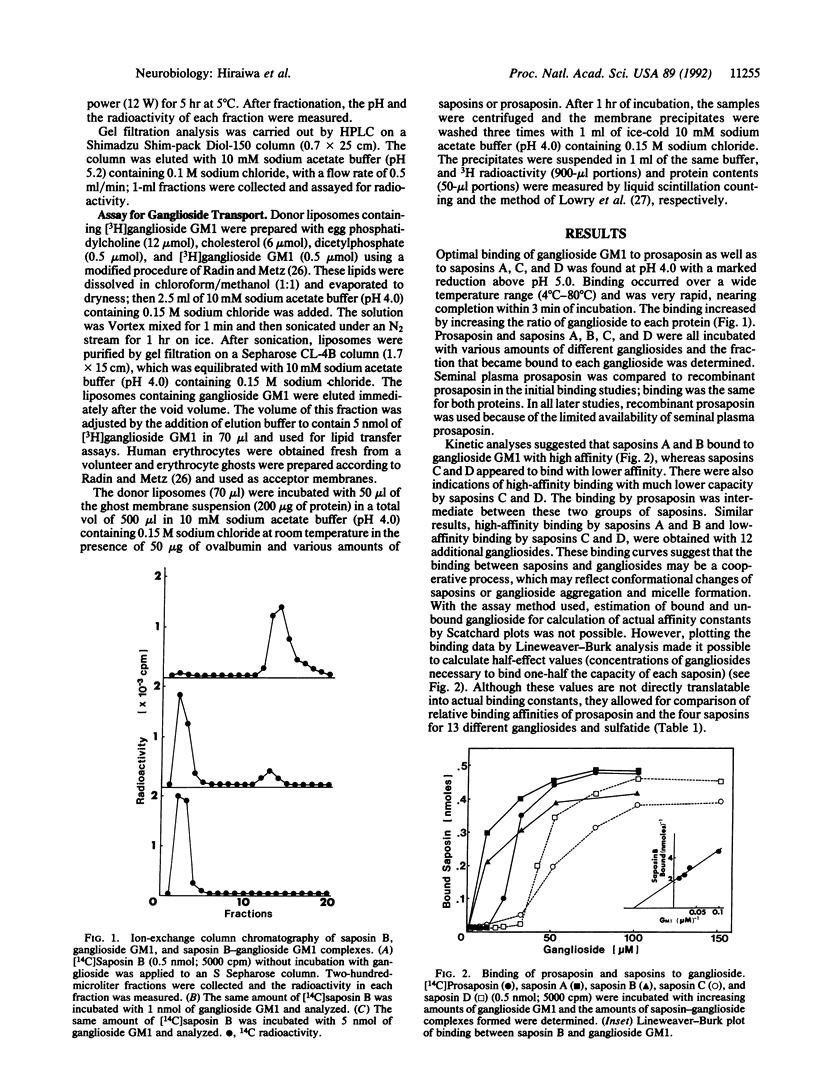
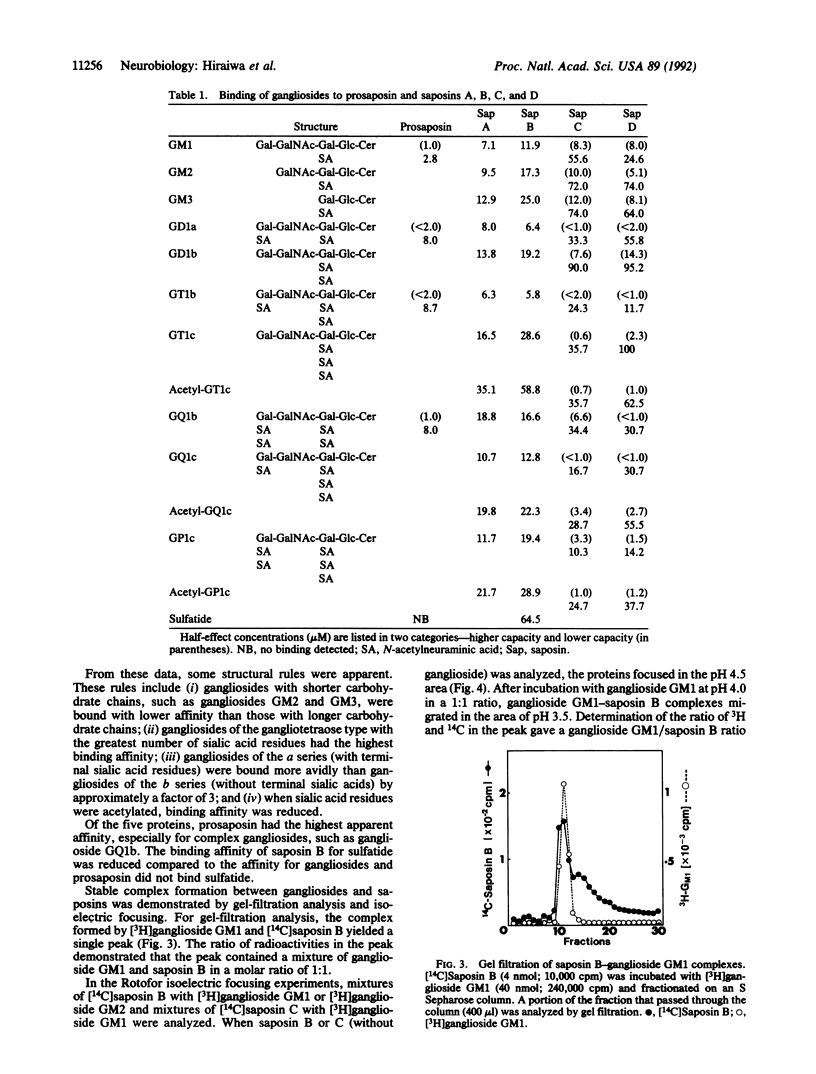
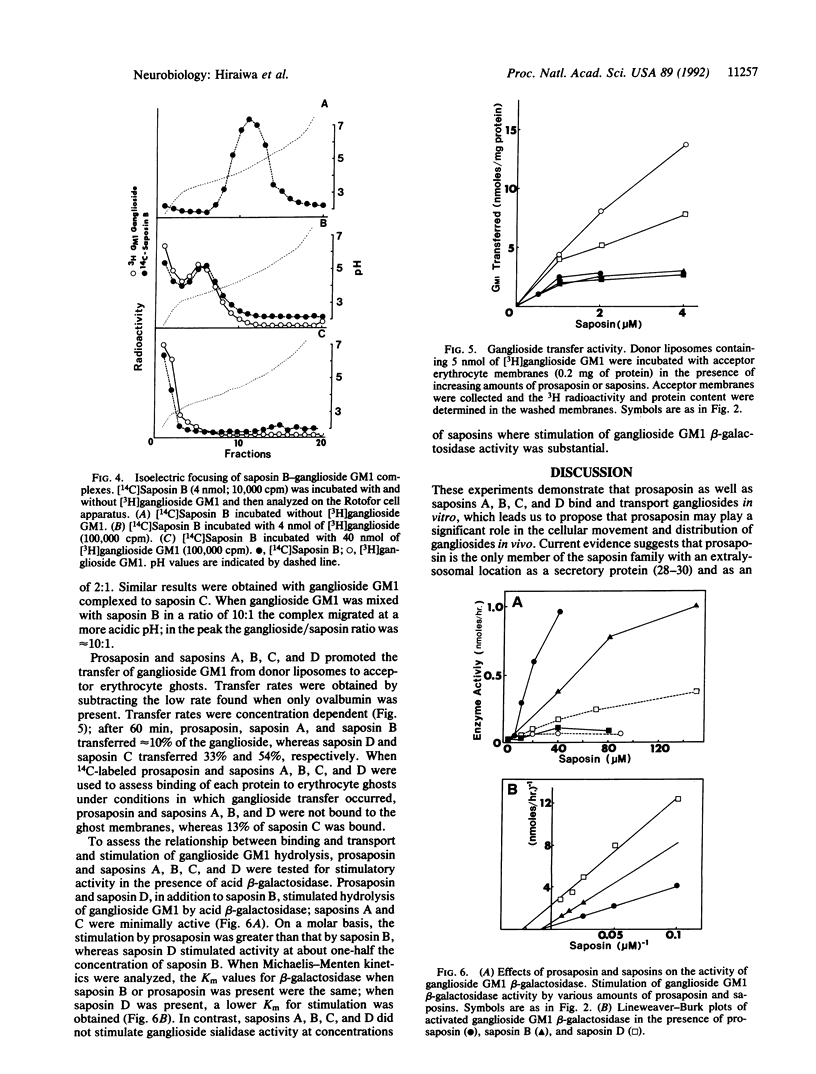
Abstract
Prosaposin, the precursor of saposins A, B, C, and D, which activate lysosomal hydrolysis of sphingolipids, exists in various tissues and body fluids and is especially abundant in the nervous system. Prosaposin and saposins A,B, C, and D formed stable complexes with 13 different gangliosides as measured by an assay using column chromatography. Gangliosides of the gangliotetraose type (a series) were bound with high affinity, whereas b series gangliosides, O-acetylated gangliosides, and gangliosides with shorter carbohydrate chains, were bound with lower affinity. Prosaposin and saposins transferred gangliosides from donor liposomes to erythrocyte ghost membranes. Prosaposin also stimulated ganglioside GM1 beta-galactosidase more than mature saposins. Prosaposin exists as a secretory protein and as an integral membrane protein, and we propose that prosaposin is active as a ganglioside binding and transport protein in vivo.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brady R. O., Fishman P. H. Biotransducers of membrane-mediated information. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1979;50:303–323. doi: 10.1002/9780470122952.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. E., Stephenson F. A., Markello T., Barenholz Y., Thompson T. E. Properties of a specific glycolipid transfer protein from bovine brain. Chem Phys Lipids. 1985 Aug 30;38(1-2):79–93. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(85)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabacungan J. C., Ahmed A. I., Feeney R. E. Amine boranes as alternative reducing agents for reductive alkylation of proteins. Anal Biochem. 1982 Aug;124(2):272–278. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus H., Louis J. C., Harth S., Mandel P. Gangliosides in cultured neurons. Neuroscience. 1980;5(9):1647–1655. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G., Jatzkewitz H. The activator of cerebroside sulphatase. Binding studies with enzyme and substrate demonstrating the detergent function of the activator protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Apr 12;481(2):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90288-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammon C. M., Vaswani K. K., Ledeen R. W. Isolation of two glycolipid transfer proteins from bovine brain: reactivity toward gangliosides and neutral glycosphingolipids. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 22;26(19):6239–6243. doi: 10.1021/bi00393a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghidoni R., Tettamanti G., Zambotti V. An improved procedure for the in vitro labeling of ganglioside. Ital J Biochem. 1974 Sep-Oct;23(5):320–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hineno T., Sano A., Kondoh K., Ueno S., Kakimoto Y., Yoshida K. Secretion of sphingolipid hydrolase activator precursor, prosaposin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 30;176(2):668–674. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80236-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraiwa M., Nishizawa M., Uda Y., Nakajima T., Miyatake T. Human placental sialidase: further purification and characterization. J Biochem. 1988 Jan;103(1):86–90. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraiwa M., Uda Y., Nishizawa M., Miyatake T. Human placental sialidase: partial purification and characterization. J Biochem. 1987 May;101(5):1273–1279. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Elwing H., Fredman P., Strannegård O., Svennerholm L. Gangliosides as receptors for bacterial toxins and Sendai virus. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1980;125:453–470. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-7844-0_40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondoh K., Hineno T., Sano A., Kakimoto Y. Isolation and characterization of prosaposin from human milk. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Nov 27;181(1):286–292. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81415-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki K., Okamura N., Kishimoto Y., Lee Y. C. Determination of gangliosides as 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazides by high-performance liquid chromatography. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):755–761. doi: 10.1042/bj2350755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto S., Yamamoto Y., O'Brien J. S., Kishimoto Y. Determination of saposin proteins (sphingolipid activator proteins) in human tissues. Anal Biochem. 1990 Nov 1;190(2):154–157. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden A. G., Tennant L. L., O'Brien J. S. GM1 ganglioside beta-galactosidase. A. Purification and studies of the enzyme from human liver. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):7969–7976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. S., Kishimoto Y. Saposin proteins: structure, function, and role in human lysosomal storage disorders. FASEB J. 1991 Mar 1;5(3):301–308. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.3.2001789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panzetta P., Maccioni H. J., Caputto R. Synthesis of retinal gangliosides during chick embryonic development. J Neurochem. 1980 Jul;35(1):100–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb12494.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purpura K. P., Baker H. J. Neurite induction in mature cortical neurones in feline GM1-ganglioside storage disease. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):553–554. doi: 10.1038/266553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radin N. S., Metz R. J. Cerebroside transfer protein. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:613–622. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijnboutt S., Aerts H. M., Geuze H. J., Tager J. M., Strous G. J. Mannose 6-phosphate-independent membrane association of cathepsin D, glucocerebrosidase, and sphingolipid-activating protein in HepG2 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):4862–4868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodden F. A., Wiegandt H., Bauer B. L. Gangliosides: the relevance of current research to neurosurgery. J Neurosurg. 1991 Apr;74(4):606–619. doi: 10.3171/jns.1991.74.4.0606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roisen F. J., Bartfeld H., Nagele R., Yorke G. Ganglioside stimulation of axonal sprouting in vitro. Science. 1981 Oct 30;214(4520):577–578. doi: 10.1126/science.7291999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzmann G., Sandhoff K. Metabolism and intracellular transport of glycosphingolipids. Biochemistry. 