Abstract
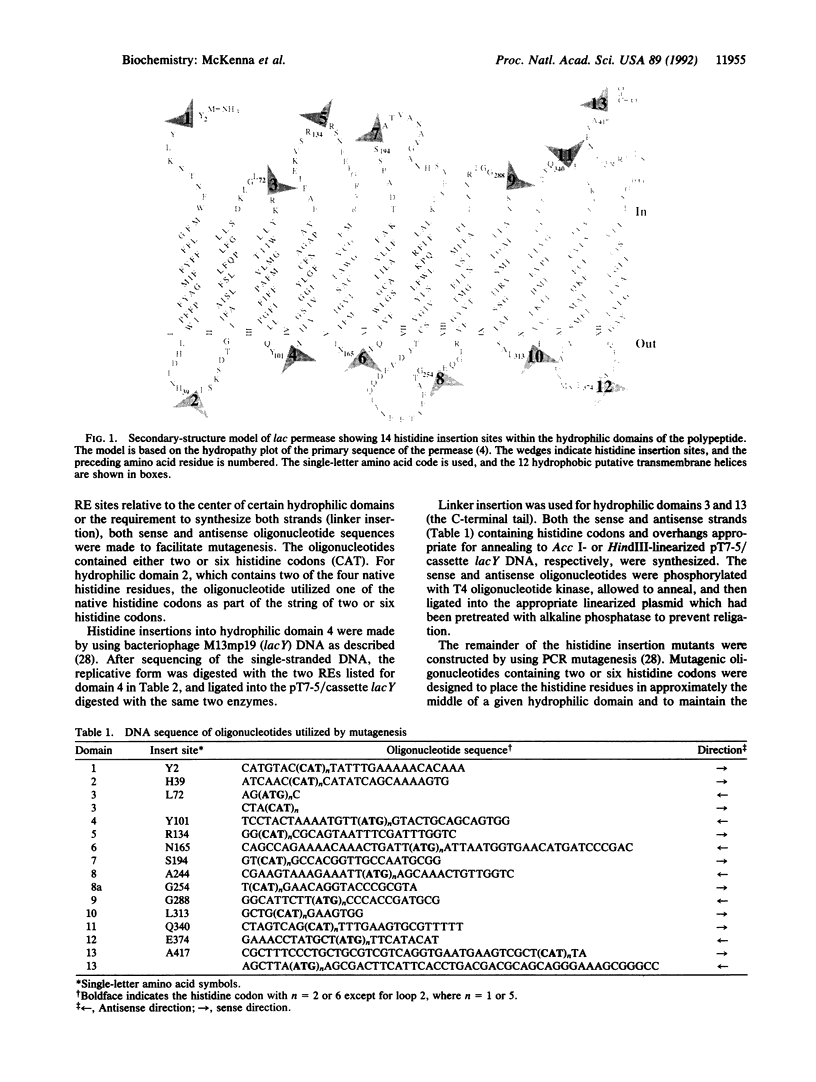
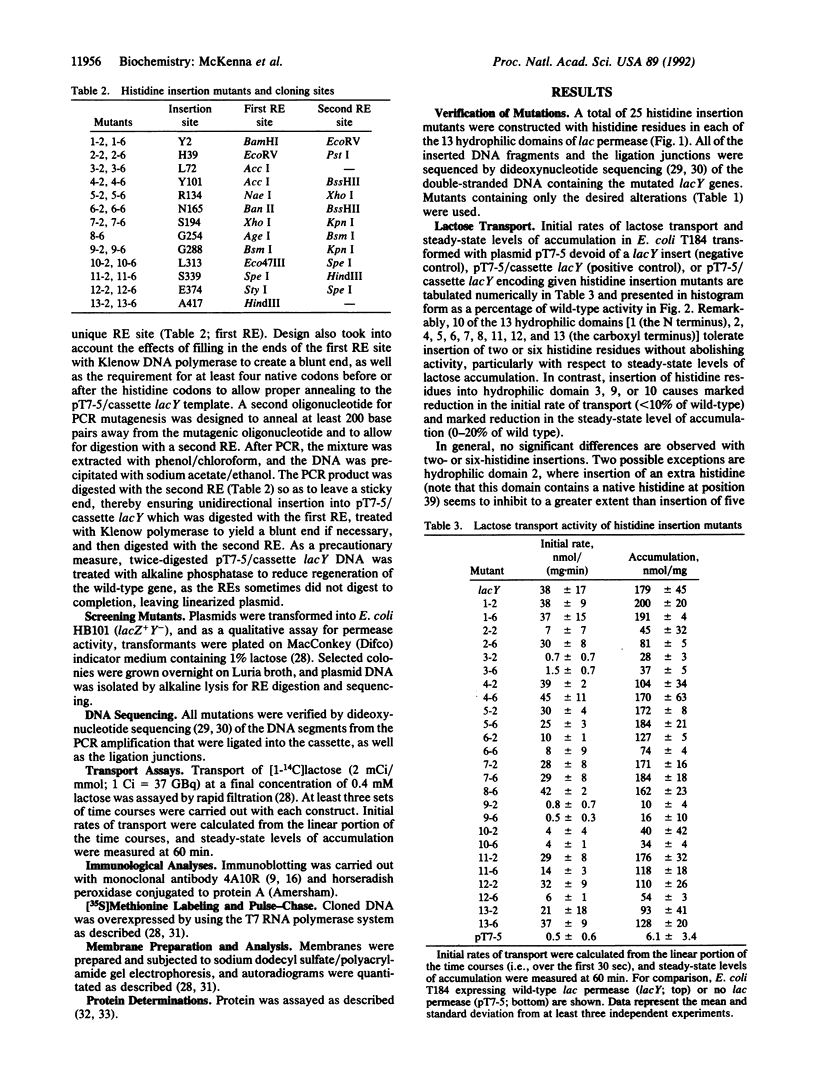
The lactose permease of Escherichia coli is a membrane transport protein postulated to contain a hydrophilic N terminus (hydrophilic domain 1), 12 hydrophobic transmembrane alpha-helices that traverse the membrane in zigzag fashion connected by hydrophilic domains, and a hydrophilic C terminus (hydrophilic domain 13). To test whether the hydrophilic domains are important for function, each domain was independently disrupted by insertion of two or six contiguous histidine residues, and the mutants were characterized with respect to initial rate of lactose transport and steady-state level of accumulation. Remarkably, histidine insertions into 10 out of 13 hydrophilic domains result in molecules that catalyze lactose accumulation effectively, although the initial rate of transport is compromised in certain cases. In contrast, insertions into hydrophilic domain 3, 9, or 10 cause a marked decrease in transport activity. As judged by immunoblots and [35S]methionine pulse-chase experiments, diminished activity is not due to decreased expression of the mutated permeases, defective insertion into the membrane, or increased rates of proteolysis after insertion. The results (i) suggest that most of the hydrophilic domains in the permease do not play an essential role in the transport mechanism and (ii) focus on the region of the permease containing putative helices IX and X as being particularly important for activity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold F. H., Haymore B. L. Engineered metal-binding proteins: purification to protein folding. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1796–1797. doi: 10.1126/science.1648261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barany F. Two-codon insertion mutagenesis of plasmid genes by using single-stranded hexameric oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4202–4206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibi E., Kaback H. R. In vivo expression of the lacY gene in two segments leads to functional lac permease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4325–4329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibi E., Stearns S. M., Kaback H. R. The N-terminal 22 amino acid residues in the lactose permease of Escherichia coli are not obligatory for membrane insertion or transport activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3180–3184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breul A., Kuchinke W., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. Linker mutagenesis in the lacZ gene of Escherichia coli yields variants of active beta-galactosidase. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jan 1;195(1):191–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15694.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calamia J., Manoil C. lac permease of Escherichia coli: topology and sequence elements promoting membrane insertion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4937–4941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco N., Herzlinger D., Mitchell R., DeChiara S., Danho W., Gabriel T. F., Kaback H. R. Intramolecular dislocation of the COOH terminus of the lac carrier protein in reconstituted proteoliposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4672–4676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco N., Tahara S. M., Patel L., Goldkorn T., Kaback H. R. Preparation, characterization, and properties of monoclonal antibodies against the lac carrier protein from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6894–6898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco N., Viitanen P., Herzlinger D., Kaback H. R. Monoclonal antibodies against the lac carrier protein from Escherichia coli. 1. Functional studies. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 31;23(16):3681–3687. doi: 10.1021/bi00311a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronan J. E., Jr Biotination of proteins in vivo. A post-translational modification to label, purify, and study proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10327–10333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. L., Boublik M., Kaback H. R. Structure of the lac carrier protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):31–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldkorn T., Rimon G., Kaback H. R. Topology of the lac carrier protein in the membrane of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3322–3326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson P. J. Proton-linked sugar transport systems in bacteria. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Aug;22(4):525–569. doi: 10.1007/BF00762961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzlinger D., Carrasco N., Kaback H. R. Functional and immunochemical characterization of a mutant of Escherichia coli energy uncoupled for lactose transport. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):221–229. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzlinger D., Viitanen P., Carrasco N., Kaback H. R. Monoclonal antibodies against the lac carrier protein from Escherichia coli. 2. Binding studies with membrane vesicles and proteoliposomes reconstituted with purified lac carrier protein. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 31;23(16):3688–3693. doi: 10.1021/bi00311a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R., Bibi E., Roepe P. D. Beta-galactoside transport in E. coli: a functional dissection of lac permease. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Aug;15(8):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90020-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. In and out and up and down with lac permease. Int Rev Cytol. 1992;137:97–125. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62674-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Molecular biology of active transport: from membrane to molecule to mechanism. Harvey Lect. 1987;83:77–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar G. B., Black P. N. Linker mutagenesis of a bacterial fatty acid transport protein. Identification of domains with functional importance. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1348–1353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Tooth P. Size and shape of the Escherichia coli lactose permease measured in filamentous arrays. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 28;26(15):4816–4823. doi: 10.1021/bi00389a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna E., Hardy D., Kaback H. R. Evidence that the final turn of the last transmembrane helix in the lactose permease is required for folding. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6471–6474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna E., Hardy D., Pastore J. C., Kaback H. R. Sequential truncation of the lactose permease over a three-amino acid sequence near the carboxyl terminus leads to progressive loss of activity and stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):2969–2973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.2969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mieschendahl M., Büchel D., Bocklage H., Müller-Hill B. Mutations in the lacY gene of Escherichia coli define functional organization of lactose permease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. G., Rosenbusch J. P. Topography of lactose permease from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15906–15914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roepe P. D., Zbar R. I., Sarkar H. K., Kaback H. R. A five-residue sequence near the carboxyl terminus of the polytopic membrane protein lac permease is required for stability within the membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):3992–3996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.3992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckler R., Möröy T., Wright J. K., Overath P. Anti-peptide antibodies and proteases as structural probes for the lactose/H+ transporter of Escherichia coli: a loop around amino acid residue 130 faces the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2403–2409. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckler R., Wright J. K., Overath P. Peptide-specific antibody locates the COOH terminus of the lactose carrier of Escherichia coli on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):10817–10820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckler R., Wright J. K. Sidedness of native membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli and orientation of the reconstituted lactose: H+ carrier. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jul 16;142(2):269–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stochaj U., Bieseler B., Ehring R. Limited proteolysis of lactose permease from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jul 15;158(2):423–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teather R. M., Bramhall J., Riede I., Wright J. K., Fürst M., Aichele G., Wilhelm U., Overath P. Lactose carrier protein of Escherichia coli. Structure and expression of plasmids carrying the Y gene of the lac operon. Eur J Biochem. 1980;108(1):223–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H., Wright J. K., Jähnig F. The structure of the lactose permease derived from Raman spectroscopy and prediction methods. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3625–3631. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S., Deng L. P., Brown M. L., Agellon L. B., Tall A. R. Structure-function studies of human cholesteryl ester transfer protein by linker insertion scanning mutagenesis. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 9;30(14):3484–3490. doi: 10.1021/bi00228a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrubel W., Stochaj U., Sonnewald U., Theres C., Ehring R. Reconstitution of an active lactose carrier in vivo by simultaneous synthesis of two complementary protein fragments. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5374–5381. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5374-5381.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Iwaarden P. R., Pastore J. C., Konings W. N., Kaback H. R. Construction of a functional lactose permease devoid of cysteine residues. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 8;30(40):9595–9600. doi: 10.1021/bi00104a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]