Abstract
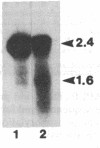
We have isolated a cDNA from a mouse brain library that encodes a protein whose predicted amino acid sequence is 42% identical and 64% similar to that of the amyloid beta protein precursor (APP). This 653-amino acid protein, which we have termed the amyloid precursor-like protein (APLP), appears to be similar to APP in overall structure as well as amino acid sequence. The amino acid homologies are concentrated within three distinct regions of the two proteins where the identities are 47%, 54%, and 56%. The APLP cDNA hybridizes to two messages of approximately 2.4 and 1.6 kilobases that are present in mouse brain and neuroblastoma cells. Polyclonal antibodies raised against a peptide derived from the C terminus of APLP stain the cytoplasm in a pattern reminiscent of Golgi staining. In addition to APP, APLP also displays significant homology to the Drosophila APP-like protein APPL and a rat testes APP-like protein. These data indicate that the APP gene is a member of a strongly conserved gene family. Studies aimed at determining the functions of the proteins encoded by this gene family should provide valuable clues to their potential role in Alzheimer disease neuropathology.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badley J. E., Bishop G. A., St John T., Frelinger J. A. A simple, rapid method for the purification of poly A+ RNA. Biotechniques. 1988 Feb;6(2):114–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birgbauer E., Solomon F. A marginal band-associated protein has properties of both microtubule- and microfilament-associated proteins. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1609–1620. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. Intracellular protein topogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1496–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxbaum J. D., Gandy S. E., Cicchetti P., Ehrlich M. E., Czernik A. J., Fracasso R. P., Ramabhadran T. V., Unterbeck A. J., Greengard P. Processing of Alzheimer beta/A4 amyloid precursor protein: modulation by agents that regulate protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):6003–6006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.6003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. J., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. NPXY, a sequence often found in cytoplasmic tails, is required for coated pit-mediated internalization of the low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3116–3123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Bloom G. S., Kreis T. E., Klausner R. D. Dissociation of a 110-kD peripheral membrane protein from the Golgi apparatus is an early event in brefeldin A action. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2295–2306. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F. S., Keim P. S., Beattie E. C., Blacher R. W., Culwell A. R., Oltersdorf T., McClure D., Ward P. J. Cleavage of amyloid beta peptide during constitutive processing of its precursor. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1122–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.2111583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandy S., Czernik A. J., Greengard P. Phosphorylation of Alzheimer disease amyloid precursor peptide by protein kinase C and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6218–6221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgaber D., Lerman M. I., McBride O. W., Saffiotti U., Gajdusek D. C. Characterization and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding brain amyloid of Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):877–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3810169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii T., Kametani F., Haga S., Sato M. The immunohistochemical demonstration of subsequences of the precursor of the amyloid A4 protein in senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1989 Mar-Apr;15(2):135–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1989.tb01216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitaguchi N., Takahashi Y., Tokushima Y., Shiojiri S., Ito H. Novel precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid protein shows protease inhibitory activity. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):530–532. doi: 10.1038/331530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo L. Q., Martin-Morris L. E., White K. Identification, secretion, and neural expression of APPL, a Drosophila protein similar to human amyloid protein precursor. J Neurosci. 1990 Dec;10(12):3849–3861. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-12-03849.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magendantz M., Solomon F. Analyzing the components of microtubules: antibodies against chartins, associated proteins from cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6581–6585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcantonio E. E., Hynes R. O. Antibodies to the conserved cytoplasmic domain of the integrin beta 1 subunit react with proteins in vertebrates, invertebrates, and fungi. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1765–1772. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moremen K. W., Touster O. Biosynthesis and modification of Golgi mannosidase II in HeLa and 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6654–6662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara O., Dorit R. L., Gilbert W. One-sided polymerase chain reaction: the amplification of cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5673–5677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oltersdorf T., Ward P. J., Henriksson T., Beattie E. C., Neve R., Lieberburg I., Fritz L. C. The Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein. Identification of a stable intermediate in the biosynthetic/degradative pathway. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4492–4497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmert M. R., Podlisny M. B., Witker D. S., Oltersdorf T., Younkin L. H., Selkoe D. J., Younkin S. G. The beta-amyloid protein precursor of Alzheimer disease has soluble derivatives found in human brain and cerebrospinal fluid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6338–6342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Gonzalez-DeWhitt P., Schilling J., Miller J., Hsu D., Greenberg B., Davis K., Wallace W., Lieberburg I., Fuller F. A new A4 amyloid mRNA contains a domain homologous to serine proteinase inhibitors. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):525–527. doi: 10.1038/331525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robakis N. K., Ramakrishna N., Wolfe G., Wisniewski H. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the cerebrovascular and the neuritic plaque amyloid peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4190–4194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen D. R., Martin-Morris L., Luo L. Q., White K. A Drosophila gene encoding a protein resembling the human beta-amyloid protein precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2478–2482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh T., Sundsmo M., Roch J. M., Kimura N., Cole G., Schubert D., Oltersdorf T., Schenk D. B. Secreted form of amyloid beta protein precursor is involved in the growth regulation of fibroblasts. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):615–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90096-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Georges G. E., Solomon F., Botstein D. Insertions of up to 17 amino acids into a region of alpha-tubulin do not disrupt function in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3799–3805. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Podlisny M. B., Joachim C. L., Vickers E. A., Lee G., Fritz L. C., Oltersdorf T. Beta-amyloid precursor protein of Alzheimer disease occurs as 110- to 135-kilodalton membrane-associated proteins in neural and nonneural tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7341–7345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisodia S. S., Koo E. H., Beyreuther K., Unterbeck A., Price D. L. Evidence that beta-amyloid protein in Alzheimer's disease is not derived by normal processing. Science. 1990 Apr 27;248(4954):492–495. doi: 10.1126/science.1691865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun J. W., DeSimone D. W., Fonda D., Patel R. S., Buck C., Horwitz A. F., Hynes R. O. Structure of integrin, a glycoprotein involved in the transmembrane linkage between fibronectin and actin. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90744-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Watkins P. C., Bruns G. A., St George-Hyslop P., Van Keuren M. L., Patterson D., Pagan S., Kurnit D. M., Neve R. L. Amyloid beta protein gene: cDNA, mRNA distribution, and genetic linkage near the Alzheimer locus. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):880–884. doi: 10.1126/science.2949367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., McClatchey A. I., Lamperti E. D., Villa-Komaroff L., Gusella J. F., Neve R. L. Protease inhibitor domain encoded by an amyloid protein precursor mRNA associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):528–530. doi: 10.1038/331528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidemann A., König G., Bunke D., Fischer P., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Beyreuther K. Identification, biogenesis, and localization of precursors of Alzheimer's disease A4 amyloid protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):115–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Sasaki H., Dohura K., Goto I., Sakaki Y. Structure and expression of the alternatively-spliced forms of mRNA for the mouse homolog of Alzheimer's disease amyloid beta protein precursor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Feb 15;158(3):906–912. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92808-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan Y. C., Bai Y., Wang L. F., Miao S. Y., Koide S. S. Characterization of cDNA encoding a human sperm membrane protein related to A4 amyloid protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2405–2408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann K., Herget T., Salbaum J. M., Schubert W., Hilbich C., Cramer M., Masters C. L., Multhaup G., Kang J., Lemaire H. G. Localization of the putative precursor of Alzheimer's disease-specific amyloid at nuclear envelopes of adult human muscle. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):367–372. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02822.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Sauvage F., Octave J. N. A novel mRNA of the A4 amyloid precursor gene coding for a possibly secreted protein. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):651–653. doi: 10.1126/science.2569763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]