Abstract
Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) is well known to occur in the promoter region of genes for transcription activation. However, when investigating the H3K4me3 profiles in the mouse cerebrum and testis, we discovered that H3K4me3 also has a significant enrichment at the 3′ end of actively transcribed (sense) genes, named as 3′-H3K4me3. 3′-H3K4me3 is associated with ∼15% of protein-coding genes in both tissues. In addition, we examined the transcriptional initiation signals including RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) binding sites and 5′-CAGE-tag that marks transcriptional start sites. Interestingly, we found that 3′-H3K4me3 is associated with the initiation of antisense transcription. Furthermore, 3′-H3K4me3 modification levels correlate positively with the antisense expression levels of the associated sense genes, implying that 3′-H3K4me3 is involved in the activation of antisense transcription. Taken together, our findings suggest that H3K4me3 may be involved in the regulation of antisense transcription that initiates from the 3′ end of sense genes. In addition, a positive correlation was also observed between the expression of antisense and the associated sense genes with 3′-H3K4me3 modification. More importantly, we observed the 3′-H3K4me3 enrichment among genes in human, fruitfly and Arabidopsis, and found that the sequences of 3′-H3K4me3-marked regions are highly conserved and essentially indistinguishable from known promoters in vertebrate. Therefore, we speculate that these 3′-H3K4me3-marked regions may serve as potential promoters for antisense transcription and 3′-H3K4me3 appear to be a universal epigenetic feature in eukaryotes. Our results provide a novel insight into the epigenetic roles of H3K4me3 and the regulatory mechanism of antisense transcription.
Keywords: Antisense initiation and activation, Antisense transcription, H3K4me3
Introduction
Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) is associated with gene activation and therefore it plays key roles in development and differentiation. H3K4me3, catalyzed by trithorax-group (trxG) proteins, activates transcription through the recruitment of nucleosome remodeling complexes and histone-modifying enzymes [1], [2], [3]. Genome-wide studies suggest that H3K4me3 often occurs at the 5′ promoter region of actively transcribed genes and associates with RNA polymerase II binding and transcriptional initiation signals [4], [5], [6], [7], [8].
Antisense transcription has been suggested to be widespread in mammalian genomes by transcriptomic studies over the past decade or so. In 2005, RIKEN Genome Exploration Research Group first reported that 50–70% of transcription units (TUs) in mouse contain antisense transcripts based on large-scale cDNA sequencing [9]. The fraction has been increased to more than 80% recently based on next-generation sequencing technologies [10], [11], [12]. Antisense RNAs have important functional roles in regulating gene expression and chromatin structure in eukaryotic cells, such as functioning in X-chromosome inactivation (Xist and Tsix) [13], genomic imprinting (Kcnq1ot1) [14], alternative splicing (RevErbAα) [15], RNA editing (Sas10) [16], mRNA stability (BACE1-AS) [17], and formation of endogenous siRNAs [18]. However, although their prevalence and regulatory roles have been well-characterized, details of the regulatory mechanisms involved in antisense transcription remain to be elucidated.
Here, we describe the enrichment of H3K4me3 at the 3′ end of a significant number of genes, when examining the profiles of H3K4me3 in the mouse cerebrum and testis. We also correlate such enrichment to transcriptional initiation signals (including RNAPII binding and 5′-CAGE-tag that marks the transcriptional start site) and antisense expression of the associated sense genes. The results show that 3′-H3K4me3 is closely associated with antisense transcription initiation and activation at the 3′ end of the associated sense genes. Therefore, we propose that H3K4me3 may play an epigenetic role in regulating antisense transcription, and antisense transcription could be initiated at the end of the sense genes.
Results
The 3′ end enrichment of H3K4me3 intervals
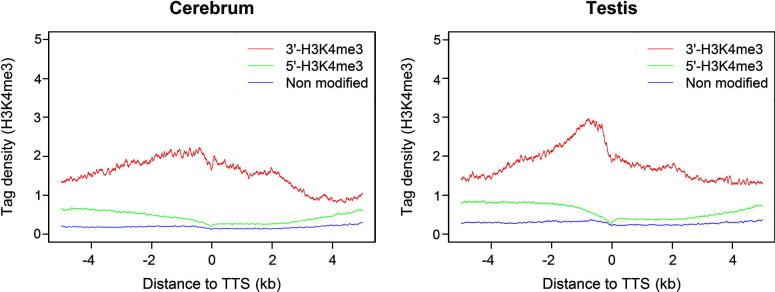
The public ChIP-seq data of H3K4me3 and pan-H3 that served as a control from the mouse cerebrum and testis were generated in our laboratory previously [19] (Manuscript No. GPB-D-12-00016). We examined the H3K4me3 enrichment intervals in the cerebrum and testis and identified 82,264 and 64,110 H3K4me3 intervals, respectively (see Table S2, S3 and S5 in [19]). Correlating H3K4me3 to the 21,215 known promoters inferred from the full-length transcripts deposited in Refseq [20], we found that 68% and 74% (ncerebrum = 14,474 and ntesits = 15,629) promoters show significant enrichment of H3K4me3 in the cerebrum and testis, respectively (see Table S7 in [19]), consistent with previous observations in mammalian cells [2], [21]. Unexpectedly, we detected obvious enrichment of H3K4me3 intervals at the 3′ end of actively transcribed (sense) genes, involving ∼15% of the mouse genes (Table S1). We named such a modification as 3′-H3K4me3 to differentiate it from the H3K4me3 enrichment at 5′ promoter regions (5′-H3K4me3). To better characterize 3′-H3K4me3, we classified mouse genes into three groups based on the ways they are modified by H3K4me3, which are 5′-H3K4me3-marked alone, 3′-H3K4me3-marked (with and without 5′-H3K4me3), and H3K4me3-unmarked. We aligned ChIP-seq reads to the 3′ end of these genes and observed that there is a considerable increase of H3K4me3 density around the 3′ end of 3′-H3K4me3-marked genes (Figure 1). The result of read profiling suggested that modified histones are concentrated both upstream and downstream of transcriptional termination sites (TTS), peaking at ∼1 kb upstream of TTS.
