Abstract
Due to the synergic relationship between medical chemistry, bioinformatics and molecular simulation, the development of new accurate computational tools for small molecules drug design has been rising over the last years. The main result is the increased number of publications where computational techniques such as molecular docking, de novo design as well as virtual screening have been used to estimate the binding mode, site and energy of novel small molecules. In this work I review some tools, which enable the study of biological systems at the atomistic level, providing relevant information and thereby, enhancing the process of rational drug design.
Keywords: Bioinformatics, de novo design, medical chemistry, molecular docking, molecular modeling, rational drug design, virtual screening
INTRODUCTION
Synergic relationship between experimental biochemistry sciences and computational theoretical methods has increased in recent years, providing significant benefits in different biological sciences areas, specially biochemistry and molecular biology. It has also brought advantages in medicinal chemistry for the rational design of drugs [1]. Regarding theoretical study of biochemical systems, one of its greatest profits is the molecular knowledge of the currently studied structures; these studies allow an exhaustive system analysis, and find meaningful answers to research questions that scientists face in their experimental laboratories.
Before exploring some of the computational methodologies currently used in drug design, it is important to consider that researchers have to draw from relevant information such as the three-dimensional structure of one or several substrates and molecular targets in order to start the theoretical study of certain biological systems. This information is essential, and in many cases, it determines the success or failure of the ongoing theoretical study. For instance, if a researcher wants to study the system formed by an endogenous or an exogenous inhibitor with its respective molecular target, the three-dimensional structure of the molecules involved in the interaction to be simulated has to be known.
The number of molecular targets with a well known structure is exponentially increasing due to the dramatic progress of spectroscopic techniques such as X-ray crystallography, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) [2], and the development of the super-resolved fluorescence microscopy that shows a 3D image of a single molecule [3]. In addition, structures which have been produced from structural genomics have also become valuable tools for the study of systems whose molecular targets have not been solved yet [4, 5]. This growth has allowed a massive and constant use of computational tools in research centers worldwide. Furthermore, the developed methodologies for the production and optimization of small molecules (as most of the substrates studied in biochemistry sciences), are already registered in special databases and have provided vital information to research and find inherent characteristics which have never been described before [6, 7].
Nowadays, there are multiple computational methodologies used as bioinformatics tools for the study of biological systems and drug discovery. The use of one or another tool is linked to the researcher interests, the calculation level intended, possible technical limitations, how and also which kind of information can be extracted from data processing and analysis. Some of the main methodologies for these studies are: Molecular Docking, de novo design, Virtual Screening (VS), Quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSAR), Molecular Dynamics simulation (MDs) and Molecular Modeling (MM) [8]. These methodologies are wieldy used for rational drug design and discovery processes, where the ligand receptor binding mode is imperative to understand the molecular interaction mechanism and the structural factors related with the bioactivity of each inhibitor in detail [9].
In this review, basic and significant elements of molecular docking, de novo design and virtual screening are shown. These are some of the greatest computational methodologies used for the analyses of biochemical sciences, which also improve the common techniques used to study proteins structures, the design of new molecules biologically relevant for pharmacological application, the structure activity relationship, among others.
Molecular Docking
Molecular Docking dates from the middle of the 19th century. Chemists Archibald Scott Couper, Friedrich August Kekulé and Aleksandr Mikhailovich introduced the valence in organic chemistry, and submitted the first structures with graphical representations of carbon atoms [10]. In 1861 Johann Josef Loschmidt produced the largest molecules collection at that time (368), including the first accurate benzene structure [11]. Due to the technological development in computational sciences, the concept of ‘force field’ was introduced from the vibrational spectroscopy, which consider the forces acting all over the atoms in a molecule. The scientific community did not adopt the concept of ‘force field’ until 1946, when the first premise about the combination of steric interactions and the Newtonian mechanics model of vibrational modes, bonds, and angles emerged.
Many other scientific advances were developed at that time, but it was in 1953 when Metropolis et al. published the study: "Equation of State Calculations by Fast Computing Machines" [12]. For the last century, the molecular modeling foundations were set, and due to the technological advances of our time, it now allows us to perform better theoretical studies and computational calculations and validates the need of using computational methods for science progress.
Molecular docking main goal is to predict as accurately as possible the best conformations (poses) of a ligand - by using a score function - in a conformational area, which is delimited by the molecular target binding site [13]. This is applied in different stages of the drug design process in order to predict the binding mode of the ligands already known [14]; it is also used to identify novel and potent ligands [15] and as a binding affinity predictive tool [16]. The first molecular docking algorithms considered translation and orientation only (degrees of freedom), and used the ligand and protein as rigid bodies. Improvements in computer science allowed the creation of new and accurate algorithms in order to use the ligand as flexible with a rigid (or nearly rigid) receptor [17].
This methodology is described as a multi-step process, where each step has one or several complexity levels. The process starts with the implementation of the molecular docking algorithms responsible for placing the ligands in the binding sites. This process is challenging, since it depends directly on the freedom levels granted to the ligands. The freedom levels sampling must be done accurately in order to identify the best conformation for the receptor-binding site. In addition, it has to be done fast enough to assess several compounds in a relatively short period of time [14].
These algorithms are complemented with scoring functions to sort different poses with the receptor regarding the union force. The scoring functions have some disadvantages because they do not take into account all the interfering forces between the ligand and the receptor; in addition, they also fail in accounting the ligand solvation, the entropic changes when bonding the receptor, the receptor flexibility and the receptor’s conformational changes induced by the same ligand interaction. Based on this, molecular docking is a technique quite fast and effective in terms of time and computational cost [18].
