Abstract
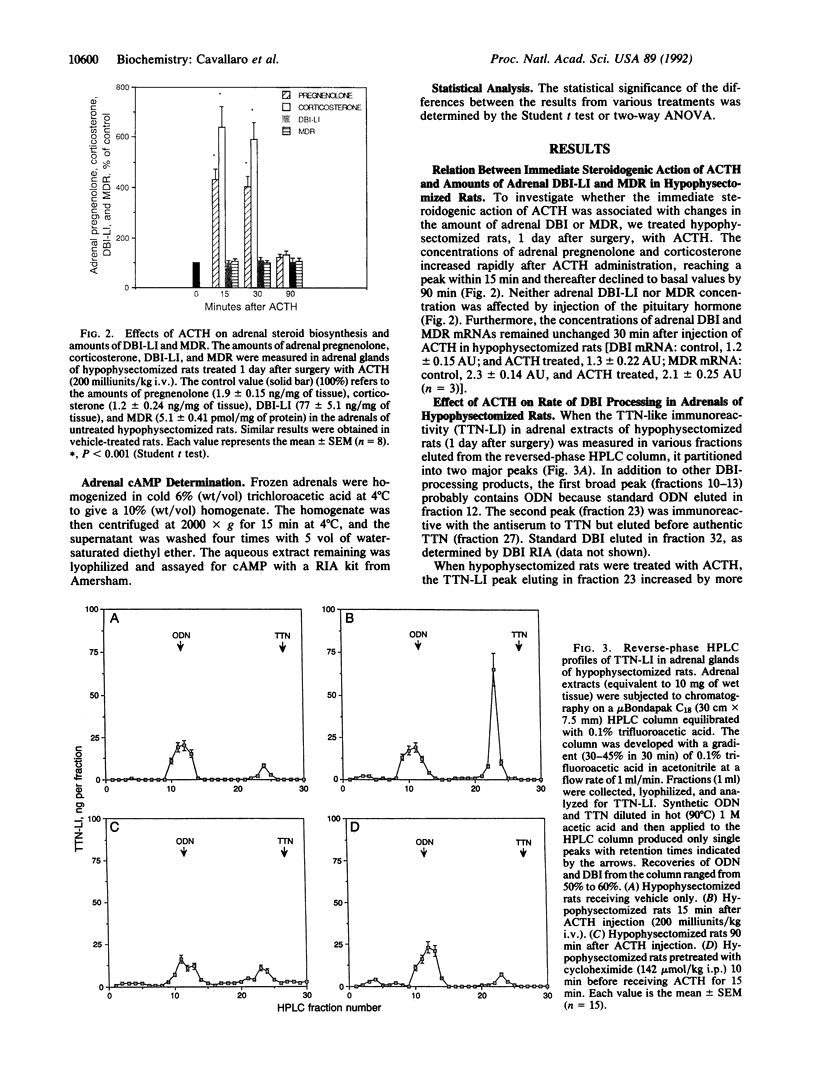
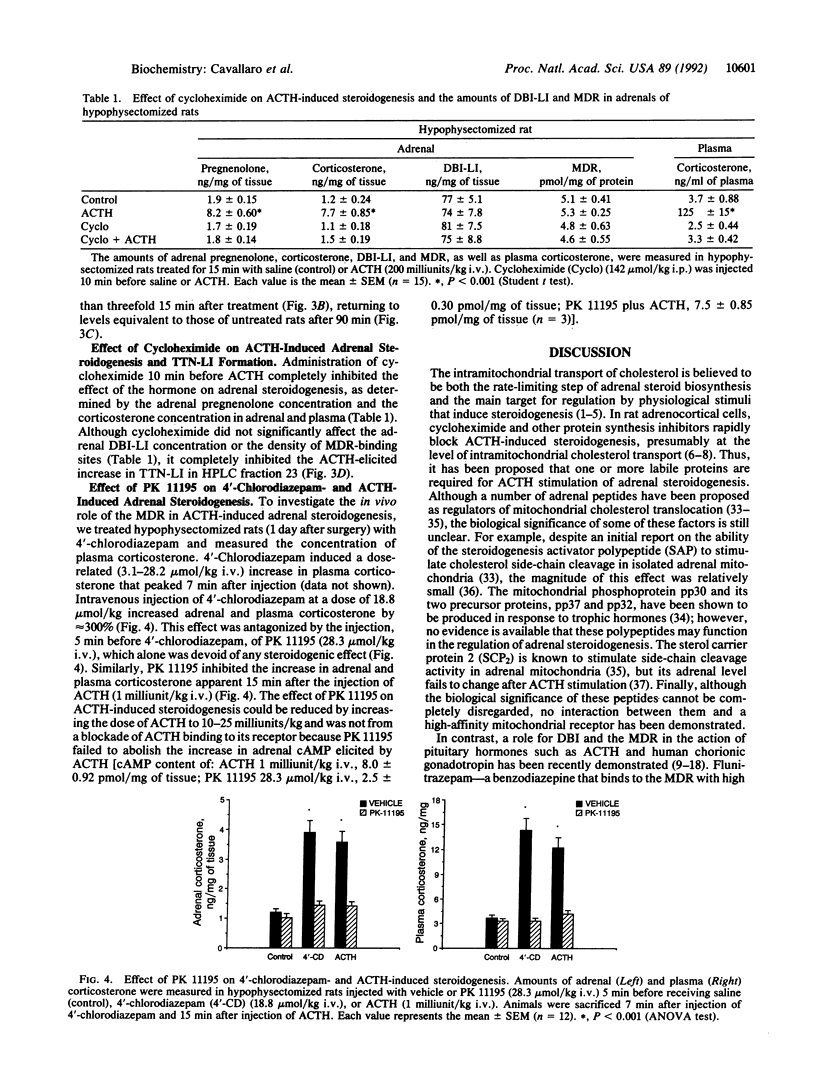
Diazepam-binding inhibitor (DBI) is a 9-kDa polypeptide that colocalizes in glial, adrenocortical, and Leydig cells with the mitochondrial DBI receptor (MDR). By binding with high affinity to the MDR, DBI and one of its processing products--DBI-(17-50)--regulate pregnenolone synthesis and have been suggested to participate in the immediate activation of adrenal steroidogenesis by adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). In adrenals of hypophysectomized rats (1 day after surgery), ACTH failed to acutely affect the amount of adrenal DBI and the density of MDR but increased the rate of DBI processing, as determined by the HPLC profile of DBI-(17-50)-like immunoreactivity. The similar latency times for this effect and for ACTH stimulation of adrenal steroidogenesis suggest that the two processes are related. The ACTH-induced increase in both adrenal steroidogenesis and rate of DBI processing were completely inhibited by cycloheximide; this result suggests the requirement for the de novo synthesis of a protein with a short half-life, probably an endopeptidase. This enzyme, under the influence of ACTH, may activate formation of a DBI-processing product that stimulates steroidogenesis via the MDR. In support of this hypothesis is the demonstration that in hypophysectomized rats the MDR antagonist PK 11195 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-N-methyl-N-(1-methylpropyl)-3-isoquinolinecarboxam ide completely inhibited the adrenal steroidogenesis stimulated by ACTH and by the high-affinity MDR ligand 4'-chlorodiazepam.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alho H., Costa E., Ferrero P., Fujimoto M., Cosenza-Murphy D., Guidotti A. Diazepam-binding inhibitor: a neuropeptide located in selected neuronal populations of rat brain. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):179–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3892688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anholt R. R., De Souza E. B., Kuhar M. J., Snyder S. H. Depletion of peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors after hypophysectomy in rat adrenal gland and testis. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Mar 26;110(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkovich A., McPhie P., Campagnone M., Guidotti A., Hensley P. A natural processing product of rat diazepam binding inhibitor, triakontatetraneuropeptide (diazepam binding inhibitor 17-50) contains an alpha-helix, which allows discrimination between benzodiazepine binding site subtypes. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;37(2):164–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besman M. J., Yanagibashi K., Lee T. D., Kawamura M., Hall P. F., Shively J. E. Identification of des-(Gly-Ile)-endozepine as an effector of corticotropin-dependent adrenal steroidogenesis: stimulation of cholesterol delivery is mediated by the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4897–4901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. S., Hall P. F., Shoyab M., Papadopoulos V. Endozepine/diazepam binding inhibitor in adrenocortical and Leydig cell lines: absence of hormonal regulation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1992 Jan;83(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(92)90189-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneely O. M., Headon D. R., Olson C. D., Ungar F., Dempsey M. E. Intramitochondrial movement of adrenal sterol carrier protein with cholesterol in response to corticotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):2970–2974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.2970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa E., Guidotti A. Diazepam binding inhibitor (DBI): a peptide with multiple biological actions. Life Sci. 1991;49(5):325–344. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90440-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crivello J. F., Jefcoate C. R. Intracellular movement of cholesterol in rat adrenal cells. Kinetics and effects of inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8144–8151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. F., Orme-Johnson N. R. Regulation of steroid hormone biosynthesis. Identification of precursors of a phosphoprotein targeted to the mitochondrion in stimulated rat adrenal cortex cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19739–19745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrarese C., Vaccarino F., Alho H., Mellstrom B., Costa E., Guidotti A. Subcellular location and neuronal release of diazepam binding inhibitor. J Neurochem. 1987 Apr;48(4):1093–1102. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb05632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garren L. D., Ney R. L., Davis W. W. Studies on the role of protein synthesis in the regulation of corticosterone production by adrenocorticotropic hormone in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jun;53(6):1443–1450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.6.1443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarneri P., Papadopoulos V., Pan B., Costa E. Regulation of pregnenolone synthesis in C6-2B glioma cells by 4'-chlorodiazepam. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5118–5122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. F., Charpponnier C., Nakamura M., Gabbiani G. The role of microfilaments in the response of adrenal tumor cells to adrenocorticotropic hormone. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9080–9084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefcoate C. R., DiBartolomeis M. J., Williams C. A., McNamara B. C. ACTH regulation of cholesterol movement in isolated adrenal cells. J Steroid Biochem. 1987;27(4-6):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(87)90142-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger K. E., Papadopoulos V. Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors mediate translocation of cholesterol from outer to inner mitochondrial membranes in adrenocortical cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15015–15022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massotti M., Slobodyansky E., Konkel D., Costa E., Guidotti A. Regulation of diazepam binding inhibitor in rat adrenal gland by adrenocorticotropin. Endocrinology. 1991 Aug;129(2):591–596. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-2-591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner R. J., Sutcliffe J. G. Gene expression in rat brain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5497–5520. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizoule J., Gauthier A., Uzan A., Renault C., Dubroeucq M. C., Guérémy C., Le Fur G. Opposite effects of two ligands for peripheral type benzodiazepine binding sites, PK 11195 and RO5-4864, in a conflict situation in the rat. Life Sci. 1985 Mar 18;36(11):1059–1068. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90491-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocchetti I., Einstein R., Brosius J. Putative diazepam binding inhibitor peptide: cDNA clones from rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7221–7225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhin A. G., Papadopoulos V., Costa E., Krueger K. E. Mitochondrial benzodiazepine receptors regulate steroid biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9813–9816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Zakut R., Shani M., Neuman S., Levy Z., Yaffe D. The nucleotide sequence of the rat cytoplasmic beta-actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1759–1771. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos V., Berkovich A., Krueger K. E., Costa E., Guidotti A. Diazepam binding inhibitor and its processing products stimulate mitochondrial steroid biosynthesis via an interaction with mitochondrial benzodiazepine receptors. Endocrinology. 1991 Sep;129(3):1481–1488. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-3-1481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos V., Berkovich A., Krueger K. E. The role of diazepam binding inhibitor and its processing products at mitochondrial benzodiazepine receptors: regulation of steroid biosynthesis. Neuropharmacology. 