Figure 1.
The enrichment of H3K4me3 at the 3′ end of sense genes H3K4me3 profiles around transcription termination sites (TTS) of actively transcribed (sense) genes in the mouse cerebrum and testis were obtained from ChIP-seq data. Mouse genes are classified into three groups based on their statuses of H3K4me3: 3′-H3K4me3-marked (including those modified at both 5′ and 3′, and 3′ alone), 5′-H3K4me3-marked (modified at 5′ alone), and H3K4me3-unmarked genes. The tag density of H3K4me3 was plotted within the regions 5 kb upstream and downstream of TTS. H3K4me3 is significantly enriched around TTS of 3′-H3K4me3-marked genes but relatively low in genes that are not marked.
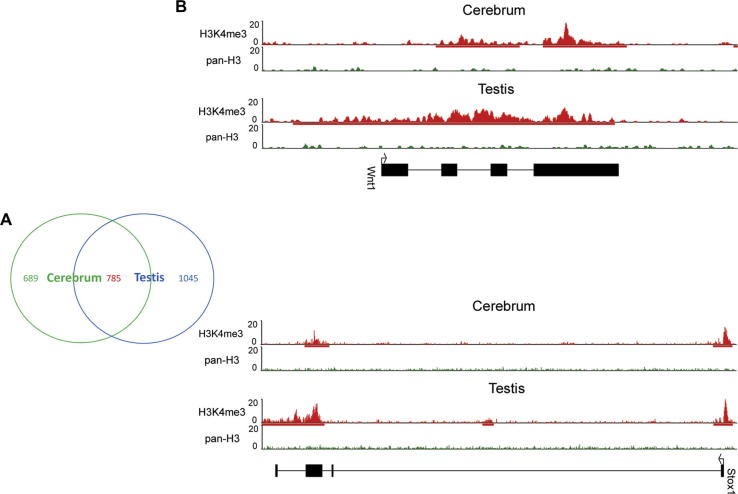
In the two mouse tissues examined, we identified 2519 genes in total associated with 3′-H3K4me3, of which 31% (785 genes) are shared by both tissues while the remaining is specific to either cerebrum or testis (Figure 2A). The majority of the 785 shared genes are primarily involved in the regulation of transcription, metabolic processes and biosynthesis, which are all essential cellular functions (Table S2). In contrast, the tissue-specific genes are related to development. For example, 689 genes that show 3′-H3K4me3 in cerebrum only are associated with cerebrum-specific expression (Table S3), and most of them are involved in neuron differentiation, axonogenesis, channel activity, and cell morphogenesis (Table S4). Similarly, 1045 genes that show testis-specific 3′-H3K4me3 exhibit testis-specific expression (Table S5), and are enriched in cell- and tissue-development related functions and transcription (Table S6), such as transcription factor activity, transcriptional regulation, endocrine system, cell fate commitment, dorsal/ventral pattern formation and gland development. For instance, Wnt1 [22] (cerebrum-specific) and Stox1 [23] (testis-specific) is involved in the Wnt signaling pathway and preeclampsia controlling polypoidization of extravillus trophoblast cells, respectively (Figure 2B). Both genes show tissue-specific 3′-H3K4me3. These results suggest that 3′-H3K4me3 is essentially tissue-specific and most likely associated with tissue-specific development.
Figure 2.
Comparison of genes with 3′-H3K4me3 between mouse cerebrum and testis (A) Numbers of tissue-specific genes modified with 3′-H3K4me3 and genes shared by both cerebrum and testis. There are 785 genes commonly modified in both tissues, 689 uniquely-modified genes in the cerebrum, and 1045 uniquely-modified genes in the testis. (B) The Wnt1 and Stox1 genes, as examples, show tissue-specific 3′ H3K4me3. We examined the densities of H3K4me3 (red) and pan-H3 (green) for both genes.
