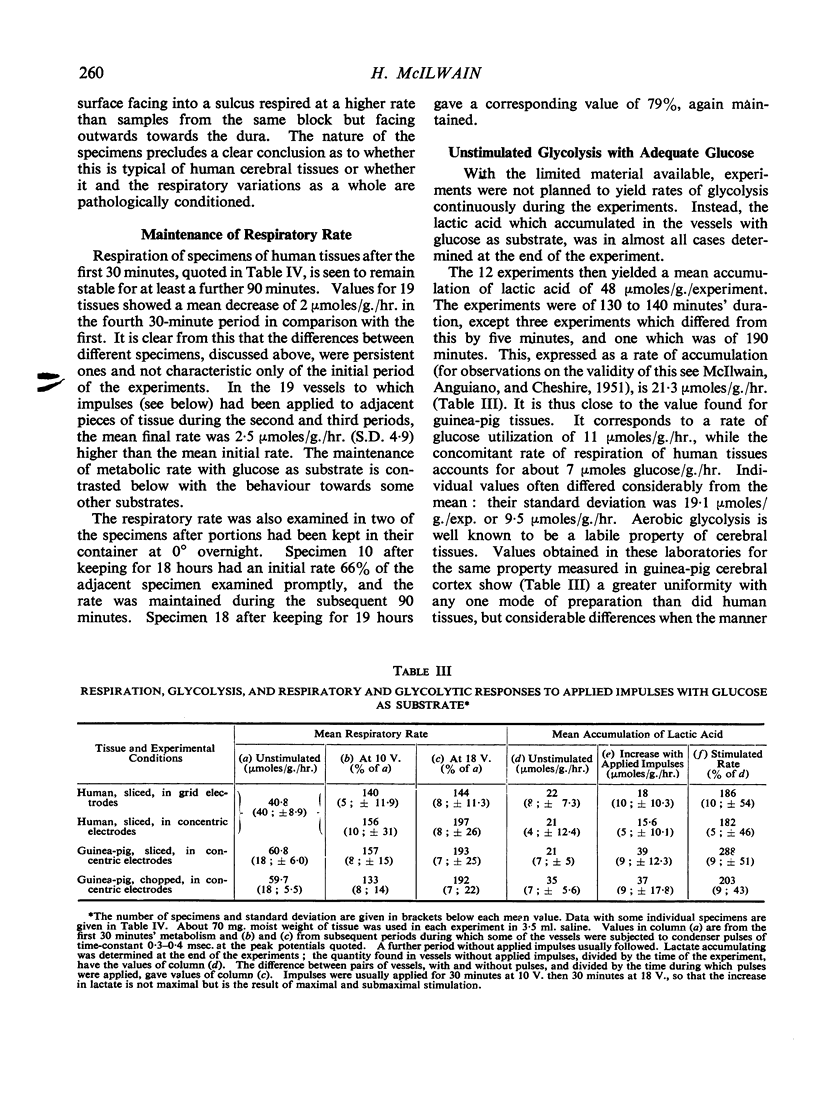
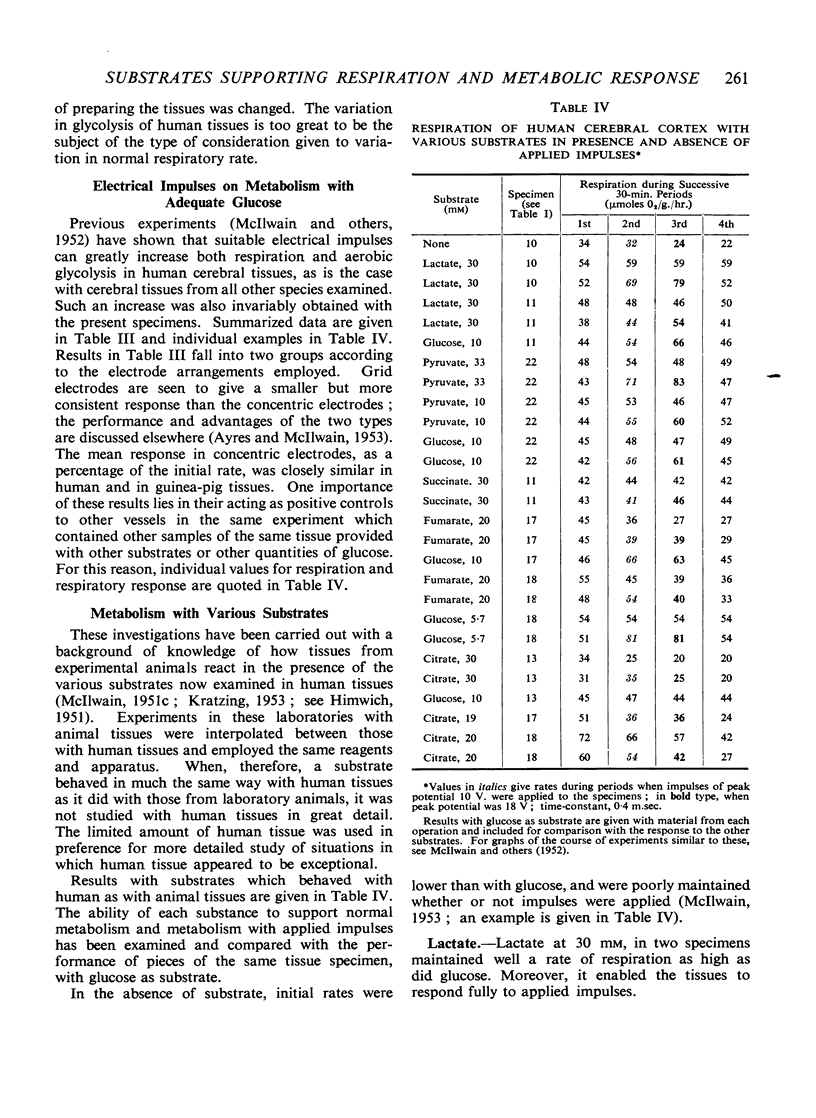
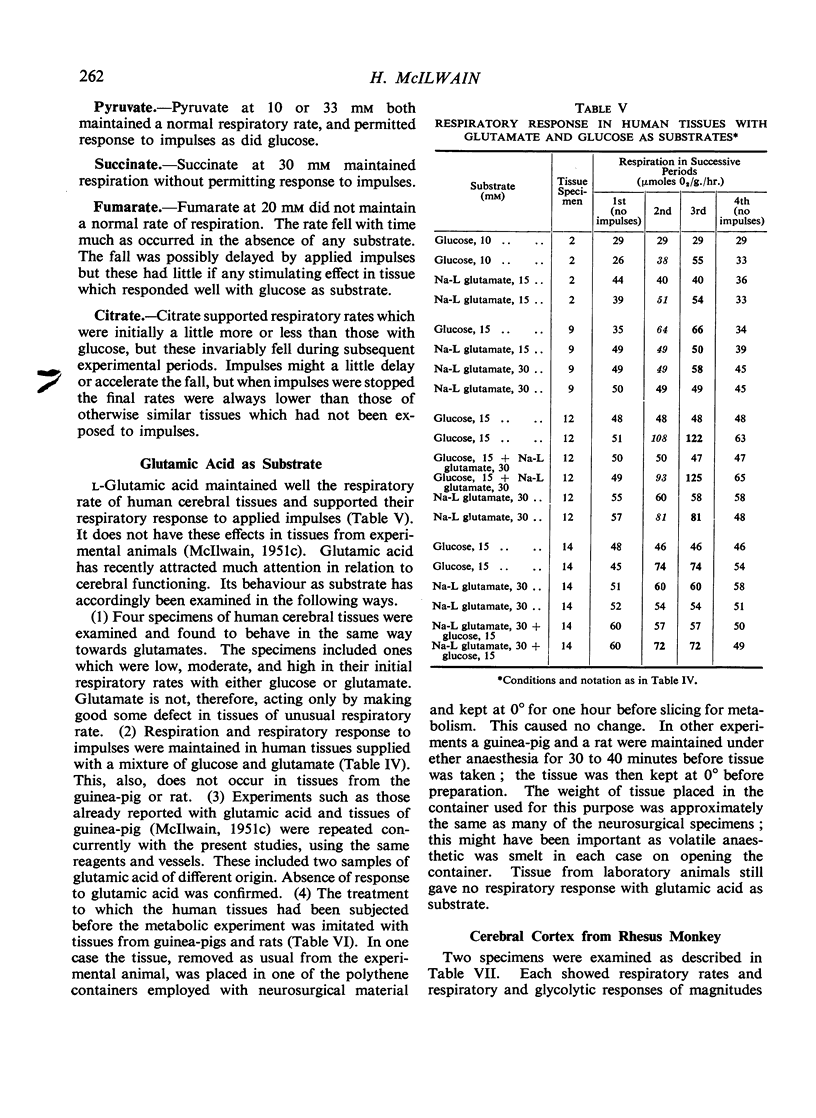
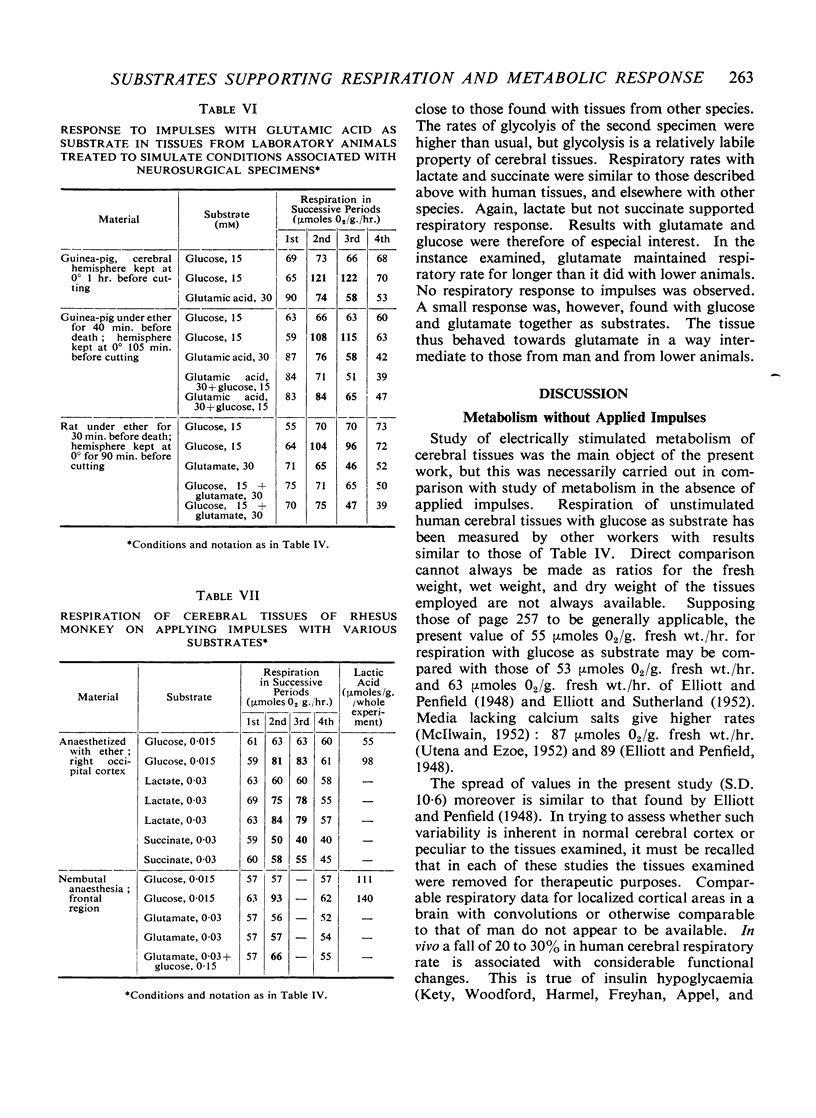
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dixon T. F., Meyer A. Respiration of brain. Biochem J. 1936 Sep;30(9):1577–1582. doi: 10.1042/bj0301577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIOTT H. W., SUTHERLAND V. C. The oxygen uptake of human cerebral cortex slices and the effects of some inhibitors. J Cell Physiol. 1952 Oct;40(2):221–241. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030400205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEYMAN A., PATTERSON J. L., Jr, JONES R. W., Jr Cerebral circulation and metabolism in uremia. Circulation. 1951 Apr;3(4):558–563. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.3.4.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRATZING C. C. The ability of some carboxylic acids to maintain phosphate levels and support electrical stimulation in cerebral tissues. Biochem J. 1953 May;54(2):312–317. doi: 