Abstract
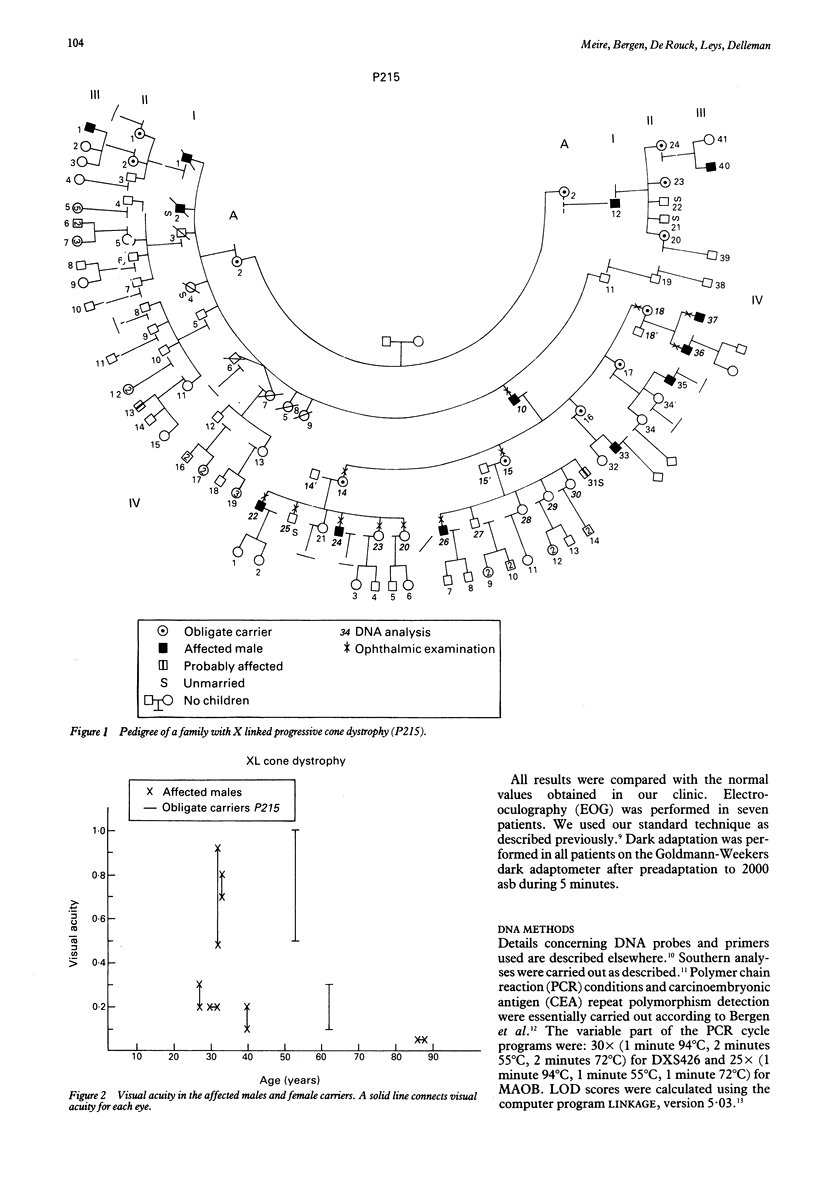
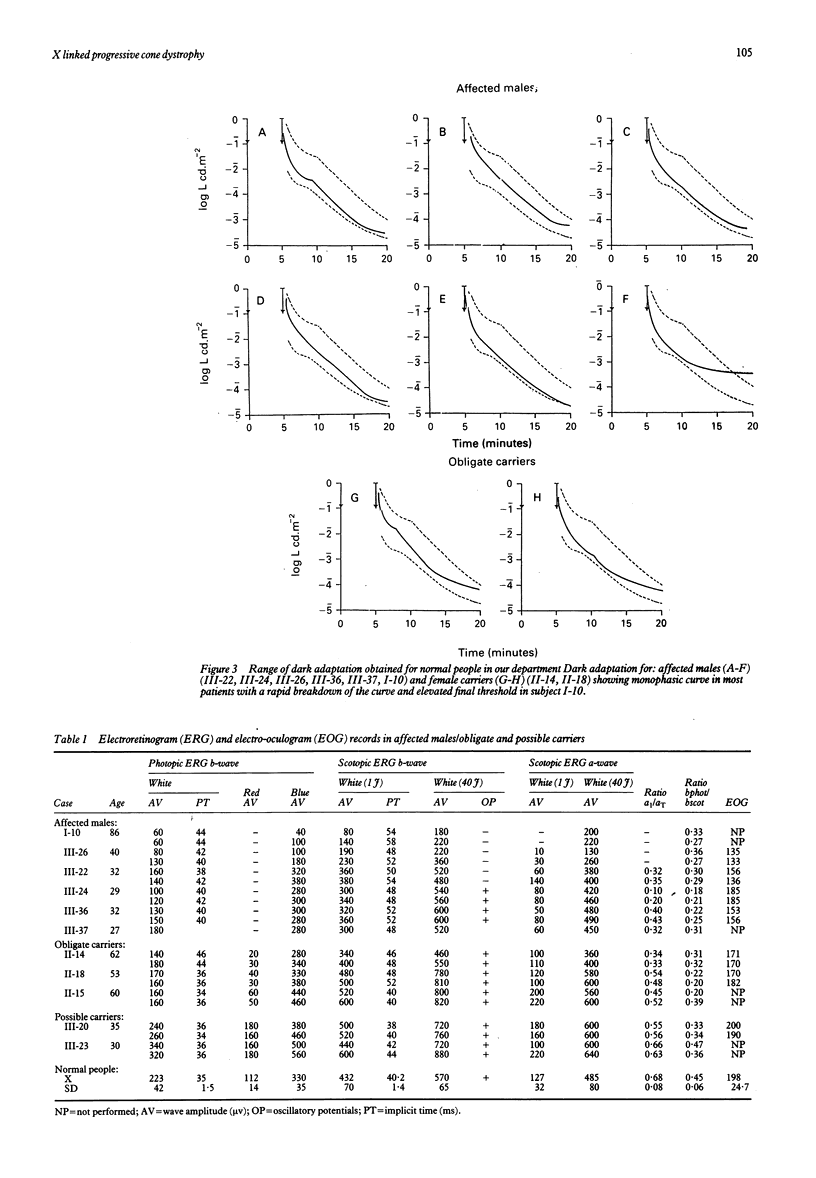
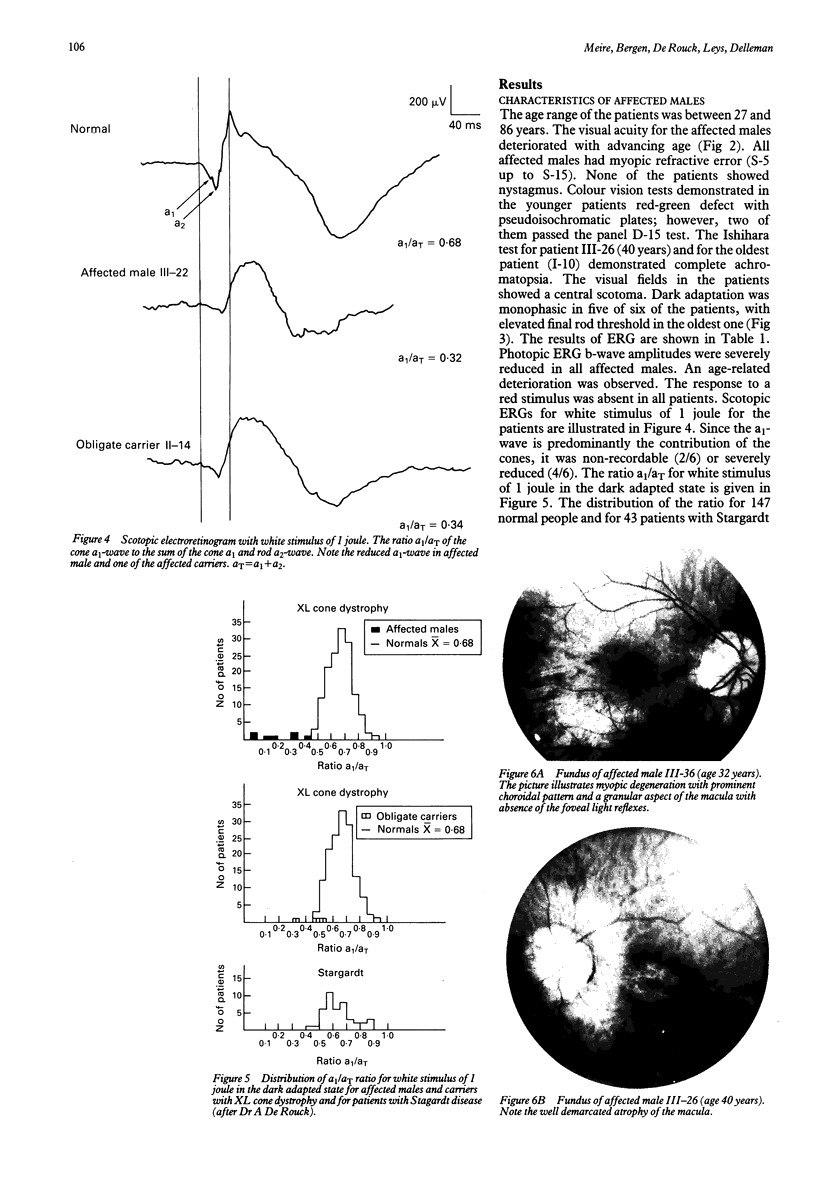
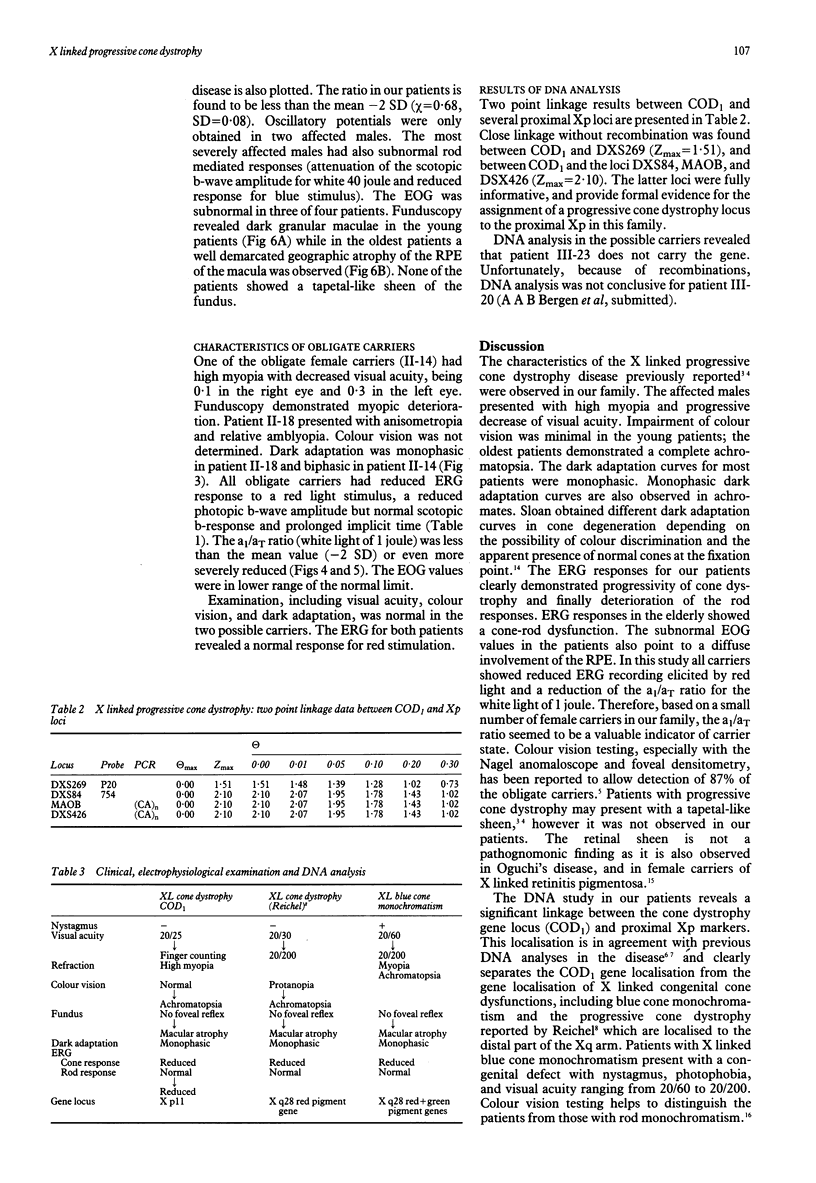
Six affected males, three female carriers, and two possible carriers were evaluated from a three generation pedigree with X linked progressive cone dystrophy. The affected males presented with progressive decrease of visual acuity, impairment of colour vision, and deterioration of electroretinogram, which ranged from absent response to red light in all young patients to abnormal cone-rod responses in the elderly ones. In most affected males dark adaptation curves were monophasic and the electro-oculogram values were reduced. While some obligate carriers showed functional anomalies, they all had reduced electroretinogram response to red light. The a1/aT ratio for 1 joule white light was an appropriate indicator for carrier state. The family was studied with seven DNA markers from the proximal part of the short arm of the human X chromosome. So far, significant linkage has been found between three DNA markers and COD1, which