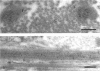
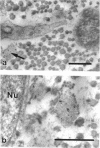
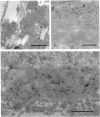
Abstract
An immunocytochemical study was conducted on elastic components in the sclera of seven aged human eyes. By conventional electron microscopy, elastic tissue consists of three distinct fibre types--elastic fibres, elaunin fibres, and oxytalan fibres. The distribution of six components associated with the elastic system (elastin, amyloid P component, laminin, fibronectin, gp 115, and vitronectin) were studied by immunogold transmission electron microscopy. The codistribution of amyloid P component and laminin was further studied by double immunolabelling. Both elastic and elaunin fibres contained elastin. The microfibrillar sheaths of elastic fibres labelled for amyloid P component, those of elaunin fibres for amyloid P and laminin, and those of oxytalan fibres for laminin only. No labelling was observed for fibronectin, gp 115, and vitronectin. In terms of the proteins investigated, the biochemical profile of the three fibre types was not completely identical and was manifest as different affinities in the binding of serum amyloid P component and an association with laminin.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander R. A., Garner A. Elastic and precursor fibres in the normal human eye. Exp Eye Res. 1983 Feb;36(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(83)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach S. M., Melrose S. M., Bhogal B., de Beer F. C., Black M. M., Pepys M. B. Immunohistochemical studies of amyloid P component distribution in normal human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Feb;80(2):86–90. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12531608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressan G. M., Castellani I., Colombatti A., Volpin D. Isolation and characterization of a 115,000-dalton matrix-associated glycoprotein from chick aorta. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):13262–13267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary E. G., Gibson M. A. Elastin-associated microfibrils and microfibrillar proteins. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1983;10:97–209. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363710-9.50009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombatti A., Bressan G. M., Castellani I., Volpin D. Glycoprotein 115, a glycoprotein isolated from chick blood vessels, is widely distributed in connective tissue. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):18–26. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombatti A., Poletti A., Carbone A., Volpin D., Bressan G. M. Extracellular matrix of lymphoid tissues in the chick. J Histochem Cytochem. 1989 May;37(5):757–763. doi: 10.1177/37.5.2703709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coria F., Castaño E., Prelli F., Larrondo-Lillo M., van Duinen S., Shelanski M. L., Frangione B. Isolation and characterization of amyloid P component from Alzheimer's disease and other types of cerebral amyloidosis. Lab Invest. 1988 Apr;58(4):454–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck K., Löfberg H., Dahlbäck B. Localization of vitronectin (S-protein of complement) in normal human skin. Acta Derm Venereol. 1986;66(6):461–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emsley J., White H. E., O'Hara B. P., Oliva G., Srinivasan N., Tickle I. J., Blundell T. L., Pepys M. B., Wood S. P. Structure of pentameric human serum amyloid P component. Nature. 1994 Jan 27;367(6461):338–345. doi: 10.1038/367338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essner E., Gordon S. R. Demonstration of microfibrils in Bruch's membrane of the eye. Tissue Cell. 1984;16(5):779–788. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(84)90009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquharson C., Robins S. P. The distribution of elastin in developing and adult rat organs using immunocytochemical techniques. J Anat. 1989 Aug;165:225–236. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmajer R., Contard P., Schwartz E., MacDonald E. D., 2nd, Jacobs L., 2nd, Sakai L. Y. Elastin-associated microfibrils (10 nm) in a three-dimensional fibroblast culture. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Oct;97(4):638–643. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12483132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawlik Z. Morphological and morphochemical properties of the elastic system in the motor organ of man. Folia Histochem Cytochem (Krakow) 1965;3(3):233–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson M. A., Hughes J. L., Fanning J. C., Cleary E. G. The major antigen of elastin-associated microfibrils is a 31-kDa glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11429–11436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson M. A., Kumaratilake J. S., Cleary E. G. The protein components of the 12-nanometer microfibrils of elastic and nonelastic tissues. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4590–4598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfischer S., Coltoff-Schiller B., Goldfischer M. Microfibrils, elastic anchoring components of the extracellular matrix, are associated with fibronectin in the zonule of Zinn and aorta. Tissue Cell. 1985;17(4):441–450. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(85)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez M. R. Ultrastructural immunocytochemical analysis of elastin in the human lamina cribrosa. Changes in elastic fibers in primary open-angle glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1992 Sep;33(10):2891–2903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano K., Kobayashi M., Kobayashi K., Hoshino T., Awaya S. Age-related changes of microfibrils in the cornea and trabecular meshwork of the human eye. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 1991;35(2):166–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoué S., Leblond C. P., Grant D. S., Rico P. The microfibrils of connective tissue: II. Immunohistochemical detection of the amyloid P component. Am J Anat. 1986 Jun;176(2):139–152. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001760204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai A., Kaufman H. E. Electron microscopic studies of the elastic fiber in human sclera. Invest Ophthalmol. 1972 Oct;11(10):816–821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumaratilake J. S., Gibson M. A., Fanning J. C., Cleary E. G. The tissue distribution of microfibrils reacting with a monospecific antibody to MAGP, the major glycoprotein antigen of elastin-associated microfibrils. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;50(1):117–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütjen-Drecoll E., Futa R., Rohen J. W. Ultrahistochemical studies on tangential sections of the trabecular meshwork in normal and glaucomatous eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1981 Oct;21(4):563–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox B. K., Sakai L. Y., Keene D. R., Glanville R. W. Connective tissue microfibrils. Isolation and characterization of three large pepsin-resistant domains of fibrillin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21381–21385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall G. E., Konstas A. G., Abraham S., Lee W. R. Extracellular matrix in aged human ciliary body: an immunoelectron microscope study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1992 Jul;33(8):2546–2560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall G. E., Konstas A. G., Bechrakis N. E., Lee W. R. An immunoelectron microscope study of the aged human lens capsule. Exp Eye Res. 1992 Mar;54(3):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(92)90051-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall G. E., Konstas A. G., Lee W. R. Collagens in the aged human macular sclera. Curr Eye Res. 1993 Feb;12(2):143–153. doi: 10.3109/02713689308999482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall G. E., Konstas A. G., Lee W. R. Immunogold localization of type IV collagen and laminin in the aging human outflow system. Exp Eye Res. 1990 Dec;51(6):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(90)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall G. E., Konstas A. G., Lee W. R. Immunogold ultrastructural localization of collagens in the aged human outflow system. Ophthalmology. 1991 May;98(5):692–700. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(91)32232-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Baltz M. L., de Beer F. C., Dyck R. F., Holford S., Breathnach S. M., Black M. M., Tribe C. R., Evans D. J., Feinstein A. Biology of serum amyloid P component. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:286–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley H. A., Dorman-Pease M. E., Brown A. E. Quantitative study of collagen and elastin of the optic nerve head and sclera in human and experimental monkey glaucoma. Curr Eye Res. 1991 Sep;10(9):877–888. doi: 10.3109/02713689109013884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai L. Y., Keene D. R., Engvall E. Fibrillin, a new 350-kD glycoprotein, is a component of extracellular microfibrils. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2499–2509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E., Goldfischer S., Coltoff-Schiller B., Blumenfeld O. O. Extracellular matrix microfibrils are composed of core proteins coated with fibronectin. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Apr;33(4):268–274. doi: 10.1177/33.4.3980980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth C. A., Berry L., Kielty C. M. Microfibrillar components in dental pulp: presence of both type VI collagen- and fibrillin-containing microfibrils. Arch Oral Biol. 1992 Dec;37(12):1079–1084. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(92)90040-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spring F. A., Anstee D. J. Lectin-binding components of normal granulocytes and leukaemic myeloid cells. Biochem J. 1983 Sep 1;213(3):661–670. doi: 10.1042/bj2130661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. F., Hughes J. L., Kumaratilake J. S., Fanning J. C., Gibson M. A., Krishnan R., Cleary E. G. Post-embedding methods for immunolocalization of elastin and related components in tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1988 Dec;36(12):1543–1551. doi: 10.1177/36.12.3142951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]