We extended the survey to other eukaryotes, such as human [5], fruitfly (Drosophila) (Sun et al., personal communication), and Arabidopsis [24]. We consistently observed the 3′ end enrichment of H3K4me3 among their genes (Table S7–S9). Moreover, most 3′-H3K4me3-assoicated genes are enriched among genes for transcription related function, metabolic/biosynthetic processes, and tissue development in human (Table S10), cytosolic ribosomal, enzyme and cytoskeleton in fly (Table S11), and response to stimulus, transcription, gene silencing, and nucleosome assembly in Arabidopsis (Table S12), respectively. Therefore, we speculate that 3′-H3K4me3 appear to be a universal epigenetic feature in eukaryotes.
The 3′-H3K4me3 association with antisense transcriptional initiation
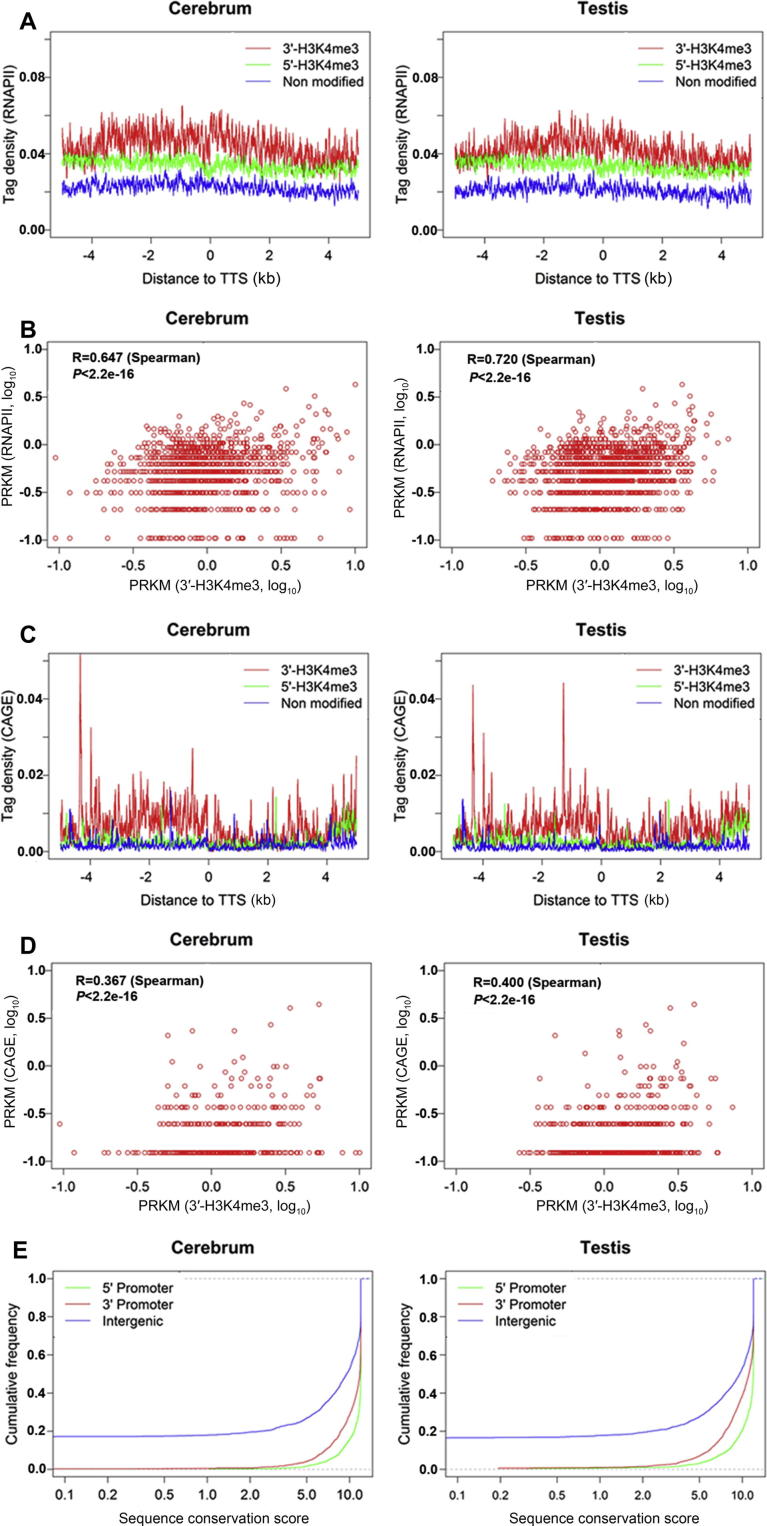
Since 5′-H3K4me3 is associated with RNAPII binding and transcriptional activation, we were curious about whether 3′-H3K4me3 has a similar function in regulating transcription. To test this possibility, we first investigated the binding of RNAPII around TTS using ChiP-seq (RNAPII) data of mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs) [4]. We observed an obvious enrichment of RNAPII at TTS of 3′-H3K4me3-marked genes (Figure 3A) but such an enrichment is absent for genes without 3′-H3K4me3. Moreover, we found that 3′-H3K4me3 levels are positively correlated with levels of RNAPII binding within ±2 kb regions of TTS according to the correlation coefficient (Figure 3B). The RNAPII enrichment upstream and downstream of TTS correlates with the presence of 3′-H3K4me3 signals, which suggests that 3′-H3K4me3 may be able to positively regulate RNAPII binding at the 3′ end of the sense genes.