1991 Dec;30(12B):1417–1423. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(11)80011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos V., Guarneri P., Kreuger K. E., Guidotti A., Costa E. Pregnenolone biosynthesis in C6-2B glioma cell mitochondria: regulation by a mitochondrial diazepam binding inhibitor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5113–5117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos V., Nowzari F. B., Krueger K. E. Hormone-stimulated steroidogenesis is coupled to mitochondrial benzodiazepine receptors. Tropic hormone action on steroid biosynthesis is inhibited by flunitrazepam. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3682–3687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen R. C., Brownie A. C. Cholesterol side-chain cleavage in the rat adrenal cortex: isolation of a cycloheximide-sensitive activator peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1882–1886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalle C. T., Crivello J. F., Jefcoate C. R. Regulation of intramitochondrial cholesterol transfer to side-chain cleavage cytochrome P-450 in rat adrenal gland. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):702–706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson E. R., McCarthy J. L., Peterson J. A. Evidence that the cycloheximide-sensitive site of adrenocorticotropic hormone action is in the mitochondrion. Changes in pregnenolone formation, cholesterol content, and the electron paramagnetic resonance spectra of cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3135–3139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. Regulation by ACTH of steroid hormone biosynthesis in the adrenal cortex. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;61(7):692–707. doi: 10.1139/o83-088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. Regulation of the synthesis of steroidogenic enzymes in adrenal cortical cells by ACTH. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:427–440. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.002235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slobodyansky E., Guidotti A., Wambebe C., Berkovich A., Costa E. Isolation and characterization of a rat brain triakontatetraneuropeptide, a posttranslational product of diazepam binding inhibitor: specific action at the Ro 5-4864 recognition site. J Neurochem. 1989 Oct;53(4):1276–1284. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slobodyansky E., Kurriger G., Kultas-Ilinsky K. Diazepam binding inhibitor processing in the rhesus monkey brain: an immunocytochemical study. J Chem Neuroanat. 1992 Mar-Apr;5(2):169–180. doi: 10.1016/0891-0618(92)90042-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengel R., Werner P., Seeburg P. H., Mukhin A. G., Santi M. R., Grayson D. R., Guidotti A., Krueger K. E. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNA encoding a peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20415–20421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vahouny G. V., Chanderbhan R., Noland B. J., Irwin D., Dennis P., Lambeth J. D., Scallen T. J. Sterol carrier protein2. Identification of adrenal sterol carrier protein2 and site of action for mitochondrial cholesterol utilization. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11731–11737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu T. S., Bowman E. P., Glass D. B., Lambeth J. D. Stimulation of adrenal mitochondrial cholesterol side-chain cleavage by GTP, steroidogenesis activator polypeptide (SAP), and sterol carrier protein2. GTP and SAP act synergistically. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6801–6807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagibashi K., Ohno Y., Nakamichi N., Matsui T., Hayashida K., Takamura M., Yamada K., Tou S., Kawamura M. Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors are involved in the regulation of cholesterol side chain cleavage in adrenocortical mitochondria. J Biochem. 1989 Dec;106(6):1026–1029. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