10.1042/bj0540312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS H. A. Body size and tissue respiration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1950 Jan;4(1-3):249–269. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(50)90032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kety S. S., Polis B. D., Nadler C. S., Schmidt C. F. THE BLOOD FLOW AND OXYGEN CONSUMPTION OF THE HUMAN BRAIN IN DIABETIC ACIDOSIS AND COMA. J Clin Invest. 1948 Jul;27(4):500–510. doi: 10.1172/JCI101997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCILWAIN H., GORE M. B. Induced loss in cerebral tissues of respiratory response to electrical impulses, and its partial restoration by additional substrates. Biochem J. 1953 May;54(2):305–312. doi: 10.1042/bj0540305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer-Gross W., Walker J. W. The effect of l-glutamic acid and other amino-acids in hypoglycaemia. Biochem J. 1949;44(1):92–97. doi: 10.1042/bj0440092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McILWAIN H., AYRES P. J. W., FORDA O. Metabolic response to electrical stimulation in separated portions of human cerebral tissues. J Ment Sci. 1952 Apr;98(411):265–272. doi: 10.1192/bjp.98.411.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McILWAIN H. Glutamic acid and glucose as substrates for mammalian brain. J Ment Sci. 1951 Oct;97(409):674–680. doi: 10.1192/bjp.97.409.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McILWAIN H. Metabolic response in vitro to electrical stimulation of sections of mammalian brain. Biochem J. 1951 Aug;49(3):382–393. doi: 10.1042/bj0490382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POND D. A., POND M. H. Glutamic acid and its salts in petit mal epilepsy. J Ment Sci. 1951 Oct;97(409):663–673. doi: 10.1192/bjp.97.409.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWERIN P., BESSMAN S. P., WAELSCH H. The uptake of glutamic acid and glutamine by brain and other tissues of the rat and mouse. J Biol Chem. 1950 May;184(1):37–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellar E., McElroy W. D. Does Glutamic Acid Have Any Effect on Learning? Science. 1948 Sep 10;108(2802):281–283. doi: 10.1126/science.108.2802.281-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone W. E. The effects of anaesthetics and of convulsants on the lactic acid content of the brain. Biochem J. 1938 Nov;32(11):1908–1918. doi: 10.1042/bj0321908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIGERMAN H., MacVICAR R. Glutamine, glutamic acid, ammonia administration, and tissue glutamine. J Biol Chem. 1951 Apr;189(2):793–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WECHSLER R. L., DRIPPS R. D., KETY S. S. Blood flow and oxygen consumption of the human brain during anesthesia produced by thiopental. Anesthesiology. 1951 May;12(3):308–314. doi: 10.1097/00000542-195105000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIL-MALHERBE H. Significance of glutamic acid for the metabolism of nervous tissue. Physiol Rev. 1950 Oct;30(4):549–568. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1950.30.4.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


