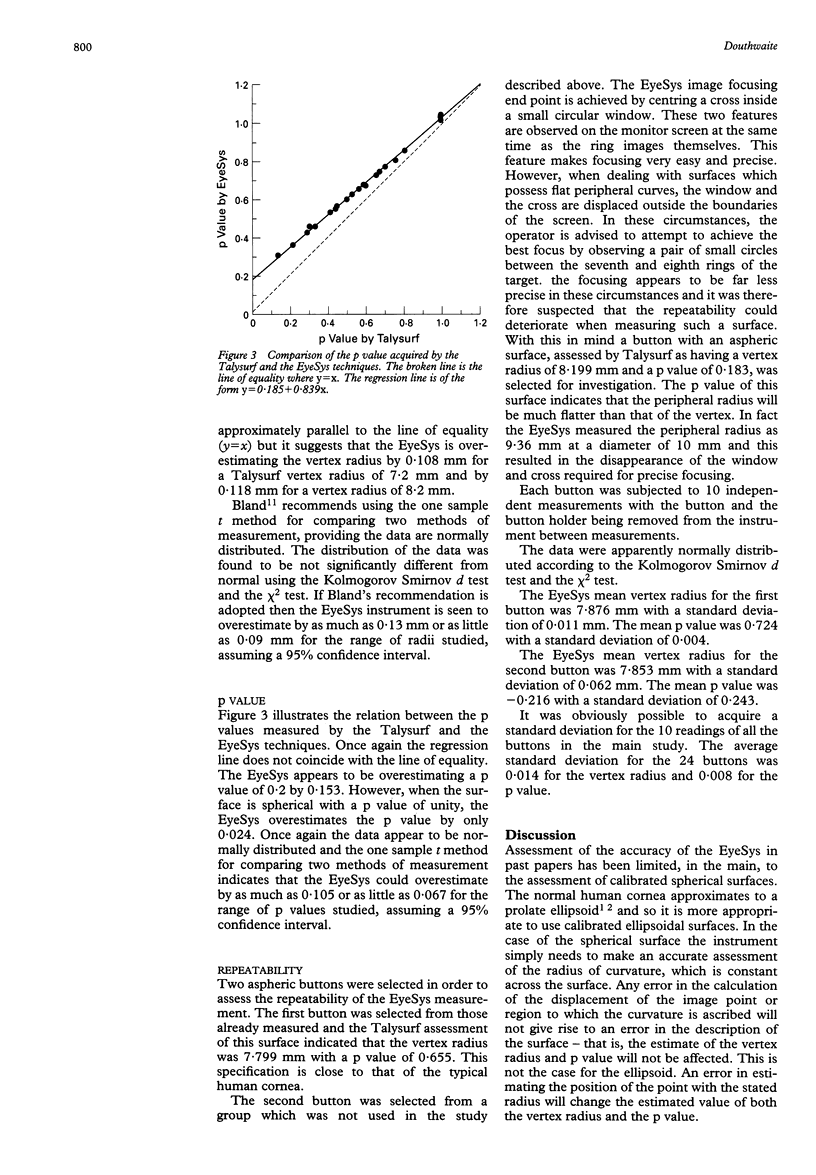
Abstract
AIMS/BACKGROUND--This study was carried out to assess the accuracy of the EyeSys videokeratoscope by using convex ellipsoidal surfaces of known form. METHODS--PMMA convex ellipsoidal buttons were calibrated using Form Talysurf analysis which allowed subsequent calculation of the vertex radius and p value of the surface. The EyeSys videokeratoscope was used to examine the same ellipsoids. The tabular data provided by the instrument software were used to plot a graph of r2 versus y2 where r is the measured radius at y, the distance from the corneal point being measured to the surface vertex. The intercept on the ordinate of this graph gives the vertex radius and the slope the p value. The results arising from the Talysurf and the EyeSys techniques were compared. RESULTS--The EyeSys videokeratoscope gave readings for both vertex radius and p value that were higher than those of the Talysurf analysis. The vertex radius was around 0.1 mm greater. The p value results were similar by the two methods for p values around unity but the EyeSys results were higher and the discrepancy increased as the p value approached that of a paraboloid. CONCLUSIONS--Although the videokeratoscope may be useful in comparative studies of the cornea, there must be some doubt about the absolute values displayed. The disagreement is sufficiently large to suggest that the instrument may not be accurate enough for contact lens fitting purposes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antalis J. J., Lembach R. G., Carney L. G. A comparison of the TMS-1 and the corneal analysis system for the evaluation of abnormal corneas. CLAO J. 1993 Jan;19(1):58–63. doi: 10.1097/00140068-199301000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A. G., Rabbetts R. B. What radius does the conventional keratometer measure? Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 1991 Jul;11(3):239–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillon M., Lydon D. P., Wilson C. Corneal topography: a clinical model. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 1986;6(1):47–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire L. J., Wilson S. E., Camp J. J., Verity S. Evaluating the reproducibility of topography systems on spherical surfaces. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993 Feb;111(2):259–262. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1993.01090020113034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarey B. E., Zurawski C. A., O'Shea D. S. Practical aspects of a corneal topography system. CLAO J. 1992 Oct;18(4):248–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. Y., Rice D. A., Klyce S. D. A new reconstruction algorithm for improvement of corneal topographical analysis. Refract Corneal Surg. 1989 Nov-Dec;5(6):379–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. E., Verity S. M., Conger D. L. Accuracy and precision of the corneal analysis system and the topographic modeling system. Cornea. 1992 Jan;11(1):28–35. doi: 10.1097/00003226-199201000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Saarloos P. P., Constable I. J. Improved method for calculation of corneal topography for any photokeratoscope geometry. Optom Vis Sci. 1991 Dec;68(12):960–965. doi: 10.1097/00006324-199112000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


