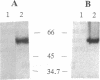
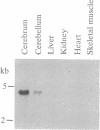
Abstract
Transport systems specific for L-glutamate and L-aspartate play an important role in the termination of neurotransmitter signals at excitatory synapses. We describe here the structure and function of a 66-kDa glycoprotein that was purified from rat brain and identified as an L-glutamate/L-aspartate transporter (GLAST). A GLAST-specific cDNA clone was isolated from a rat brain cDNA library. The cDNA insert encodes a polypeptide with 543 amino acid residues (59,697 Da). The amino acid sequence of GLAST suggests a distinctive structure and membrane topology, with some conserved motifs also present in prokaryotic glutamate transporters. The transporter function has been verified by amino acid uptake studies in the Xenopus laevis oocyte system. GLAST is specific for L-glutamate and L-aspartate, shows strict dependence on Na+ ions, and is inhibited by DL-threo-3-hydroxy-aspartate. In situ hybridization reveals a strikingly high density of GLAST mRNA in the Purkinje cell layer of cerebellum, presumably in the Bergmann glia cells, and a less dense distribution throughout the cerebrum. These data suggest that GLAST may be involved in the regulation of neurotransmitter concentration in central nervous system.
Full text
PDF

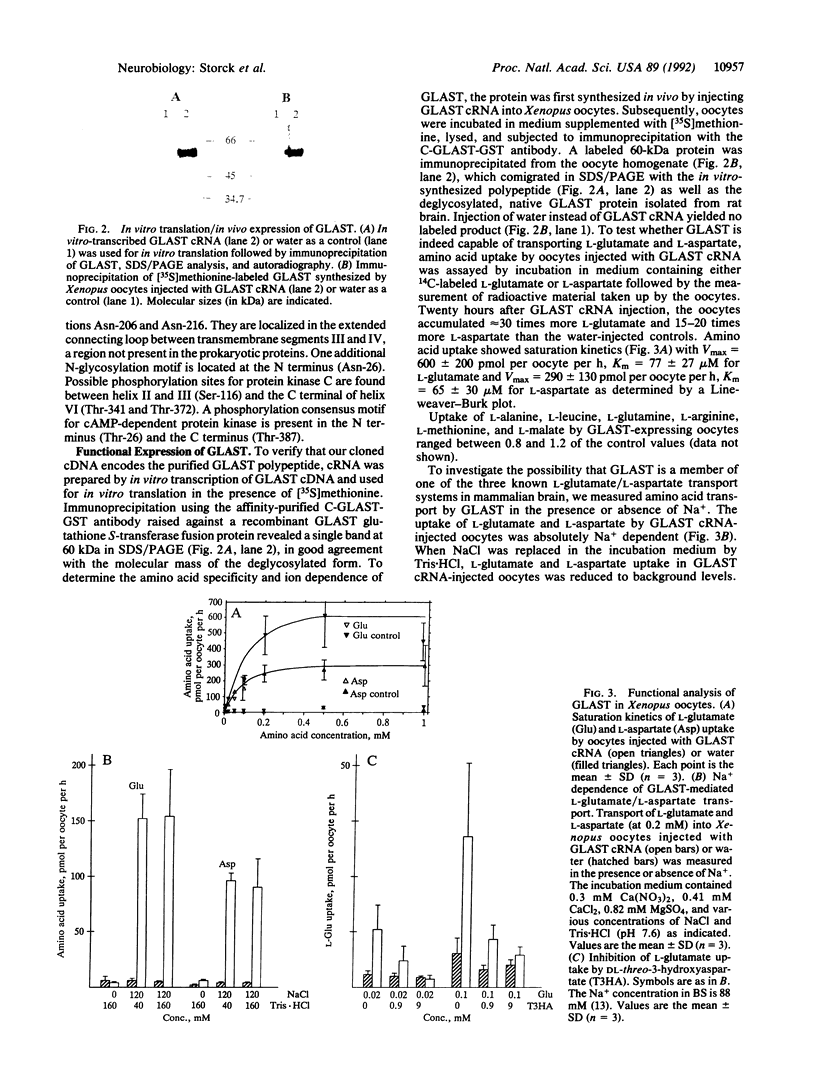
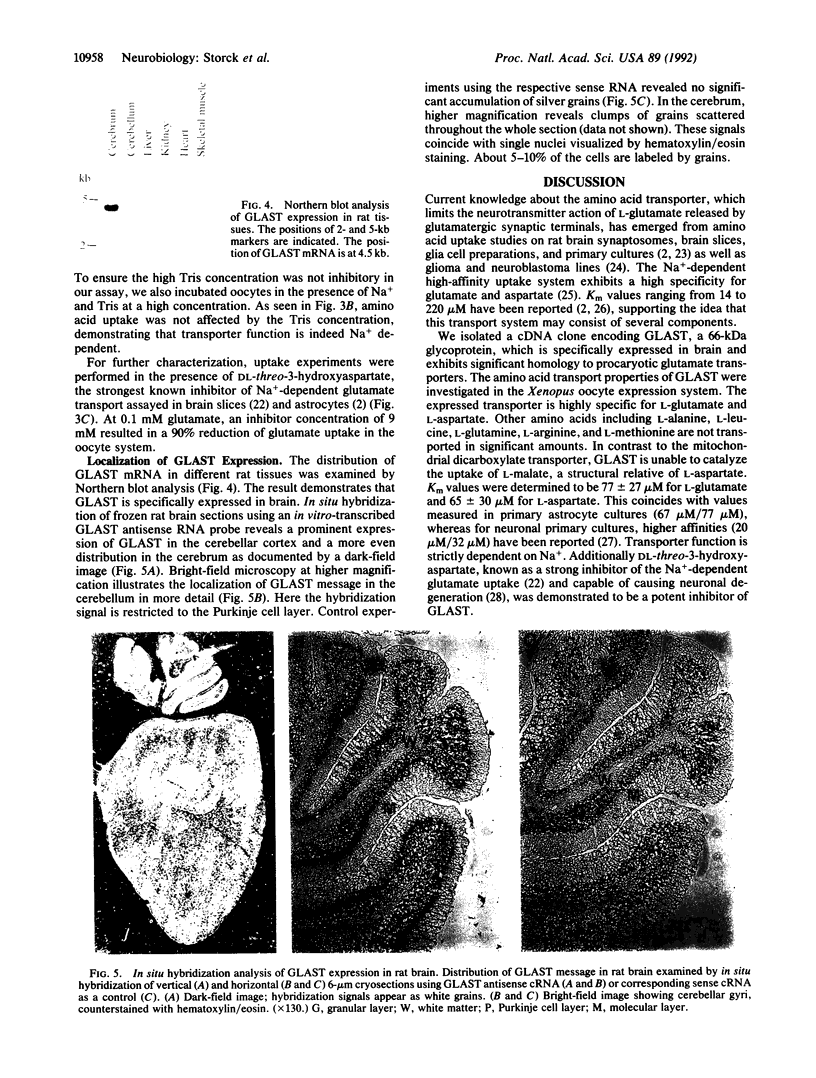

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balcar V. J., Johnston G. A. The structural specificity of the high affinity uptake of L-glutamate and L-aspartate by rat brain slices. J Neurochem. 1972 Nov;19(11):2657–2666. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakely R. D., Berson H. E., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Caron M. G., Peek M. M., Prince H. K., Bradley C. C. Cloning and expression of a functional serotonin transporter from rat brain. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):66–70. doi: 10.1038/354066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danbolt N. C., Pines G., Kanner B. I. Purification and reconstitution of the sodium- and potassium-coupled glutamate transport glycoprotein from rat brain. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 17;29(28):6734–6740. doi: 10.1021/bi00480a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi Y., Yamato I., Anraku Y. Nucleotide sequence of gltS, the Na+/glutamate symport carrier gene of Escherichia coli B. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21704–21708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drejer J., Larsson O. M., Schousboe A. Characterization of uptake and release processes for D- and L-aspartate in primary cultures of astrocytes and cerebellar granule cells. Neurochem Res. 1983 Feb;8(2):231–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00963923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Schwarz E., Komaromy M., Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flott B., Seifert W. Characterization of glutamate uptake systems in astrocyte primary cultures from rat brain. Glia. 1991;4(3):293–304. doi: 10.1002/glia.440040307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonnum F. Glutamate: a neurotransmitter in mammalian brain. J Neurochem. 