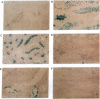
Abstract
Alterations to the mammalian genome that occur during the development of germ cells, in particular during meiosis, can be introduced into the population upon fertilization. These alterations can occur through homologous recombination, genome rearrangement, or mutagenesis. Such events usually occur infrequently for any particular sequence. Because of the difficulty in analyzing a large number of offspring in a mammalian cross, we have developed a marker to detect these events in sperm, since a large number of these meiotic progeny are produced during male gametogenesis. We have expressed the Escherichia coli lacZ gene during spermatogenesis in transgenic mice and quantitated the levels of beta-galactosidase activity in single sperm with the fluorescence-activated cell sorter and a fluorogenic substrate, 5-dodecanoylaminofluorescein di-beta-D-galactopyranoside. Detection of rare positives was demonstrated in mixed sperm populations with as few as 0.01% positive sperm. Although the distribution of beta-galactosidase activity in caudal epididymal sperm populations is bimodal, it appears that beta-galactosidase, like other proteins that have been expressed postmeiotically, is distributed between transgene-positive and transgene-negative sperm.
Full text
PDF

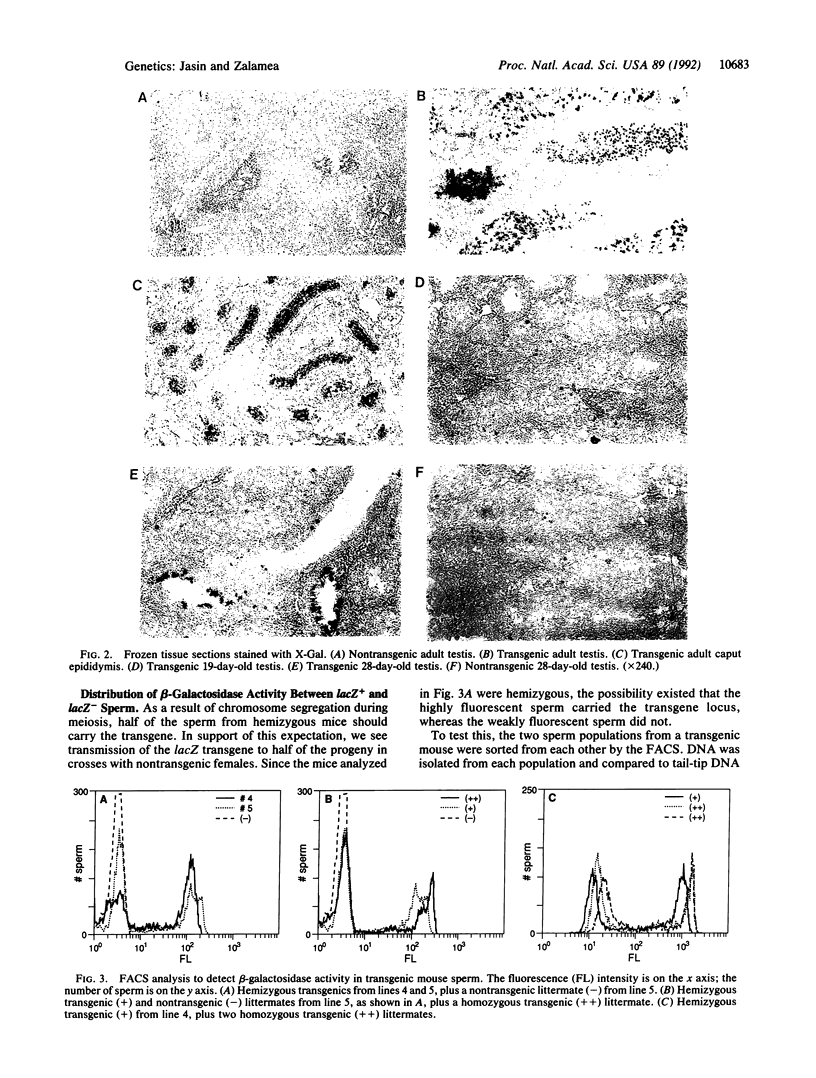

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURGOS M. H., FAWCETT D. W. Studies on the fine structure of the mammalian testis. I. Differentiation of the spermatids in the cat (Felis domestica). J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1955 Jul 25;1(4):287–300. doi: 10.1083/jcb.1.4.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beddington R. S., Morgernstern J., Land H., Hogan A. An in situ transgenic enzyme marker for the midgestation mouse embryo and the visualization of inner cell mass clones during early organogenesis. Development. 1989 May;106(1):37–46. doi: 10.1242/dev.106.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun R. E., Behringer R. R., Peschon J. J., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Genetically haploid spermatids are phenotypically diploid. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):373–376. doi: 10.1038/337373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun R. E., Lo D., Pinkert C. A., Widera G., Flavell R. A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Infertility in male transgenic mice: disruption of sperm development by HSV-tk expression in postmeiotic germ cells. Biol Reprod. 1990 Oct;43(4):684–693. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod43.4.684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun R. E., Peschon J. J., Behringer R. R., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Protamine 3'-untranslated sequences regulate temporal translational control and subcellular localization of growth hormone in spermatids of transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):793–802. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell K. A., Handel M. A. Protamine transcript sharing among postmeiotic spermatids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2407–2411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson R. P. Post-meiotic gene expression. Trends Genet. 1990 Aug;6(8):264–269. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90209-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAWCETT D. W., ITO S., SLAUTTERBACK D. The occurrence of intercellular bridges in groups of cells exhibiting synchronous differentiation. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 May 25;5(3):453–460. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.3.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiering S. N., Roederer M., Nolan G. P., Micklem D. R., Parks D. R., Herzenberg L. A. Improved FACS-Gal: flow cytometric analysis and sorting of viable eukaryotic cells expressing reporter gene constructs. Cytometry. 1991;12(4):291–301. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990120402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., White R. G., Dunham R. G., Kanda P. Effect of basic and nonbasic amino acid substitutions on transport induced by simian virus 40 T-antigen synthetic peptide nuclear transport signals. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2722–2729. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. H., Gyllensten U. B., Cui X. F., Saiki R. K., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Amplification and analysis of DNA sequences in single human sperm and diploid cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):414–417. doi: 10.1038/335414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEBEL B. R., AMAROSE A. P., HACKET E. M. Calendar of gametogenic development in the prepuberal male mouse. Science. 1961 Sep 22;134(3482):832–833. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3482.832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G. P., Fiering S., Nicolas J. F., Herzenberg L. A. Fluorescence-activated cell analysis and sorting of viable mammalian cells based on beta-D-galactosidase activity after transduction of Escherichia coli lacZ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2603–2607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L. Differential regulation of metallothionein-thymidine kinase fusion genes in transgenic mice and their offspring. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):701–710. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peschon J. J., Behringer R. R., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Spermatid-specific expression of protamine 1 in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5316–5319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroishi T., Sagai T., Hanzawa N., Gotoh H., Moriwaki K. Genetic control of sex-dependent meiotic recombination in the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):681–686. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. Z., Naleway J. J., Larison K. D., Huang Z. J., Haugland R. P. Detecting lacZ gene expression in living cells with new lipophilic, fluorogenic beta-galactosidase substrates. FASEB J. 1991 Dec;5(15):3108–3113. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.15.1720751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]