Figure 3.
Biological features associated with 3′-H3K4me3 in the two tissues (A) RNAPII binding profiles around the TTS of sense genes. RNAPII data is from mouse embryonic stem cells. The tag density of RNAPII binding was plotted within the 5 kb regions upstream and downstream of TTS. RNAPII binding shows obvious enrichment around TTS of the 3′-H3K4me3-marked genes but is relatively low in 3′-H3K4me3-unmarked genes. (B) The correlation between 3′-H3K4me3 and RNAPII binding. Among 3′-H3K4me3-marked genes, 3′-H3K4me3 levels are positively correlated with the density of RNAPII binding. (C) 5′-CAGE-tag profiles around TTS of sense genes. 5′-CAGE tags data is from multiple mouse tissues published by the Fantom3 project. Antisense 5′-CAGE-tag profiles were plotted within the regions 5 kb upstream and downstream of TTS. 5′-CAGE-tags show obvious enrichment around TTS of 3′-H3K4me3-marked genes but are relative low in 3′-H3K4me3-unmarked genes. (D) The correlation between 3′-H3K4me3 and 5′-CAGE-tag density. Among 3′-H3K4me3-marked genes, 3′-H3K4me3 levels show positive correlation with 5′-CAGE-tag density. (E) Sequence conservation of 3′-H3K4me3-marked regions. Cumulative distribution of sequence conservation values are shown across mammals for the known promoters (5′ promoter), 3′-H3K4me3-marked regions (3′ promoter), and intergenic regions (intergenic). The conservative values are derived from an alignment of 29 vertebrate genomes to the mouse genome.
We next obtained 5′-CAGE-tags (generated by capturing the 7-methylguanosine cap at the 5′ end of RNAPII transcripts in the Fantom3 project from mouse multiple tissues) that mark transcriptional start sites (TSS) and examined their distribution around TTS [25]. We found a noticeable enrichment of 5′-CAGE-tags in the antisense direction from the TTS in 3′-H3K4me3-marked genes (Figure 3C). In contrast, the tag coverage was relatively poor for genes without 3′-H3K4me3. The enrichment of 5′-CAGE-tags (relative to sense genes) provides direct evidence to support antisense transcriptional initiation from the 3′ end of 3′-H3K4me3-marked genes. Furthermore, we found that the density of 5′-CAGE-tags in the antisense direction from TTS is positively correlated with 3′-H3K4me3 levels. These results suggest that 3′-H3K4me3 may be directly involved in controlling antisense transcriptional initiation (Figure 3D).
Since 3′-H3K4me3 is associated with antisense transcriptional initiation, we speculated that 3′-H3K4me3-marked regions may serve as potential promoters for antisense transcription. We further investigated sequence conservation for potential promoters using conservation scores from an alignment of 29 vertebrate genomes to the mouse genome, and found that these potential promoter sequences are highly conserved and essentially indistinguishable from known promoters (Figure 3E). This evolutionary conservation indicates that these potential promoters may undergo strong selection to maintain their functional roles.
We also examined the tag distribution of antisense transcripts across sense genes. We found that antisense transcripts show more pronounced tag distribution within gene body regions but not outside the 5′ and 3′ boundaries among 3′-H3K4me3-marked genes (Figure S1). This phenomenon is more obvious for genes that only have 3′-H3K4me3 but do not have 5′-H3K4me3 (3′-H3K4me3 alone, ∼2% of total genes). These clear boundaries and the distribution of antisense transcripts for genes with 3′-H3K4me3 only further supported the idea that antisense transcription may be initiated from the 3′ end of sense genes.
The correlation between 3′-H3K4me3 and antisense transcriptional level
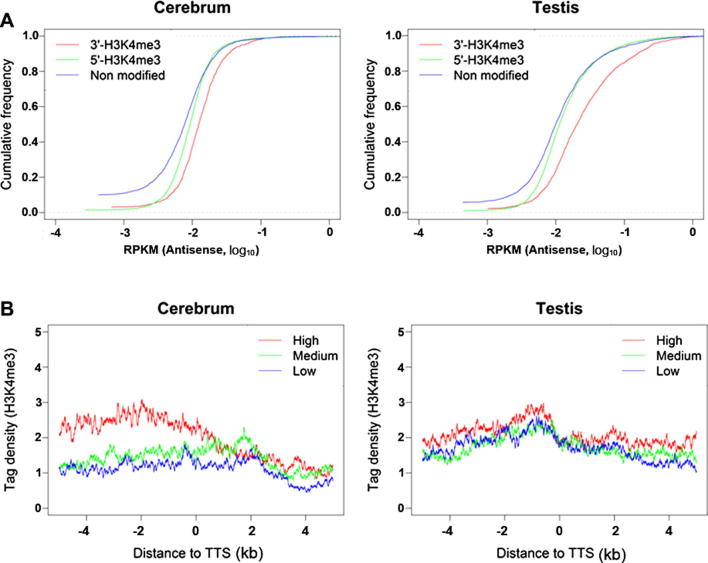
Since 3′-H3K4me3 is associated with antisense transcriptional initiation, we investigated the relationship between 3′-H3K4me3 and antisense expression level of the associated sense genes. We obtained strand-specific gene expression profiles from the mouse cerebrum and testis using the RNA-seq method. We measured the antisense expression levels by calculating the density of uniquely-mapped reads as “reads per kilobase of gene model per million mapped reads” (RPKM). We found that 3′-H3K4me3-marked genes have much higher antisense transcription activity than those without 3′-H3K4me3 (Figure 4A). Moreover, there is a positive correlation between the levels of antisense expression and 3′-H3K4me3 among 3′-H3K4me3-marked genes (Figure 4B). Genes with higher 3′-H3K4me3 levels show significantly higher antisense expression.