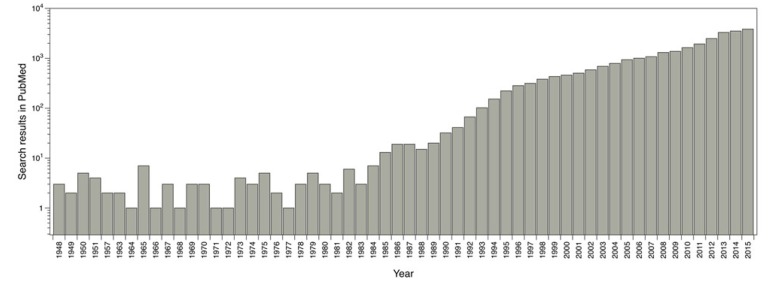
The main software and algorithms developers performing molecular docking are focused on improving aspects such as: receptor’s flexibility, solvation, coupling fragment, post-processing, molecular docking in homology models and comparisons between couplings. Main progress regarding this technique has taken place in the scoring functions area. The use of this methodology has been enhanced over the years; for instance, by doing a single search in PubMed using the word ‘docking’ as a search criterion, it shows the evolution of the publications where molecular docking has been used (Fig. 1).
Fig. (1).
Reported publications number where molecular docking was used. Results from PubMed using the word ‘docking’ as search criteria.
Many authors have demonstrated that molecular docking software can produce "accurate" binding modes, providing acceptable solutions to the sampling problem; however, the main challenge between the programs and algorithms developers is the poses scoring problem [19]. In this sense, the molecular docking tools are powerful in the prediction of correct binding poses but have critical issues to estimate accurately the corresponding binding affinities.
An effort to improve affinity prediction, a rescoring process with other simple functions or solvated-based scoring functions is typically performed. The poses generated by docking program are taken, and methods such as MM/PBSA (Molecular Mechanics/ Poisson-Boltzmann Surface Area) and MM/GBSA (Molecular Mechanics/ Generalized-Born Surface Area) [19-21] include implicit solvent and can be used in order to correct scoring function values and improve docking accuracy. Other strategy is the use of molecular dynamics simulation (MDs) to get conformational sampling of the complex obtained using docking, performing then a subsequent calculation of the binding energy by averaging the score values for different poses extracted from the trajectory [22-24]. Under this approach, the receptor flexibility and the presence of explicit water molecules contribute to a more realistic description of the system, which could have an influence in binding energy calculations. However, the biggest challenge of molecular docking (and also the principal problem) is the accurate prediction of the binding energies, which has major implications for the prediction of novel effective drugs. This process is performed by using scoring functions that score the predicted poses [25].
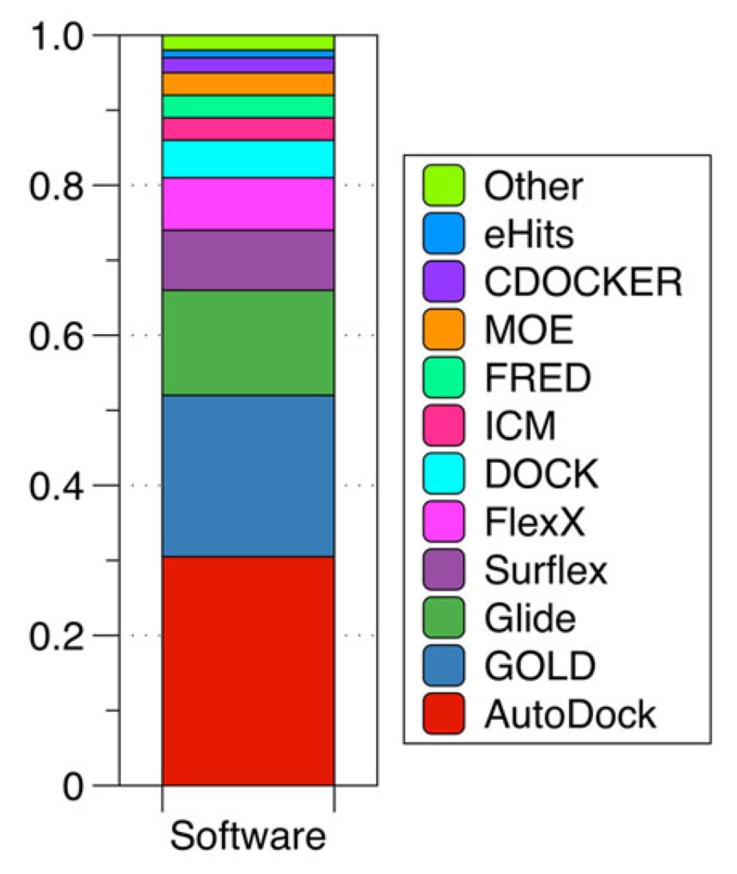
Several classes of scoring functions have been developed [25]. These consider the protein as a rigid body [26, 27], or as a soft body [28-30]. They also may consider flexible side chains [31] or certain flexible domains in the target [32-34]. Other empirical scoring functions have shown be useful in the virtual screening and filtering of databases of drug-like compounds at the early stage of drug development processes [34]. Frequently, scoring functions try to reproduce experimental binding affinities, but the ones with popular docking programs do not always yield the best predictions. New programs have arisen in recent years advertising the importance of Molecular Docking in the study of biochemistry sciences and drug design, the most widely used are AutoDock [33, 34] with 29.5% followed by GOLD [37] with 17.5% and Glide [27, 36] with 13.2% (Fig. 2).
Fig. (2).
Use of molecular docking programms between 2010 and 2011. Based on a PubMed search. (Taken and adapted from [18] ).
