Abstract
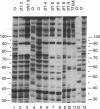
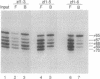
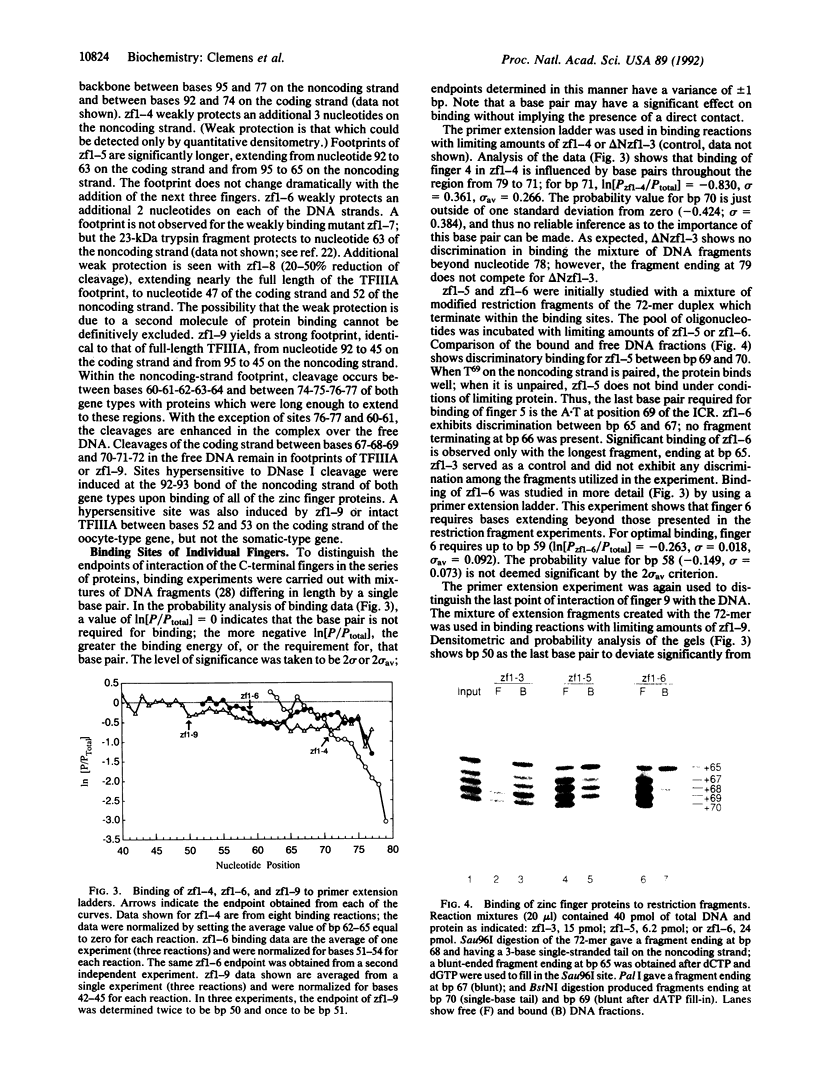
A series of polypeptides containing increasing numbers of zinc fingers of Xenopus transcription factor IIIA has been generated and binding to the 5S RNA gene internal control region has been studied in order to elucidate the mode of interaction of the individual fingers with DNA. By using a combination of DNase I footprinting, methylation interference, and differential binding to mixtures of DNA fragments differing in length by single base pairs, the binding sites for individual fingers have been defined. These results have led to a model for the interaction of transcription factor IIIA with the internal control region in which fingers 1-3 bind in the major groove of the promoter C block, fingers 7-9 bind in the major groove of the A block, and finger 5 binds in the major groove of the intermediate element. Fingers 4 and 6 each bind across the minor groove, spanning these promoter elements.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg J. M. Zinc finger domains: hypotheses and current knowledge. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1990;19:405–421. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.19.060190.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill M. E., Tullius T. D., Klug A. Mode of interaction of the zinc finger protein TFIIIA with a 5S RNA gene of Xenopus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5528–5532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairall L., Rhodes D., Klug A. Mapping of the sites of protection on a 5 S RNA gene by the Xenopus transcription factor IIIA. A model for the interaction. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):577–591. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90278-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg A. M., King B. O., Roeder R. G. Xenopus 5S gene transcription factor, TFIIIA: characterization of a cDNA clone and measurement of RNA levels throughout development. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):479–489. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90455-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J. M. DNA sequence-directed nucleosome reconstitution on 5S RNA genes of Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1612–1622. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda B. M., Roeder R. G. Association of a 5S gene transcription factor with 5S RNA and altered levels of the factor during cell differentiation. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90160-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochoyan M., Havel T. F., Nguyen D. T., Dahl C. E., Keutmann H. T., Weiss M. A. Alternating zinc fingers in the human male associated protein ZFY: 2D NMR structure of an even finger and implications for "jumping-linker" DNA recognition. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 9;30(14):3371–3386. doi: 10.1021/bi00228a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao X. B., Clemens K. R., Tennant L., Wright P. E., Gottesfeld J. M. Specific interaction of the first three zinc fingers of TFIIIA with the internal control region of the Xenopus 5 S RNA gene. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 20;223(4):857–871. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90248-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Johnson H. N., Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. The DNA binding domain and bending angle of E. coli CAP protein. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):995–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90814-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Albers M. W., Chen C. M., Schreiber S. L., Walsh C. T. Cloning, expression, and purification of human cyclophilin in Escherichia coli and assessment of the catalytic role of cysteines by site-directed mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2304–2308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacFerrin K. D., Terranova M. P., Schreiber S. L., Verdine G. L. Overproduction and dissection of proteins by the expression-cassette polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1937–1941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod M., Stein M., Beach D. The product of the mei3+ gene, expressed under control of the mating-type locus, induces meiosis and sporulation in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):729–736. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04814.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Brown D. D. A specific transcription factor that can bind either the 5S RNA gene or 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Hamm J., Roeder R. G. The 5S gene internal control region is composed of three distinct sequence elements, organized as two functional domains with variable spacing. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90359-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds W. F., Gottesfeld J. M. Torsional stress induces an S1 nuclease-hypersensitive site within the promoter of the Xenopus laevis oocyte-type 5S RNA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4018–4022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D. Structural analysis of a triple complex between the histone octamer, a Xenopus gene for 5S RNA and transcription factor IIIA. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3473–3482. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04106.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J. Characterization of the equilibrium binding of Xenopus transcription factor IIIA to the 5 S RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17593–17600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Brown D. D. Contact points between a positive transcription factor and the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):395–405. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands M. S., Bogenhagen D. F. The carboxyterminal zinc fingers of TFIIIA interact with the tip of helix V of 5S RNA in the 7S ribonucleoprotein particle. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19(8):1791–1796. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.8.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroth G. P., Cook G. R., Bradbury E. M., Gottesfeld J. M. Transcription factor IIIA induced bending of the Xenopus somatic 5S gene promoter. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):487–488. doi: 10.1038/340487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroth G. P., Gottesfeld J. M., Bradbury E. M. TFIIIA induced DNA bending: effect of low ionic strength electrophoresis buffer conditions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):511–516. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Jackson I. J., Brown D. D. Domains of the positive transcription factor specific for the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90396-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Van Den Berg D. J., Korn L. J. Structure of the gene for Xenopus transcription factor TFIIIA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2187–2200. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B. Map of distamycin, netropsin, and actinomycin binding sites on heterogeneous DNA: DNA cleavage-inhibition patterns with methidiumpropyl-EDTA.Fe(II). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5470–5474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrana K. E., Churchill M. E., Tullius T. D., Brown D. D. Mapping functional regions of transcription factor TFIIIA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1684–1696. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing Y. Y., Worcel A. The C-terminal domain of transcription factor IIIA interacts differently with different 5S RNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):499–514. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasui W., Ryoji M. Presence of multiple species of polypeptides immunologically related to transcription factor TFIIIA in adult Xenopus tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5597–5610. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- You Q. M., Veldhoen N., Baudin F., Romaniuk P. J. Mutations in 5S DNA and 5S RNA have different effects on the binding of Xenopus transcription factor IIIA. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 5;30(9):2495–2500. doi: 10.1021/bi00223a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]