1984 Jan;42(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb09689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. M., Kanner B. I. Partial purification of the sodium- and potassium-coupled L-glutamate transport glycoprotein from rat brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Sep 15;944(1):90–96. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90320-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guastella J., Nelson N., Nelson H., Czyzyk L., Keynan S., Miedel M. C., Davidson N., Lester H. A., Kanner B. I. Cloning and expression of a rat brain GABA transporter. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1303–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.1975955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. J., Mezey E., Brownstein M. J. Cloning of a serotonin transporter affected by antidepressants. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):579–580. doi: 10.1126/science.1948036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., Harnecker J., Seifert W. Calcium ions induce glutamate transport into rat brain membrane vesicles in the absence of sodium and chloride. Evidence for a novel uptake site? FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 8;228(1):74–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80588-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., Seifert W. Glutamate transport and not glutamate receptor binding is stimulated by gangliosides in a Ca2+-dependent manner in rat brain synaptic plasma membranes. J Neurochem. 1989 Sep;53(3):716–723. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb11763.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J., Gu B. H., Albright L. M., Nixon B. T. Conservation between coding and regulatory elements of Rhizobium meliloti and Rhizobium leguminosarum dct genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5244–5253. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5244-5253.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalman M., Gentry D. R., Cashel M. Characterization of the Escherichia coli K12 gltS glutamate permease gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Mar;225(3):379–386. doi: 10.1007/BF00261677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilty J. E., Lorang D., Amara S. G. Cloning and expression of a cocaine-sensitive rat dopamine transporter. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):578–579. doi: 10.1126/science.1948035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelberg H. K., Pang S., Treble D. H. Excitatory amino acid-stimulated uptake of 22Na+ in primary astrocyte cultures. J Neurosci. 1989 Apr;9(4):1141–1149. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-04-01141.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurth J., Stoffel W. A facile method for the isolation and preparation of proteins and peptides for sequence analysis in the picomolar range. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1990 Aug;371(8):675–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan W. J., Snyder S. H. Unique high affinity uptake systems for glycine, glutamic and aspartic acids in central nervous tissue of the rat. Nature. 1971 Dec 3;234(5327):297–299. doi: 10.1038/234297b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBean G. J., Roberts P. J. Neurotoxicity of L-glutamate and DL-threo-3-hydroxyaspartate in the rat striatum. J Neurochem. 