Figure 4.
The correlation between 3′-H3K4me3 level and antisense transcriptional level in mouse cerebrum and testis (A) Cumulative distribution of antisense expression (RPKM values) for 3′-H3K4me3-marked, 5′-H3K4me3-marked, and H3K4me3-unmarked genes. 3′-H3K4me3-marked genes show higher antisense expression. (B) 3′-H3K4me3 profiles around TTS of sense genes. 3′-H3K4me3-marked genes are classified into high, medium, and low antisense-expression according to their antisense expression levels. 3′-H3K4me3 levels are positively correlated with the antisense expression level.
The correlation between sense and antisense expression
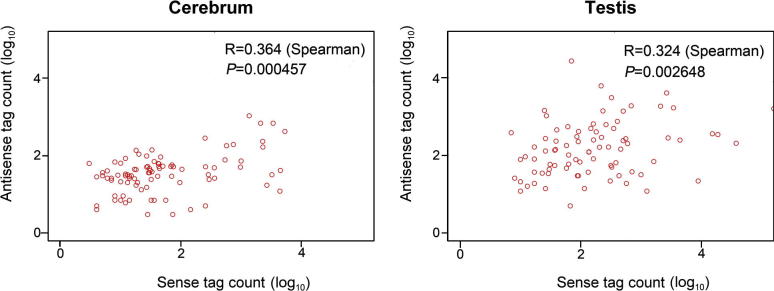
To investigate the potential role of antisense activation, we investigated the relationship between sense and antisense expression among 3′-H3K4me3-marked genes. We found that there is a positive correlation between sense and antisense expression among 3′-H3K4me3-marked genes (Figure 5). This result suggested that antisense activation might play a role in promoting sense expression of the associated genes, which is also consistent with previous reports that expression levels of antisense transcripts can be positively correlated with their sense transcripts [9], [26].
Figure 5.
The correlation between sense and antisense expression among 3′-H3K4me3-marked genes in both tissues We plotted the number of tags within exonic regions as a function of gene expression levels.
Discussion
In this study, we discovered that H3K4me3, which is highly represented in promoter regions, tends to occur at the 3′ end of actively transcribed (sense) genes. Modified histones are concentrated upstream and downstream of transcriptional termination sites (peaking ∼1 kb upstream of TTS). Such 3′ end enrichment of H3K4me3 is observed not only in the mouse, but also in the human, Drosophila, and Arabidopsis, suggesting that it represents a universal epigenetic feature of eukaryotes. Further analyzes suggest that 3′-H3K4me3 is associated with antisense transcriptional initiation and activation. Therefore, we hypothesize that 3′-H3K4me3 plays a key role in the regulation of antisense transcription.
Antisense transcription initiating at the end of genes is an important molecular process. In fact, by examining the distribution of antisense transcripts across genes, we found that antisense transcripts show more pronounced tag density within body regions but not outside the 5′ and 3′ boundaries among 3′-H3K4me3-marked genes (Figure S1). The phenomenon is more obvious for genes that only have 3′-H3K4me3 but do not have 5′-H3K4me3. Since 5′-H3K4me3 is often associated with the enrichment of promoter-associated small RNAs [27], [28], [29], a clear boundary of antisense transcripts may not be observed at the 5′ end if the genes have 5′-H3K4me3. These clear boundaries and the distribution of antisense transcripts for genes with only 3′-H3K4me3 further supported the idea that antisense transcription may be initiated from the 3′ end of sense genes. Moreover, this result implies that antisense transcription may be elongated and eventually terminated at their 5′ end. However, there are two concerns about this implication. First, the enrichment of antisense transcripts within gene body regions and the weak signals beyond the 5′ and 3′ gene boundaries seem to contradict previous reports that antisense transcripts are enriched in both promoter and terminal regions of the sense genes [27], [28], [29], [30], [31], [32]. The promoter- and terminus-associated antisense transcripts belong to a small RNA class [31], [32]. For promoter-associated antisense RNAs that have been well-characterized, they are thought to be produced by divergent transcriptional activity, and overlap with paused RNA polymerase II and active chromatin marks, such as H3K4me3, and the observation suggested a role for local RNA accumulation in maintaining the dynamic chromatin state that is required for promoter activity [29], [30]. In fact, the enrichment of promoter-associated antisense RNAs can be found in the present datasets, and is also well associated with genes possessing 5′-H3K4me3. However, the presence of these antisense RNAs leads to difficulty in observing enrichment of antisense transcripts within gene body regions. Therefore, our finding is consistent with previous studies, but also indicates that antisense transcripts are indeed enriched across gene body regions. The second concern is that the enrichment of antisense transcripts within the gene body is obvious in mouse testis, but unclear in the cerebrum. Currently, we speculate that this inconsistency may be tissue-specific.