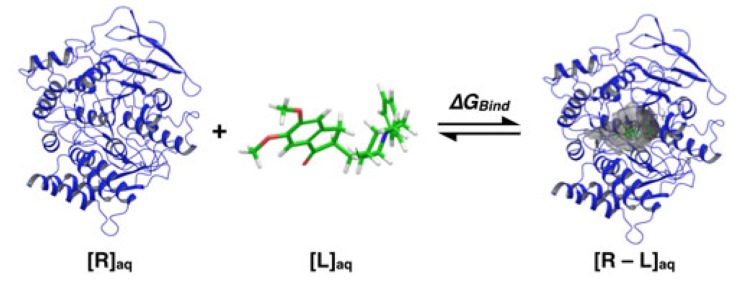
Generally speaking, theoretical molecular docking aspects are within the thermodynamics principles, where the main goal is to accurately predict the complex Receptor-Ligand structure [R - L] in equilibrium conditions (Equation 1). As an example in Fig. (3) it was set the Receptor [R] (acetylcholinesterase), the ligand [L] (donepezil), and the complex [R - L] for this particular system.
Fig. (3).
Ligand donepezil binding to acetylcholinesterase (based on the crystalline structure PDB: 1EVE [39] ).
| (1) |
Fig. (3) illustrates the ligand Donepezil [39] union (drug used in pharmacological therapy against Alzheimer's disease [40]) to the receptor Acetylcholinesterase described through the Gibbs free energy of binding (∆GBind); this energy is related to the binding affinity by the ratio of Equation 2:
| (2) |
KA is the affinity constant and Ki is the inhibition constant. The prediction for the accurate structure of the [R - L] complex does not require the experimental information of the constants; however, the prediction of the ligand biological activity does. The terms influencing the scoring function can be classified as follows: Consideration of the [R - L] complex, where aspects such as the ligand and receptor deformation, hydrogen bonds, and electrostatic and steric factors are important. When the equilibrium is considered (Equation 1), the most important factors are: desolvation, rotational and translational entropy.
Molecular docking has been widely used in rational drug design in the past decades with extensive applications in several issues such as:
The theoretical study of antitubulin agents with anti-cancer activity [41].
The study of the estrogen receptor binding domains [42].
Shityakov et al. have studied the blood-barrier permeation by In silico predictive models [43, 44], the dimer complexes of dopamine and levodopa derivatives to assess drug delivery to the central nervous system [45], and the interaction of nanoparticles with multidrug resistance protein [46].
The prediction of anti-cancer drugs for the treatment of hypopharyngeal cancer [47].
Sabogal et al. established a protocol to identify an interaction pattern between the sea anemone neurotoxins and the potassium channel Kv1.3 [48].
Yi et al. studied the metabolic behavior of anisole by using Molecular Docking [49].
Academically, the amount of research groups who use this technique to study biological systems have increased. In biology, computational techniques have taken great strength, especially in the structural biochemistry field. To prove it, a large number of articles such as the Structural Biochemistry Group at the University of Edinburgh for instance (website: http://www.bch.ed.ac.uk/index.php) have been published. In addition, at multidisciplinary centers of study such as the Department of Molecular and structural Biochemistry of the North Carolina State University - USA (website: http://biochem.ncsu.edu), study programs like biochemistry, molecular biology and biophysics in undergraduate, masters and doctorate levels have been created. This allows students to familiarize with the technique, including it in their academic activities. For these reasons, molecular docking is not only used in the pharmaceutical industry for drug discovery, but also for anyone interested in the study of biological systems and receptor-ligand interactions.
de novo Design
Another computer-based drug design method known as ‘de novo design’ have been implemented to find new potent and selective ligands. de novo design serves as a tool for the discovery of new ligands for biological targets as well as optimization of new ligands [50]. These tools produce (from scratch) novel molecular structures with desired pharmacological properties [51]; subsequently the new structures are docked to find the binding affinities and interacting modes. This new tools and algorithms identify potent ligand-protein interaction characteristics in the binding site, and construct novel molecular structures by assembling atoms and molecular fragments either combined or sequentially. de novo design is a powerful tool, and some authors have reported most potent ligands designed by this tool that their precursors [52], revealing the importance of this tool in the drug design process. Some of these new tools are shown in Table. 1.
Table 1.
de novo design tools (taken and adapted from [53]).
| Tool | Concept | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Builder | Combinatory search by recombination of docked molecules | [54] |
| Caveat | Database search for fragment fitting | [55] |
| Concerts | Fragment-based, stochastic search | [56] |
| Dynamic ligand design | Atom-based, structure sampling by simulated annealing | [57] |
| GenStar | Atom-Based, molecules growth based on an enzyme contact model | [58] |
| GroupBuild | Fragment-based, combinatorial search | [59] |
| Grow | Peptide design, sequential growth | [60] |
| Growmol | Fragment-based, sequential growth, stochastic search | [61] |
| Hook | Linker search for fragments placed by MCSS | [62] |
| Legend | Atom-based, stochastic search | [63] |
| LUDI | Fragment-based, combinatorial search | [64] |
| MCDNLG | Atom-based, stochastic search | [65] |
| MCSS | Fragment-based, stochastic sampling | [66] |
| MolMaker | Graph-theoretical 3D design | [67] |
| NewLead | Fragment-based, builds on 3D pharmacophore-models | [68] |
| Pro-Ligand | Fragment-based search | [69] |
| Pro-Select | Fragment-based, scaffold-linker approach | [70] |
| Skelgen | Small-fragment based, Monte-Carlo search | [71] |
| SME | Peptide design, whole-molecule optimization | [72] |
| SMoG | Fragment-based, sequential growth, stochastic search | [73] |
| Splice | Recombination of ligands retrieved by a 3D database search | [74] |
| Sprout | Fragment-based, sequential growth, combinatorial search | [75] |
| Topas | Fragment-based, evolutionary search | [76] |
Automated de novo design is a very useful tool for hit and lead-ligand identification; design molecules, provide ideas for medical chemist and pharmaceutical industries, and to develop novel leads with desired chemical characteristics.
