Abstract
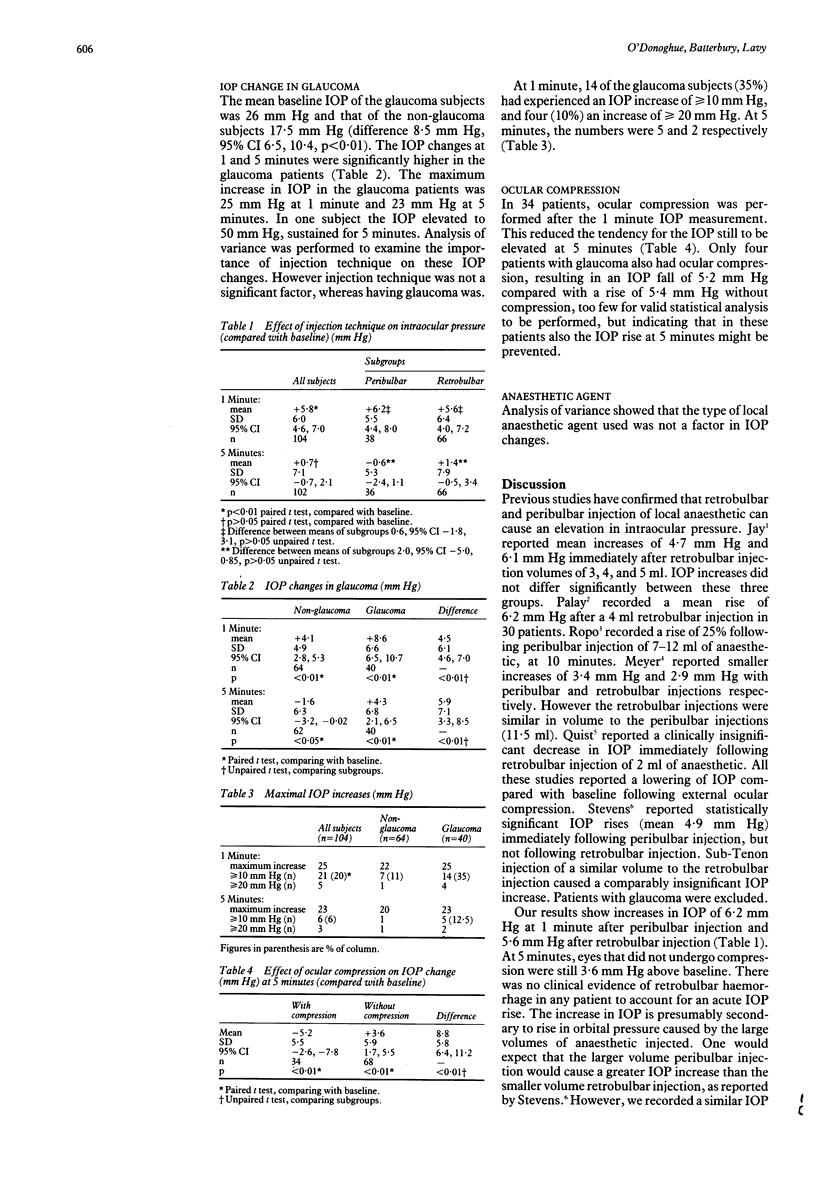
A total of 104 eyes undergoing intraocular surgery were studied to investigate the effect on intraocular pressure (IOP) of peribulbar and retrobulbar anaesthesia in eyes with and without glaucoma. Forty eyes had glaucoma. Intraocular pressure was measured before, immediately after, and 5 minutes after injection of local anaesthetic. Mean IOP rose by 5.8 mm Hg at 1 minute (p < 0.01) and 0.7 mm Hg at 5 minutes (p > 0.05). However, in eyes not receiving external ocular compression after the 1 minute measurement (n = 70, 67%), IOP was still 3.6 mm Hg higher than baseline (p < 0.01), compared with 5.2 mm Hg lower than baseline (p < 0.01) where compression was used. Patients with glaucoma experienced higher and more persistent increases in IOP than those without glaucoma. The increase in IOP varied greatly between patients: the maximum rise was 25 mm Hg, and in one glaucoma patient an IOP of 50 mm Hg occurred, persisting for 5 minutes. At 1 minute, 14 of the glaucoma subjects (35%) had experienced an IOP rise of > or = 10 mm Hg, and four (10%) a rise of > or = 20 mm Hg. These results suggest that the changes in IOP in patients with glaucoma, with an acute increase in IOP being succeeded by an acute decrease on entry into the anterior chamber, may be hazardous. The implications for clinical practice are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Jay W. M., Carter H., Williams B., Green K. Effect of applying the Honan intraocular pressure reducer before cataract surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 1985 Oct 15;100(4):523–527. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(85)90674-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell P. J., Quigley H. A., Maumenee A. E., Stark W. J., Hutchins G. M. The Honan intraocular pressure reducer. An experimental study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1985 Mar;103(3):422–425. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1985.01050030118035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D., Hamilton R. C., Loken R. G., Gimbel H. V. Effect of combined peribulbar and retrobulbar injection of large volumes of anesthetic agents on the intraocular pressure. Can J Ophthalmol. 1992 Aug;27(5):230–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palay D. A., Stulting R. D. The effect of external ocular compression on intraocular pressure following retrobulbar anesthesia. Ophthalmic Surg. 1990 Jul;21(7):503–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quist L. H., Stapleton S. S., McPherson S. D., Jr Preoperative use of the Honan intraocular pressure reducer. Am J Ophthalmol. 1983 Apr;95(4):536–538. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(83)90277-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ropo A., Nikki P., Ruusuvaara P., Kivisaari L. Comparison of retrobulbar and periocular injections of lignocaine by computerised tomography. Br J Ophthalmol. 1991 Jul;75(7):417–420. doi: 10.1136/bjo.75.7.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ropo A., Ruusuvaara P., Paloheimo M., Maunuksela E. L., Nikki P. Effect of ocular compression (Autopressor) on intraocular pressure in periocular anaesthesia. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1990 Apr;68(2):227–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1990.tb01911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


