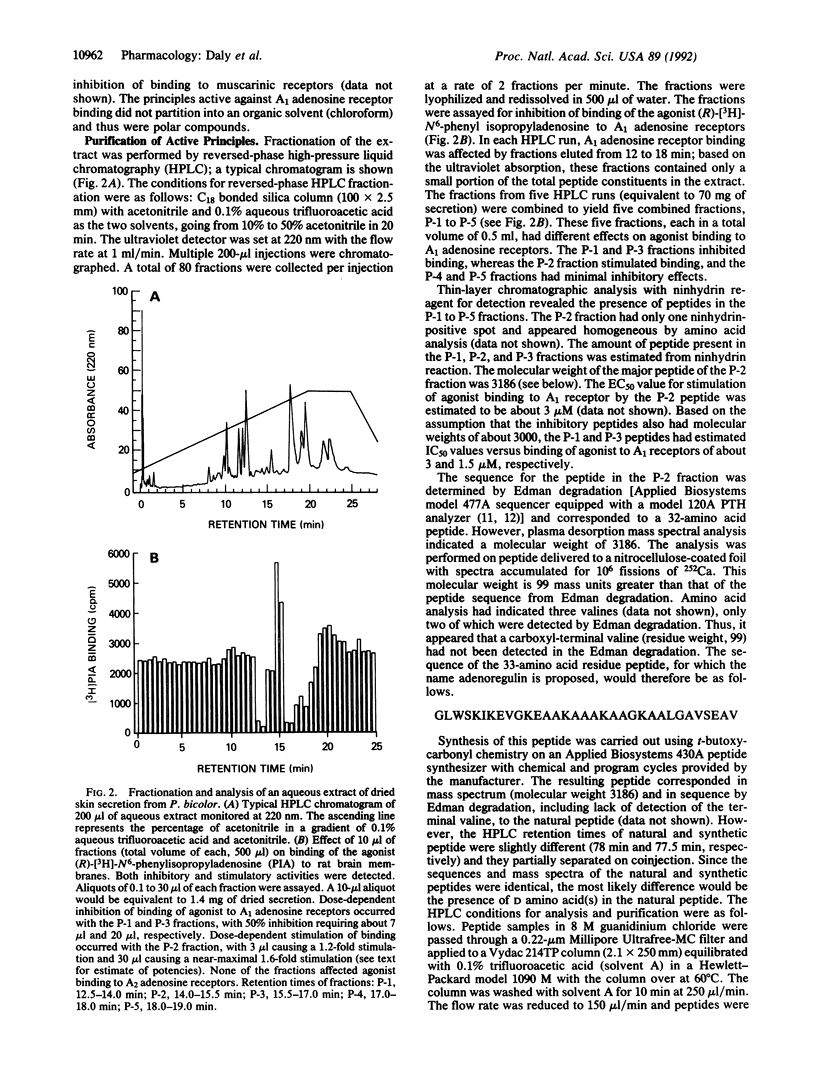
Abstract
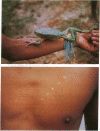
A frog used for "hunting magic" by several groups of Panoan-speaking Indians in the borderline between Brazil and Peru is identified as Phyllomedusa bicolor. This frog's skin secretion, which the Indians introduce into the body through fresh burns, is rich in peptides. These include vasoactive peptides, opioid peptides, and a peptide that we have named adenoregulin, with the sequence GLWSKIKEVGKEAAKAAAKAAGKAALGAVSEAV as determined from mass spectrometry and Edman degradation. The natural peptide may contain a D amino acid residue, since it is not identical in chromatographic properties to the synthetic peptide. Adenoregulin enhances binding of agonists to A1 adenosine receptors; it is accompanied in the skin secretion by peptides that inhibit binding. The vasoactive peptide sauvagine, the opioid peptides, and adenoregulin and related peptides affect behavior in mice and presumably contribute to the behavioral sequelae observed in humans.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruns R. F., Lu G. H., Pugsley T. A. Characterization of the A2 adenosine receptor labeled by [3H]NECA in rat striatal membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;29(4):331–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erspamer V., Falconieri Erspamer G., Cei J. M. Active peptides in the skins of two hundred and thirty American amphibian species. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1986;85(1):125–137. doi: 10.1016/0742-8413(86)90063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erspamer V., Melchiorri P., Falconieri-Erspamer G., Negri L., Corsi R., Severini C., Barra D., Simmaco M., Kreil G. Deltorphins: a family of naturally occurring peptides with high affinity and selectivity for delta opioid binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5188–5192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R., Berrie C. P., Birdsall N. J., Burgen A. S., Hulme E. C. Pirenzepine distinguishes between different subclasses of muscarinic receptors. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):90–92. doi: 10.1038/283090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson K. A., Ukena D., Kirk K. L., Daly J. W. [3H]xanthine amine congener of 1,3-dipropyl-8-phenylxanthine: an antagonist radioligand for adenosine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4089–4093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor: demonstration in nervous tissue. Science. 1973 Mar 9;179(4077):1011–1014. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4077.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Katims J. J., Annau Z., Bruns R. F., Daly J. W. Adenosine receptors and behavioral actions of methylxanthines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3260–3264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone K. L., Williams K. R. High-performance liquid chromatographic peptide mapping and amino acid analysis in the sub-nanomole range. J Chromatogr. 1986 May 30;359:203–212. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(86)80074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempst P., Riviere L. Examination of automated polypeptide sequencing using standard phenyl isothiocyanate reagent and subpicomole high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis. Anal Biochem. 1989 Dec;183(2):290–300. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90482-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]