1990 Dec 11;29(49):10865–10871. doi: 10.1021/bi00501a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnino S., Chigorno V., Valsecchi M., Pitto M., Tettamanti G. Specific ganglioside-cell protein interactions: a study performed with GM1 ganglioside derivative containing photoactivable azide and rat cerebellar granule cells in culture. Neurochem Int. 1992 Apr;20(3):315–321. doi: 10.1016/0197-0186(92)90046-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvester S. R., Morales C., Oko R., Griswold M. D. Sulfated glycoprotein-1 (saposin precursor) in the reproductive tract of the male rat. Biol Reprod. 1989 Nov;41(5):941–948. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod41.5.941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Arai Y., Kishimoto Y. Characterization and regional distribution of individual gangliosides in goldfish central nervous system. J Neurochem. 1989 Jun;52(6):1931–1936. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07279.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiemeyer M., Swank-Hill P., Schnaar R. L. A membrane receptor for gangliosides is associated with central nervous system myelin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11990–11999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiemeyer M., Yasuda Y., Schnaar R. L. Ganglioside-specific binding protein on rat brain membranes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1671–1681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji S., Arita M., Nagai Y. GQ1b, a bioactive ganglioside that exhibits novel nerve growth factor (NGF)-like activities in the two neuroblastoma cell lines. J Biochem. 1983 Jul;94(1):303–306. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel A., Schwarzmann G., Sandhoff K. Glycosphingolipid specificity of the human sulfatide activator protein. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Sep 1;200(2):591–597. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates A. J. Gangliosides in the nervous system during development and regeneration. Neurochem Pathol. 1986 Dec;5(3):309–329. doi: 10.1007/BF02842941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