Virtual Screening
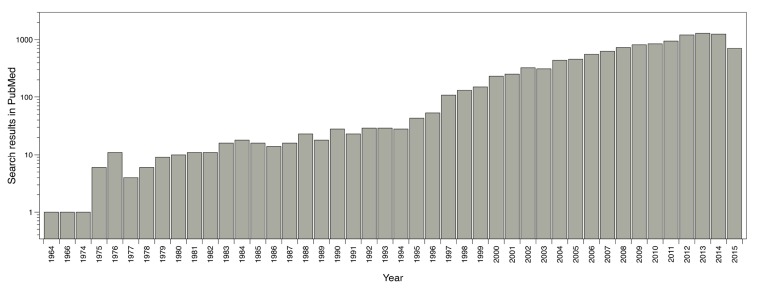
A computational technique widely used in drug design is Virtual Screening (VS). Its main objective is to search for specific information in compounds or molecules libraries with similar structural properties that can acceptably interact with a therapeutic target and is an important tool to access novel drug-like compounds [77]. Prior to the VS, massive molecular docking was used but it had a big computational cost and spent a lot of computational time; due to this, a technique - which enables the efficiency improvement to search for compounds in large molecular libraries - was needed. The use of VS (as well as molecular docking) has increased in recent years, rising from an average of 10 publications reported in the 70s - 80s, to an average of more than 1000 publications reported in previous years (Fig. 4).
Fig. (4).
Reported publications number where virtual screening was used. Results from PubMed using the words ‘virtual screening’ as search criteria.
Virtual screening can be performed through two approaches, Ligand-Based Virtual Screening (LBVS) and Structure-Based Virtual Screening (SBVS). LBVS is used when there is not knowledge about the three-dimensional structure of the therapeutic target (receptor), and yet you have a group of molecules with some biological activity against that target; in that sense, structure relationships can be determined. The molecules group with reported activity can also establish the molecular characteristics. These characteristics allow the interaction between the molecules and the molecular target. Based on those (such as acceptor and donors hydrogen bonds, metals, hydrophobic moieties, aromatic rings among others), researchers can screen databases to find other molecules to fit in the profile of the initial group – with the same molecular descriptors – which can possibly present biological activity against the studied therapeutic target [78]. In the LBSV the lead-ligands generated are ranked based on their similarity score obtained by different methods or algorithms [77].
On the other hand, Structure-Based Virtual Screening (SBVS) establishes its action mechanism in the studied molecular target structure and begins with the identification of the potential ligand-binding site on the target. Then, one of its greatest challenges is to determine the target 3D structure by NMR, X-ray crystallography or molecular modeling. Later, an automated and rapid docking of a large number of chemical compounds against the 3D structure of the molecular target is done. This technique has helped with the identification of potential therapeutic molecules for specific pathologies [77].
To use this technique in an effective way, a protocol with several stages should be established:
Ligands Database Preparation It is necessary to prepare all the molecules to be studied with the SBVS. Tautomers, isomers, protonation states, ionization states, enantiomers, etc. must be considered. This database must be prepared in accordance with the software to use.
Receptor Preparation Next, the molecular target (Receptor) must be provided. It may uses the same ligands database preparation software.
Molecular Docking It is necessary to determine the common pharmacophore in the ligand database; after this - and through the appropriate program - massive molecular docking is carried out.
Post-Processing The post-processing is performed in accordance with the user requirements through the analysis of the score function, geometric analysis, shape complementarity, solvation corrections, entropic changes, pose clustering, etc.
Compounds Selection The final step is the compounds selection for biological tests, or to be further analyzed by other computational techniques [79].
Nowadays, there are several comprehensive programs used to perform VS such as: AutoDock Vina [35], Glide [28, 38, 80], DOCK [81], FlexX [82], GOLD [37], ICM [83], among others. Additionally - and due to the high computational cost for the SBVS implementation - several research groups around the world have developed free software and algorithms to be accessed through virtual platforms. These developers also have the advantage of having extensive updated databases, which allows the virtual screening of millions of molecules. For instance, among the major online servers to perform VS there is the ZINCPharmer, sponsored by the University of Pittsburgh (website: http://zincpharmer.csb.pitt.edu) [84]. This software allows researchers to perform online SBVS for free, mainly based on the established ligand pharmacophore used as input. The screening is basically performed in the ZINC database [7], a non-commercial database with more than 22 million compounds.
In recent years, researchers who use this technique in their computational research have increased, and the establishment of data sets for potential therapeutic agents from VS can be observed, for example: SENP2 inhibitors [85], kinases proteins agonists [86], inhibitors with vasodilator activity [87], inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase [88], among others.
The development of these dataset has allowed the access and use of information more efficiently, by evaluating compounds against new molecular targets and finding many potential drug candidates (better than those before the implementation of this technique).
On the other hand, VS is used as a mechanism for the evaluation of new potential drugs against certain molecular targets in rational drug design. In biochemical terms, this enables the computational evaluation of large molecules quantities in a short time with a relatively low computational cost. It means that after a screening, score, post-processing and visual inspection, it can continue to the laboratory to perform in vitro testing with the best candidates obtained via VS allowing the properties evaluation such as the biological activity, the enzyme kinetics, among others. This contributes with the biological system study in the drug discovery process.
Several bioactive molecules identified, optimized or designed by using molecular docking, de novo design or VS methods (Table. 2) let us understand the importance of the application and use of them as computational tools for drug discovery to explore the chemical space of a binding site and present novel, potent and selective pharmacological alternatives in medical chemistry and drug discovery.
Table 2.