assigns the progressive cone dystrophy gene (COD1) in this family to Xp21-p11.1. Differential diagnosis with congenital cone dystrophies is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergen A. A., Samanns C., Schuurman E. J., van Osch L., van Dorp D. B., Pinckers A. J., Bakker E., Gal A., van Ommen G. J., Bleeker-Wagemakers E. M. Multipoint linkage analysis in X-linked ocular albinism of the Nettleship-Falls type. Hum Genet. 1991 Dec;88(2):162–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00206065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berson E. L., Sandberg M. A., Rosner B., Sullivan P. L. Color plates to help identify patients with blue cone monochromatism. Am J Ophthalmol. 1983 Jun;95(6):741–747. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(83)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman G. A., Weinberg A. B., McMahon T. T. X-linked recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Clinical characteristics of carriers. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986 Sep;104(9):1329–1335. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1986.01050210083030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- François J., Verriest G., Matton-Van Leuven T., De Rouck A., Manavian D. Atypical achromatopia of sex-linked recessive inheritance. Am J Ophthalmol. 1966 May;61(5 Pt 2):1101–1108. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(66)90231-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckenlively J. R., Weleber R. G. X-linked recessive cone dystrophy with tapetal-like sheen. A newly recognized entity with Mizuo-Nakamura phenomenon. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986 Sep;104(9):1322–1328. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1986.01050210076029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson D. M., Thompson H. S., Bartley J. A. X-linked progressive cone dystrophy. Clinical characteristics of affected males and female carriers. Ophthalmology. 1989 Jun;96(6):885–895. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(89)32808-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keunen J. E., van Everdingen J. A., Went L. N., Oosterhuis J. A., van Norren D. Color matching and foveal densitometry in patients and carriers of an X-linked progressive cone dystrophy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990 Dec;108(12):1713–1719. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1990.01070140067031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Davenport C. M., Maumenee I. H., Lewis R. A., Hejtmancik J. F., Litt M., Lovrien E., Weleber R., Bachynski B., Zwas F. Molecular genetics of human blue cone monochromacy. Science. 1989 Aug 25;245(4920):831–838. doi: 10.1126/science.2788922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinckers A., Deutman A. F. X-linked cone dystrophy. An overlooked diagnosis? Int Ophthalmol. 1987 Aug;10(4):241–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00155631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichel E., Bruce A. M., Sandberg M. A., Berson E. L. An electroretinographic and molecular genetic study of X-linked cone degeneration. Am J Ophthalmol. 1989 Nov 15;108(5):540–547. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(89)90431-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]