1985 Jan;44(1):247–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Bridges R. J., Cotman C. W. The excitatory amino acid receptors: their classes, pharmacology, and distinct properties in the function of the central nervous system. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1989;29:365–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.29.040189.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Sekiguchi M. Synaptic receptors and intracellular signal transduction in the cerebellum. Neurosci Res. 1991 Jan;9(4):213–237. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(91)90023-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacholczyk T., Blakely R. D., Amara S. G. Expression cloning of a cocaine- and antidepressant-sensitive human noradrenaline transporter. Nature. 1991 Mar 28;350(6316):350–354. doi: 10.1038/350350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer A. M., Procter A. W., Stratmann G. C., Bowen D. M. Excitatory amino acid-releasing and cholinergic neurones in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1986 May 15;66(2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pin J. P., Bockaert J., Recasesn M. The Ca2+/C1- dependent L-[3H]glutamate binding: a new receptor or a particular transport process? FEBS Lett. 1984 Sep 17;175(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80563-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines G., Kanner B. I. Counterflow of L-glutamate in plasma membrane vesicles and reconstituted preparations from rat brain. Biochemistry. 1990 Dec 25;29(51):11209–11214. doi: 10.1021/bi00503a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada S., Kitayama S., Lin C. L., Patel A., Nanthakumar E., Gregor P., Kuhar M., Uhl G. Cloning and expression of a cocaine-sensitive dopamine transporter complementary DNA. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):576–578. doi: 10.1126/science.1948034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolner B., Poolman B., Wallace B., Konings W. N. Revised nucleotide sequence of the gltP gene, which encodes the proton-glutamate-aspartate transport protein of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(7):2391–2393. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.7.2391-2393.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usdin T. B., Mezey E., Chen C., Brownstein M. J., Hoffman B. J. Cloning of the cocaine-sensitive bovine dopamine transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11168–11171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waniewski R. A., Martin D. L. Characterization of L-glutamic acid transport by glioma cells in culture: evidence for sodium-independent, chloride-dependent high affinity influx. J Neurosci. 1984 Sep;4(9):2237–2246. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-09-02237.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaczek R., Balm M., Arlis S., Drucker H., Coyle J. T. Quisqualate-sensitive, chloride-dependent transport of glutamate into rat brain synaptosomes. J Neurosci Res. 1987;18(3):425–431. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490180307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]