Some active compounds identified by computational methods.
| Compound structure | Use | Computational method | References |
|---|---|---|---|
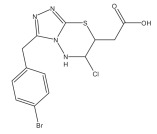 |
Antimycobacterial agents | Virtual Screening | [89] |
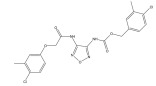 |
SENP2 inhibitors | Virtual screening, Molecular Docking | [85] |
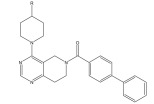 |
TASK-3 channel antagonist | Pharmacophore based virtual screening | [90] |
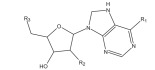 |
GAPGH inhibitor | Combinatorial docking | [91] |
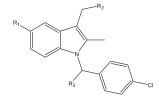 |
Aldose reductase inhibitor | LBVS | [92] |
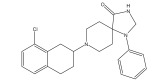 |
Ca2+ antagonist | Pharmacophore searching | [93] |
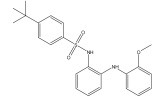 |
Kv1.5 channel blocker | Fragment based, de novo design | [76] |
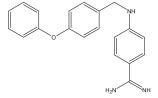 |
Thrombin inhibitor | Combinatorial docking, de novo design | [94] |
 |
Antiretroviral agent | Virtual Screening | [95] |
CONCLUSION
Although in appearance, a direct relationship between the computational methodologies - molecular docking and virtual screening - with research in biological and medical sciences does not exist, in recent years most of the authors whom develop biological systems research in areas such as biochemistry, medicinal chemistry, pharmacology, organic chemistry, theoretical chemistry, etc., use computational methods to support, improve and reinforce their research. The structural studies of these systems at theoretical level assist with the construction of a wide and accurate perspective of the issue, and enable the knowledge consolidation.
In addition, there is still a long way to develop methodologies with “thinner” approaches (accurate and precise). Although methodologies such as the molecular docking and virtual screening are effective (in terms of time and computational cost), they have also a poor predictive capability. There are other methods involving a higher calculation level for researchers who study dynamic biological systems (Molecular Dynamics), or bonds and interactions in an electronic level (Quantum Mechanics). These like the other methods are more time-consuming in terms of computational cost, but may provide better results; it all depends on the researcher interests and funding. However, to improve computational techniques such as Molecular Docking and Virtual Screening, a change in the structural paradigm is needed, and this will be achieved when the understanding of the interactions between a drug and a receptor improves.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I thank to Universidad de Talca for doctoral scholarship.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The author confirms that this article content has no conflict of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Zheng M., Liu X., Xu Y., Li H., Luo C., Jiang H. Computational methods for drug design and discovery: focus on China. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013;34(10):549–559. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2013.08.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Blundell T.L., Jhoti H., Abell C. High-throughput crystallography for lead discovery in drug design. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002;1(1):45–54. doi: 10.1038/nrd706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hsiao-lu D.L., Sahl S.J., Lew M.D., Moerner W.E. The double-helix microscope microscope super-resolves extended biological structures by localizing single blinking molecules in three dimensions with nanoscale precision. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012;100(15):153701. doi: 10.1063/1.3700446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Berman H.M., Bhat T.N., Bourne P.E., Feng Z., Gilliland G., Weissig H., Westbrook J. The protein data bank and the challenge of structural genomics. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2000;7:957–959. doi: 10.1038/80734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Westbrook J., Feng Z., Chen L., Yang H., Berman H.M. The protein data bank and structural genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31(1):489–491. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Seiler K.P., George G.A., Happ M.P., Bodycombe N.E., Carrinski H.A., Norton S., Brudz S., Sullivan J.P., Muhlich J., Serrano M. others. Chembank: a small-molecule screening and cheminformatics resource database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36(Suppl. 1):D351–D359. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Irwin J.J., Shoichet B.K. ZINC-a free database of commercially available compounds for virtual screening. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2005;45(1):177–182. doi: 10.1021/ci049714+. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mandal S., Moudgil M., Mandal S.K. Rational drug design. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009;625(1):90–100. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.06.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.De-la-Torre P., Treuer A. V, Gutierrez M., Poblete H., Alzate-Morales J. H., Trilleras J., Astudillo-Saavedra L., Caballero J. Synthesis and in silico analysis of the quantitative structure-activity relationship of heteroaryl-acrylonitriles as ache inhibitors. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. . 2015 [Google Scholar]
- 10.Brown H.C. Foundations of the structural theory. J. Chem. Educ. 1959;36(3):104. doi: 10.1021/ed036p104.1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wiswesser W.J. Johann Josef Loschmidt (1821-1895): A forgotten genius. Aldrichim Acta. 1989;22:17–19. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Metropolis N., Rosenbluth A.W., Rosenbluth M.N., Teller A.H., Teller E. Equation of state calculations by fast computing machines. J. Chem. Phys. 1953;21(6):1087–1092. doi: 10.1063/1.1699114. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Takahashi O., Masuda Y., Muroya A., Furuya T. Theory of docking scores and its application to a customizable scoring function. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2010;21(5-6):547–558. doi: 10.1080/1062936X.2010.502299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kitchen D.B., Decornez H., Furr J.R., Bajorath J. Docking and scoring in virtual screening for drug discovery: Methods and applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004;3(11):935–949. doi: 10.1038/nrd1549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mohan V., Gibbs A.C., Cummings M.D., Jaeger E.P., DesJarlais R.L. Docking: successes and challenges. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005;11(3):323–333. doi: 10.2174/1381612053382106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Krovat E.M., Steindl T., Langer T. Recent advances in docking and scoring. Curr. Comput. Aided. Drug Des. 2005;1(1):93–102. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Leach A.R., Shoichet B.K., Peishoff C.E. Prediction of protein-ligand interactions. Docking and scoring: successes and gaps.docking and scoring in virtual screening for drug discovery: Methods and applications. J. Med. Chem. 2006;49(20):5851–5855. doi: 10.1021/jm060999m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yuriev E., Ramsland P.a. Latest developments in molecular docking: 2010-2011 in review. J. Mol. Recognit. 2013;26(5):215–239. doi: 10.1002/jmr.2266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yuriev E., Agostino M., Ramsland P.A. Challenges and advances in computational docking: 2009 in review. J. Mol. Recognit. 