In addition, some data used for this analysis are not from the mouse cerebrum and testis, such as RNAPII binding data from ESCs and 5′-CAGE-tags from multiple mouse tissues. Since these biological processes are expected to vary among cell types or tissues, it is reasonable to expect that there are discrepancies between our calculations and those made from the same cell type or tissue. The finding reported here should therefore be considered as a lower bound of the actual results.
Conclusion
In summary, based on an integrated analysis of chromatin signatures, including H3K4me3, antisense RNA profiling, RNAPII binding, and 5′-CAGE-tagging in mouse tissues, we proposed that H3K4me3 is involved in the regulation of antisense transcription initiated from the 3′ end of the sense genes. This study significantly advances our understanding of the molecular processes of antisense transcription and its epigenetic regulation.
Materials and methods
Datasets
We obtained genome-wide profiles of H3K4me3 and pan-H3 based on ChIP-seq data and defined sense and antisense expression based on rmRNA-seq data for the cerebrum and testis. Both datasets were generated in our lab that can be publicly available at the NCBI (SRA009022, SRA010955 and SRA039962). We collected ChIP-seq data for RNAPII from mouse embryonic stem cells (ftp://ftp.broad.mit.edu/pub/papers/chipseq/) and 5′-CAGE tags from multiple mouse tissues published by the Fantom3 project (http://www.fantom3.gsc.riken.jp/db/). In addition, we obtained the H3K4me3 profiles of human T cells from a public release (http://www.dir.nhlbi.nih.gov/papers/lmi/epigenomes/hgtcell.aspx), Drosophila S2 cell (unpublished data), and Arabidopsis under water-stress conditions from NCBI (GSE11658).
Identification of H3K4me3-enriched intervals
We defined H3K4me3-enriched intervals using the SICER program (v1.03) [33]. We ran this program with a control library (pan-H3). Significant islands were found with a window and gap sizes of 200 bp as well as 1E-3 for False Discovery Rate (FDR). We also used the default parameters for other organisms (Human, fruitfly, and Arabidopsis) to define H3K4me3-enriched intervals with or without control libraries (200-bp window, 600-bp gap, and 1E-3 FDR for samples with control libraries; 200-bp window, 400-bp gap, and 1E-2 FDR for samples without control libraries).
Definition of 3′-H3K4me3 and 5′-H3K4me3
Initially, we obtained transcription start sites and transcription termination sites based on full-length transcripts deposited in RefSeq. 3′-H3K4me3 was defined as H3K4me3-enriched intervals overlapping with downstream TTS of sense genes (2 kb for mouse and human; 200 bp for Drosophila and Arabidopsis). To make sure that 3′-H3K4me3 does not overlap with flanking genes, we removed genes whose minimal distances between the two flanking genes are less than 4 kb (mouse and human) or 400 bp (Drosophila and Arabidopsis). 5′-H3K4me3 was defined as H3K4me3-enriched intervals overlapping with the upstream TSS regions of sense genes (2 kb for mouse and human; 200 bp for fruitfly and Arabidopsis).
Strand specificity of rmRNA-seq data
We used our rmRNA-seq data to define antisense expression in the mouse testis. We evaluated the strand specificity of rmRNA-seq data using the SOLiD sequencing platform and based on the fact that antisense transcripts undergo fewer splicing events. By mapping the reads to an exon-exon junction database, we verified that ∼99.99% of the junction reads were in the sense orientation in both tissues and the result suggested that rmRNA-seq data can be used to determine directionality of the transcripts. The exon-junction database was constructed by extracting 25 nt donor and 25 nt acceptor sequences from all possible exon–exon junction combinations based on RefSeq gene annotation [20]. The junction database not only includes normal junction sequences but also possible exon-exon junction sequences due to exon-skipping events. Furthermore, we estimated the percentage of sense and antisense reads within exon regions, and found that ∼98% reads are attributable to sense exons and the rest (∼2%) belong to antisense exons. Since antisense transcripts show much lower tag abundance than sense transcripts, this result is also useful for determining the directionality of transcripts based on rmRNA-seq data.
Sense and antisense expression levels
Sense and antisense expression levels were measured by calculating the density of uniquely-mapped reads as “reads per kilobase of gene model per million mapped reads” (RPKM) [12]. To be more accurate, we removed reads within 1 kb regions downstream of TSS for antisense expression since they are associated with divergent transcription from TSS and are highly abundant.