2011;24(2):149–164. doi: 10.1002/jmr.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lee M.R., Sun Y. Improving docking accuracy through molecular mechanics generalized born optimization and scoring. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2007;3(3):1106–1119. doi: 10.1021/ct6003406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Adasme-Carreño F., Muñoz-Gutierrez C., Caballero J., Alzate-Morales J.H. Performance of the mm/gbsa scoring using a binding site hydrogen bond network-based frame selection: the protein kinase case. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014;16(27):14047–14058. doi: 10.1039/c4cp01378f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mena-Ulecia K., Vergara-Jaque A., Poblete H., Tiznado W., Caballero J. Study of the affinity between the protein kinase pka and peptide substrates derived from kemptide using molecular dynamics simulations and MM/GBSA. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e109639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pak Y., Wang S. Application of a molecular dynamics simulation method with a generalized effective potential to the flexible molecular docking problems. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2000;104(2):354–359. doi: 10.1021/jp993073h. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Caballero J., Alzate-Morales J.H. Molecular dynamics of protein kinase-inhibitor complexes: a valid structural information. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012;18(20):2946–2963. doi: 10.2174/138161212800672705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Elokely K.M., Doerksen R.J. Docking challenge: protein sampling and molecular docking performance. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013;53(8):1934–1945. doi: 10.1021/ci400040d. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.McGann M.R., Almond H.R., Nicholls A., Grant J.A., Brown F.K. Gaussian docking functions. Biopolymers. 2003;68(1):76–90. doi: 10.1002/bip.10207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.McGaughey G.B., Sheridan R.P., Bayly C.I., Culberson J.C., Kreatsoulas C., Lindsley S., Maiorov V., Truchon J-F., Cornell W.D. Comparison of topological, shape, and docking methods in virtual screening. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2007;47(4):1504–1519. doi: 10.1021/ci700052x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Friesner R.A., Banks J.L., Murphy R.B., Halgren T.A., Klicic J.J., Mainz D.T., Repasky M.P., Knoll E.H., Shelley M., Perry J.K. others. Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. method and assessment of docking accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004;47(7):1739–1749. doi: 10.1021/jm0306430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jones G., Willett P., Glen R.C. Molecular recognition of receptor sites using a genetic algorithm with a description of desolvation. J. Mol. Biol. 1995;245(1):43–53. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(95)80037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jones G., Willett P., Glen R.C., Leach A.R., Taylor R. Development and validation of a genetic algorithm for flexible docking. J. Mol. Biol. 1997;267(3):727–748. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Barreca M.L., Iraci N., De Luca L., Chimirri A. Induced-fit docking spproach provides insight into the binding mode and mechanism of action of HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. Chem. Med. Chem. 2009;4(9):1446–1456. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.200900166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Cavasotto C.N., Abagyan R.A. Protein flexibility in ligand docking and virtual screening to protein kinases. J. Mol. Biol. 2004;337(1):209–225. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Davis I.W., Baker D. Rosettaligand docking with full ligand and receptor flexibility. J. Mol. Biol. 2009;385(2):381–392. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.11.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Shityakov S., Förster C. In silico structure-based screening of versatile p-glycoprotein inhibitors using polynomial empirical scoring functions. Adv. Appl. Bioinform. Chem. 2014;7:1. doi: 10.2147/AABC.S56046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Trott O., Olson A.J. Autodock vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010;31(2):455–461. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Goodsell D.S., Morris G.M., Olson A.J. Automated docking of flexible ligands: applications of auto dock. J. Mol. Recognit. 1996;9(1):1–5. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1352(199601)9:1<1::AID-JMR241>3.0.CO;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Verdonk M.L., Cole J.C., Hartshorn M.J., Murray C.W., Taylor R.D. Improved protein-ligand docking using gold. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinforma. 2003;52(4):609–623. doi: 10.1002/prot.10465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Halgren T.A., Murphy R.B., Friesner R.A., Beard H.S., Frye L.L., Pollard W.T., Banks J.L. Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 2. Enrichment factors in database screening. J. Med. Chem. 2004;47(7):1750–1759. doi: 10.1021/jm030644s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kryger G., Silman I., Sussman J.L. Structure of acetylcholinesterase complexed with E2020 (Aricept®): implications for the design of new anti-alzheimer drugs. Structure. 1999;7(3):297–307. doi: 10.1016/S0969-2126(99)80040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Krishnan K.R., Charles H.C., Doraiswamy P.M., Mintzer J., Weisler R., Yu X., Perdomo C., Ieni J.R., Rogers S. Randomized. Placebo-Controlled Trial of the Effects of Donepezil on Neuronal Markers and Hippocampal Volumes in Alzheimer’s Disease; 2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Penthala N.R., Zong H., Ketkar A., Madadi N.R., Janganati V., Eoff R.L., Guzman M.L., Crooks P.A. Synthesis, anticancer activity and molecular docking studies on a series of heterocyclic trans-cyanocombretastatin analogues as antitubulin agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015;92:212–220. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.12.050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Subramanian S.R., Zuckerman D.M. Docking to the highly flexible estrogen receptor ligand binding domain via mixed-resolution Monte Carlo. Biophys. J. 2015;108(2):319a. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.11.1735. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Shityakov S., Neuhaus W., Dandekar T., Förster C. Analysing molecular polar surface descriptors to predict blood-brain barrier permeation. Int. J. Comput. Biol. Drug Des. 2013;6(1-2):146–156. doi: 10.1504/IJCBDD.2013.052195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Shityakov S., Förster C. In silico predictive model to determine vector-mediated transport properties for the blood-brain barrier choline transporter. Adv. Appl. Bioinform. Chem. 2014;7:23. doi: 10.2147/AABC.S63749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Shityakov S., Broscheit J., Foerster C. α-cyclodextrin dimer complexes of dopamine and levodopa derivatives to assess drug delivery to the central nervous system: adme and molecular docking studies.in silico predictive model to determine vector-mediated transport properties for the blood--brain barrier choline transporter. Int. J. Nanomedicine. 2012;7:3211. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S31373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Shityakov S., Förster C. Multidrug resistance protein P-Gp interaction with nanoparticles (fullerenes and carbon nanotube) to assess their drug delivery potential: A theoretical molecular docking study. Int. J. Comput. Biol. Drug Des. 2013;6(4):343–357. doi: 10.1504/IJCBDD.2013.056801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Gao J., Chao L.V. Molecular docking to predict hypopharyngeal cancer treatment drugs: tiliroside-noscapine interaction. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2014;33(8):1397–1399. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sabogal-arango A., Barreto G.E., Ramírez-sánchez D., González-mendoza J., Barreto V., Morales L., González J. Computational insights of the interaction among sea anemones neurotoxins and Kv1.3 channel. Bioinform. Biol. Insights. 2014;8:73–81. doi: 10.4137/BBI.S13403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Yi Z., Lu M. Deep understanding of metabolic behaviour of alisol a using molecular docking. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2014;33(3):522–524. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kutchukian P.S., Shakhnovich E.I. de novo design: balancing novelty and confined chemical space. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2010;5(8):789–812. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2010.497534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Schneider G., Fechner U. Computer-based de novo design of drug-like molecules. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005;4(8):649–663. doi: 10.1038/nrd1799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Chirapu S.R., Pachaiyappan B., Nural H.F., Cheng X., Yuan H., Lankin D.C., Abdul-Hay S.O., Thatcher G.R., Shen Y., Kozikowski A.P. others. Molecular modeling, synthesis, and activity studies of novel biaryl and fused-ring bace1 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009;19(1):264–274. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2008.10.096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Schneider G., Böhm H.J. Virtual screening and fast automated docking methods. Drug Discov. Today. 2002;7(1):64–70. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6446(01)02091-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Roe D.C., Kuntz I.D. BUILDER v. 2: Improving the chemistry of a de novo design strategy. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 1995;9(3):269–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00124457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Lauri G., Bartlett P.A. CAVEAT: A program to facilitate the design of organic moleculesimproving the chemistry of a de novo design strategy.. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 1994;8(1):51–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00124349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Pearlman D.A., Murcko M.A. CONCERTS: Dynamic connection of fragments as an approach to de novo ligand design. J. Med. Chem. 1996;39(8):1651–1663. doi: 10.1021/jm950792l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Miranker A., Karplus M. An automated method for dynamic ligand design. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinforma. 1995;23(4):472–490. doi: 10.1002/prot.340230403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Rotstein S.H., Murcko M.A. GenStar: a method for de novo drug design. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 1993;7(1):23–43. doi: 10.1007/BF00141573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Rotstein S.H., Murcko M.A. GroupBuild: a fragment-based method for de novo drug design. J. Med. Chem. 1993;36(12):1700–1710. doi: 10.1021/jm00064a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Moon J.B., Howe W.J. Computer design of bioactive molecules: a method for receptor-based de novo ligand designan automated method for dynamic ligand design.. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinforma. 1991;11(4):314–328. doi: 10.1002/prot.340110409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Bohacek R.S., McMartin C. Multiple highly diverse structures complementary to enzyme binding sites: results of extensive application of a de novo design method incorporating combinatorial growth. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994;116(13):5560–5571. doi: 10.1021/ja00092a006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Eisen M.B., Wiley D.C., Karplus M., Hubbard R.E. HOOK: a program for finding novel molecular architectures that satisfy the chemical and steric requirements of a macromolecule binding site. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinforma. 1994;19(3):199–221. doi: 10.1002/prot.340190305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Nishibata Y., Itai A. Automatic creation of drug candidate structures based on receptor structure. Starting point for artificial lead generation. Tetrahedron. 1991;47(43):8985–8990. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4020(01)86503-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Böhm H-J. The computer program LUDI: s new method for the de novo design of enzyme inhibitors. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 1992;6(1):61–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00124387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Gehlhaar D.K., Moerder K.E., Zichi D., Sherman C.J., Ogden R.C., Freer S.T. de novo design of enzyme inhibitors by monte carlo ligand generation. J. Med. Chem. 1995;38(3):466–472. doi: 10.1021/jm00003a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Miranker A., Karplus M. Functionality maps of binding sites: A multiple copy simultaneous search method. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinforma. 1991;11(1):29–34. doi: 10.1002/prot.340110104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Clark D.E., Firth M.A., Murray C.W. MOLMAKER: de novo generation of 3D databases for use in drug design. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1996;36(1):137–145. doi: 10.1021/ci9502055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Tschinke V., Cohen N.C. The NEWLEAD program: A new method for the design of candidate structures from pharmacophoric hypotheses. J. Med. Chem. 1993;36(24):3863–3870. doi: 10.1021/jm00076a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Clark D.E., Frenkel D., Levy S.A., Li J., Murray C.W., Robson B., Waszkowycz B., Westhead D.R. PRO_LIGAND: An approach to de novo molecular design. 1. Application to the design of organic molecules. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 1995;9(1):13–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00117275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Murray C.W., Clark D.E., Auton T.R., Firth M.A., Li J., Sykes R.A., Waszkowycz B., Westhead D.R., Young S.C. PRO_SELECT: Combining structure-based drug design and combinatorial chemistry for rapid lead discovery. 1. Technology. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 1997;11(2):193–207. doi: 10.1023/A:1008094712424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Todorov N.P., Dean P.M. Evaluation of a method for controlling molecular scaffold diversity in de novo ligand design. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 1997;11(2):175–192. doi: 10.1023/A:1008042711516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Schneider G., Schrödl W., Wallukat G., Müller J., Nissen E., Rönspeck W., Wrede P., Kunze R. Peptide design by artificial neural networks and computer-based evolutionary search. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1998;95(21):12179–12184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.21.12179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.DeWitte R.S., Ishchenko A.V., Shakhnovich E.I. SMoG: de novo design method based on simple, fast, and accurate free energy estimates. 2. Case studies in molecular design. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997;119(20):4608–4617. doi: 10.1021/ja963689+. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Ho C.M., Marshall G.R. FOUNDATION: A program to retrieve all possible structures containing a user-defined minimum number of matching query elements from three-dimensional databases. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 1993;7(1):3–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00141572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Mata P., Gillet V.J., Johnson A.P., Lampreia J., Myatt G.J., Sike S., Stebbings A.L. SPROUT: 3D structure generation using templates. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1995;35(3):479–493. doi: 10.1021/ci00025a016. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Schneider G., Lee M-L., Stahl M., Schneider P. de novo design of molecular architectures by evolutionary assembly of drug-derived building blocks. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2000;14(5):487–494. doi: 10.1023/A:1008184403558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Reddy, a S., Pati S. P., Kumar P. P., Pradeep H. N., Sastry G. N. Virtual screening in drug discovery - a computational perspective. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2007;8(4):329–351. doi: 10.2174/138920307781369427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Koeppen H., Kriegl J., Lessel U., Tautermann C. S., Wellenzohn B. Structure-based virtual screening: an overview. Drug Discov. 2011;7(20):1047–1055. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6446(02)02483-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Lyne P.D. Structure-based virtual screening: an overview. Drug Discov. Today. 2002;7(20):1047–1055. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6446(02)02483-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Friesner R.A., Murphy R.B., Repasky M.P., Frye L.L., Greenwood J.R., Halgren T.A., Sanschagrin P.C., Mainz D.T. Extra precision glide: docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006;49(21):6177–6196. doi: 10.1021/jm051256o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Ewing T.J., Makino S., Skillman A.G., Kuntz I.D. DOCK 4.0: search strategies for automated molecular docking of flexible molecule databases. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2001;15(5):411–428. doi: 10.1023/A:1011115820450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Schellhammer I., Rarey M. FlexX-Scan: fast, structure-based virtual screening. PROTEINS Struct. Funct. Bioinforma. 2004;57(3):504–517. doi: 10.1002/prot.20217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Abagyan R., Totrov M., Kuznetsov D. ICM-a new method for protein modeling and design: applications to docking and structure prediction from the distorted native conformation. J. Comput. Chem. 1994;15(5):488–506. doi: 10.1002/jcc.540150503. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Koes D. R., Camacho C. J. ZINC Pharmer: Pharmacophore search of the ZINC database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(Web Server issue):W409–W414. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Kumar A., Ito A., Takemoto M., Yoshida M., Zhang K.Y. Identification of 1, 2, 5-oxadiazoles as a new class of SENP2 inhibitors using structure based virtual screening. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014;54(3):870–880. doi: 10.1021/ci4007134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Jain A., Trivedi V. Docking and virtual screening to identify pkc agonists: potentials in anticancer therapeutics. Curr. Comput. Aided. Drug Des. 2014;10(1):50–58. doi: 10.2174/15734099113096660035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Mittal A., Paliwal S., Sharma M., Singh A., Sharma S., Yadav D. Pharmacophore based virtual screening, molecular docking and biological evaluation to identify novel PDE5 inhibitors with vasodilatory activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014;24(14):3137–3141. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Hecht F.M., Grant R.M., Petropoulos C.J., Dillon B., Chesney M.A., Tian H., Hellmann N.S., Bandrapalli N.I., Digilio L., Branson B. others. Sexual transmission of an HIV-1 variant resistant to multiple reverse-transcriptase and protease inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998;339(5):307–311. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199807303390504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Kincaid V.A., London N., Wangkanont K., Wesener D.A., Marcus S.A., Heroux A., Nedyalkova L., Talaat A.M., Forest K.T., Shoichet B.K. others. Virtual screening for UDP-Galactopyranose mutase ligands identifies a new class of antimycobacterial agents. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015 doi: 10.1021/acschembio.5b00370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Coburn C., Luo Y., Cui M., Wang J., Soll R., Dong J., Hu B., Lyon M., Santarelli V. P., Kraus R. L., Gregan Y., Wang Y., Fox S. V, Binns J., Doran S. M., Reiss D. R., Tannenbaum P. L., Gotter A. L., Meinke P. T., Renger J. J. Discovery of a pharmacologically active antagonist of the two-pore-domain potassium channel K2P9.1 (TASK-3). Chem. Med. Chem. 2012;7(1):123–133. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201100351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Bressi J.C., Verlinde C.L., Aronov A.M., Le Shaw M., Shin S.S., Nguyen L.N., Suresh S., Buckner F.S., Van Voorhis W.C., Kuntz I.D. others. Adenosine analogues as selective inhibitors of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase of trypanosomatidae via structure-based drug design. J. Med. Chem. 2001;44(13):2080–2093. doi: 10.1021/jm000472o. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Iwata Y., Arisawa M., Hamada R., Kita Y., Mizutani M.Y., Tomioka N., Itai A., Miyamoto S. Discovery of novel aldose reductase inhibitors using a protein structure-based approach: 3D-database search followed by design and synthesis. J. Med. Chem. 2001;44(11):1718–1728. doi: 10.1021/jm000483h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Schneider G., Clément-Chomienne O., Hilfiger L., Schneider P., Kirsch S., Böhm H-J., Neidhart W. Virtual screening for bioactive molecules by evolutionary de novo design. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000;39(22):4130–4133. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20001117)39:22<4130::AID-ANIE4130>3.0.CO;2-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Böhm H-J., Banner D.W., Weber L. Combinatorial docking and combinatorial chemistry: design of potent non-peptide thrombin inhibitors. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 1999;13(1):51–56. doi: 10.1023/A:1008040531766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Shityakov S., Dandekar T. Lead Expansion and virtual screening of indinavir derivate HIV-1 protease inhibitors using pharmacophoric-shape similarity scoring function. Bioinformation. 2010;4(7):295. doi: 10.6026/97320630004295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]