Modification level of RNAPII and 5′-CAGE
The level of RNAPII binding and 5′-CAGE-tag coverage around the 3′ end of genes were measured by counting the number of reads within the vicinity of upstream and downstream 2 kb sequences centered at TTS. Moreover, we normalized modification level by calculating RPKM for target regions.
Conservation of 3′-H3K4me3-associated promoters
To estimate the conservation of 3′-H3K4me3-associated promoters, we used conservative scores derived from an alignment of 29 vertebrate genomes to mouse genome from the UCSC database [34]. We calculated maximal scores in a 12 bp window and a step length of 1 bp for every 3′-H3K4me3-associated promoter (from TTS of a sense gene to 2 kb downstream), 5′ promoter (2 kb upstream from TSS of a sense gene), and random intergenic region (2 kb length).
Competing interests
The authors have declared that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
J Y, S H., F S and P C designed this analysis. P C, W L and Y Z carried out data analysis and drafted the manuscript. Q L, F D and C X participated in data collection and sequence alignment. S S and J G helped to analyze the data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by Knowledge Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. KSCX2-EW-R-01-04), Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 90919024 and 30900831) and the National Basic Research Program (973 Program) from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. 2011CB944100).
Footnotes
Supplementary data associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2012.05.001.
Contributor Information
Songnian Hu, Email: husn@big.ac.cn.
Jun Yu, Email: junyu@big.ac.cn.
Appendix Supplementary. material
Figure S1. Antisense read distribution across gene loci. Genes were classified into three groups based on the status of H3K4me3: 3′-H3K4me3 (modified at both 5′ and 3′, and 3′ alone), 5′-H3K4me3 (modified at 5′ alone), and non-modified (without H3K4me3). We further separated a new gene groups, 3′-H3K4me3 alone (modified at 3′ alone), from 3′-H3K4me3. We plotted the antisense read density over these genes in the different groups. Antisense transcripts show an obvious enrichment within the gene body regions of the genes with only 3′-H3K4me3 and a sharp decrease outside the 5′ and 3′ boundaries.
Table S9. List of genes with 3′-H3K4me3 modification in Arabidopsis.
Table S10. Functional classification of the genes with 3′-H3K4me3 in human CD4+ T cells.
Table S11. Functional classification of the genes with 3′-H3K4me3 in Drosophila.
Table S12. Functional classification of the genes with 3′-H3K4me3 in Arabidopsis.
Table S1. List of genes with H3K4me3 modification in cerebrum and testis.
Table S2. Functional classification of genes modified with 3′-H3K4me3 in both cerebrum and testis.
Table S3. The result of aligning 689 cerebrum-specific genes with 3′-H3K4me3 to Uniprot Tissue database.
Table S4. Functional classification of cerebrum-specific genes with 3′-H3K4me3.
Table S5. The result of aligning 1,045 testis-specific genes with 3′-H3K4me3 to Uniprot Tissue database.
Table S6. Functional classification of testis-specific genes with 3′-H3K4me3.
Table S7. List of genes with 3′-H3K4me3 modification in human CD4+ T cells.
Table S8. List of genes with 3′-H3K4me3 modification in Drosophila.
References
- 1.Santos-Rosa H. Active genes are tri-methylated at K4 of histone H3. Nature. 2002;419:407–411. doi: 10.1038/nature01080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bernstein B.E. Genomic maps and comparative analysis of histone modifications in human and mouse. Cell. 2005;120:169–181. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wysocka J. Histone arginine methylation and its dynamic regulation. Front Biosci. 2006;11:344–355. doi: 10.2741/1802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mikkelsen T.S. Genome-wide maps of chromatin state in pluripotent and lineage-committed cells. Nature. 2007;448:553–560. doi: 10.1038/nature06008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Barski A. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell. 2007;129:823–837. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wei G. Global mapping of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 reveals specificity and plasticity in lineage fate determination of differentiating CD4+ T cells. Immunity. 2009;30:155–167. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.12.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cui K. Chromatin signatures in multipotent human hematopoietic stem cells indicate the fate of bivalent genes during differentiation. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;4:80–93. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2008.11.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zhao X.D. Whole-genome mapping of histone H3 Lys4 and 27 trimethylations reveals distinct genomic compartments in human embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2007;1:286–298. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2007.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Katayama S. Antisense transcription in the mammalian transcriptome. Science. 2005;309:1564–1566. doi: 10.1126/science.1112009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cui P. A comparison between ribo-minus RNA-sequencing and polyA-selected RNA-sequencing. Genomics. 2010;96:259–265. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2010.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Faghihi M.A., Wahlestedt C. Regulatory roles of natural antisense transcripts. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:637–643. doi: 10.1038/nrm2738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mortazavi A. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods. 2008;5:621–628. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ohhata T. Crucial role of antisense transcription across the Xist promoter in Tsix-mediated Xist chromatin modification. Development. 2008;135:227–235. doi: 10.1242/dev.008490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pandey R.R. Kcnq1ot1 antisense noncoding RNA mediates lineage-specific transcriptional silencing through chromatin-level regulation. Mol Cell. 2008;32:232–246. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.08.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hastings M.L. Expression of the thyroid hormone receptor gene, erbAalpha, in B lymphocytes: alternative mRNA processing is independent of differentiation but correlates with antisense RNA levels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:4296–4300. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.21.4296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Peters N.T. RNA editing and regulation of Drosophila 4f-rnp expression by sas-10 antisense readthrough mRNA transcripts. RNA. 2003;9:698–710. doi: 10.1261/rna.2120703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Faghihi M.A. Expression of a noncoding RNA is elevated in Alzheimer’s disease and drives rapid feed-forward regulation of beta-secretase. Nat Med. 2008;14:723–730. doi: 10.1038/nm1784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Borsani O. Endogenous siRNAs derived from a pair of natural cis-antisense transcripts regulate salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Cell. 2005;123:1279–1291. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.11.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cui P., Liu W., Zhao Y., Lin Q., Zhang D., Ding F. Comparative analyses of H3K4 and H3K27 trimethylations between the mouse cerebrum and testis. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2012;10:82–93. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2012.05.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pruitt K.D. NCBI reference sequences (RefSeq): a curated non-redundant sequence database of genomes, transcripts and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:D61–65. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kim T.H. A high-resolution map of active promoters in the human genome. Nature. 2005;436:876–880. doi: 10.1038/nature03877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bejsovec A. Wnt signalling shows its versatility. Curr Biol. 1999;9:R684–R687. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(99)80439-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.van Dijk M. Maternal segregation of the Dutch preeclampsia locus at 10q22 with a new member of the winged helix gene family. Nat Genet. 2005;37:514–519. doi: 10.1038/ng1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.van Dijk K. Dynamic changes in genome-wide histone H3 lysine 4 methylation patterns in response to dehydration stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2010;10:238. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Carninci P. The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science. 2005;309:1559–1563. doi: 10.1126/science.1112014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Okada Y. Comparative expression analysis uncovers novel features of endogenous antisense transcription. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17:1631–1640. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.He Y. The antisense transcriptomes of human cells. Science. 2008;322:1855–1857. doi: 10.1126/science.1163853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Core L.J. Nascent RNA sequencing reveals widespread pausing and divergent initiation at human promoters. Science. 2008;322:1845–1848. doi: 10.1126/science.1162228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Seila A.C. Divergent transcription from active promoters. Science. 2008;322:1849–1851. doi: 10.1126/science.1162253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Preker P. RNA exosome depletion reveals transcription upstream of active human promoters. Science. 2008;322:1851–1854. doi: 10.1126/science.1164096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Borel C. Mapping of small RNAs in the human ENCODE regions. Am J Hum Genet. 2008;82:971–981. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.02.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kapranov P. RNA maps reveal new RNA classes and a possible function for pervasive transcription. Science. 2007;316:1484–1488. doi: 10.1126/science.1138341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zang C. A clustering approach for identification of enriched domains from histone modification ChIP-Seq data. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:1952–1958. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Miller W. 28-Way vertebrate alignment and conservation track in the UCSC Genome Browser. Genome Res. 2007;17:1797–1808. doi: 10.1101/gr.6761107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1. Antisense read distribution across gene loci. Genes were classified into three groups based on the status of H3K4me3: 3′-H3K4me3 (modified at both 5′ and 3′, and 3′ alone), 5′-H3K4me3 (modified at 5′ alone), and non-modified (without H3K4me3). We further separated a new gene groups, 3′-H3K4me3 alone (modified at 3′ alone), from 3′-H3K4me3. We plotted the antisense read density over these genes in the different groups. Antisense transcripts show an obvious enrichment within the gene body regions of the genes with only 3′-H3K4me3 and a sharp decrease outside the 5′ and 3′ boundaries.
Table S9. List of genes with 3′-H3K4me3 modification in Arabidopsis.
Table S10. Functional classification of the genes with 3′-H3K4me3 in human CD4+ T cells.
Table S11. Functional classification of the genes with 3′-H3K4me3 in Drosophila.
Table S12. Functional classification of the genes with 3′-H3K4me3 in Arabidopsis.
Table S1. List of genes with H3K4me3 modification in cerebrum and testis.
Table S2. Functional classification of genes modified with 3′-H3K4me3 in both cerebrum and testis.
Table S3. The result of aligning 689 cerebrum-specific genes with 3′-H3K4me3 to Uniprot Tissue database.
Table S4. Functional classification of cerebrum-specific genes with 3′-H3K4me3.
Table S5. The result of aligning 1,045 testis-specific genes with 3′-H3K4me3 to Uniprot Tissue database.
Table S6. Functional classification of testis-specific genes with 3′-H3K4me3.
Table S7. List of genes with 3′-H3K4me3 modification in human CD4+ T cells.
Table S8. List of genes with 3′-H3K4me3 modification in Drosophila.