Abstract
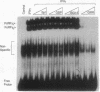
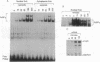
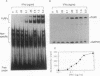
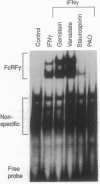
Interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) transcriptionally activates several early-response genes in monocytes that are important for the ultimate phenotype of the activated macrophage. One of these genes is the high-affinity Fc receptor for IgG (Fc gamma RI). Recently, Pearse et al. [Pearse, R.N., Feinman, R. & Ravetch, J. V. (1991) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 11305-11309] defined within the promoter region of the Fc gamma RI gene an element, the gamma response region, which was necessary for IFN-gamma-induced enhancement of Fc gamma RI. In this report we describe the induction by IFN-gamma of a DNA-binding factor, FcRF gamma (Fc gamma RI DNA-binding factor, IFN-gamma induced), that specifically recognizes the gamma response region element. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSAs) demonstrated the presence of FcRF gamma in human monocytes within 1 min after exposure to IFN-gamma. On EMSA, FcRF gamma consisted of two complexes termed FcRF gamma 1 and FcRF gamma 2. The nuclear concentration of FcRF gamma rapidly increased, peaked at 15 min, and then fell after 1-2 hr. Dose-response studies revealed (i) as little as 0.05 ng of IFN-gamma per ml induced FcRF gamma, (ii) maximum activation occurred at 1 ng/ml, and (iii) steady-state levels of Fc gamma RI mRNA closely paralleled that of FcRF gamma. Since FcRF gamma was activated in cells normally not expressing Fc gamma RI RNA, other regulatory mechanisms must control Fc gamma RI-restricted tissue expression. Activation of FcRF gamma by IFN-gamma was inhibited by pretreatment with 500 nM staurosporin and 25 microM phenyl arsine oxide. These data suggest that a kinase and possibly a phosphatase activity are required for IFN-gamma-induced signaling of FcRF gamma in monocytes.
Full text
PDF
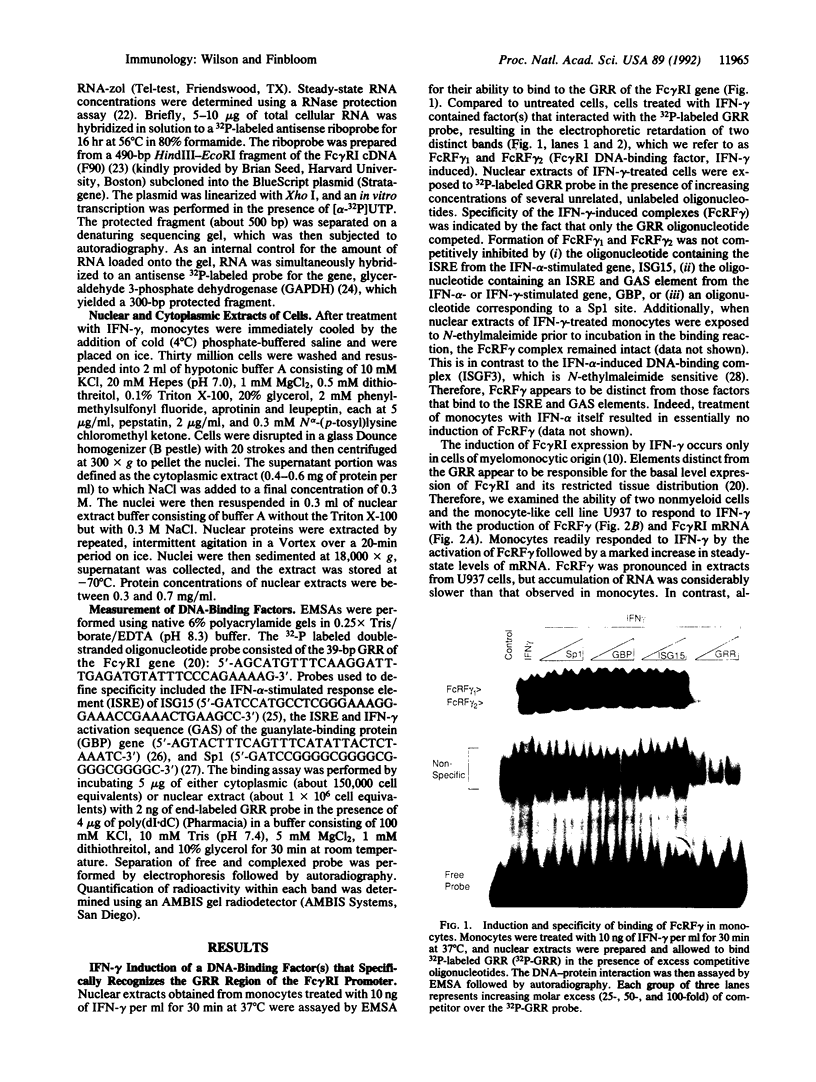
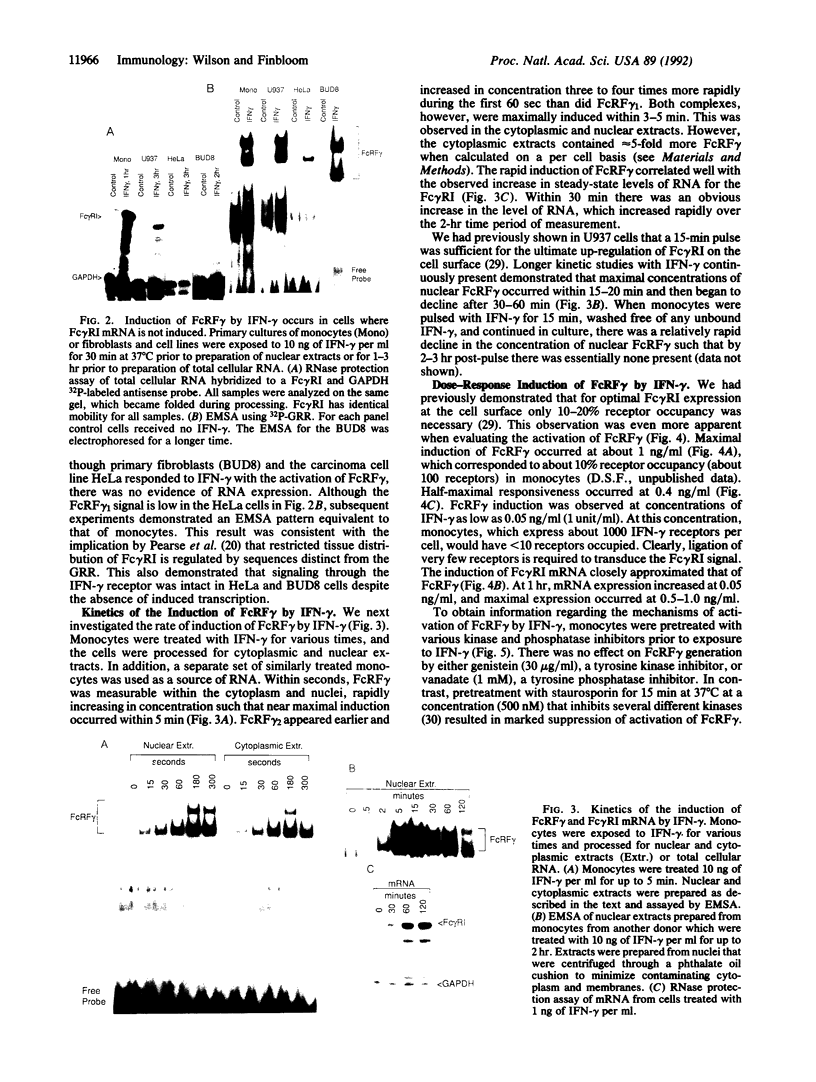
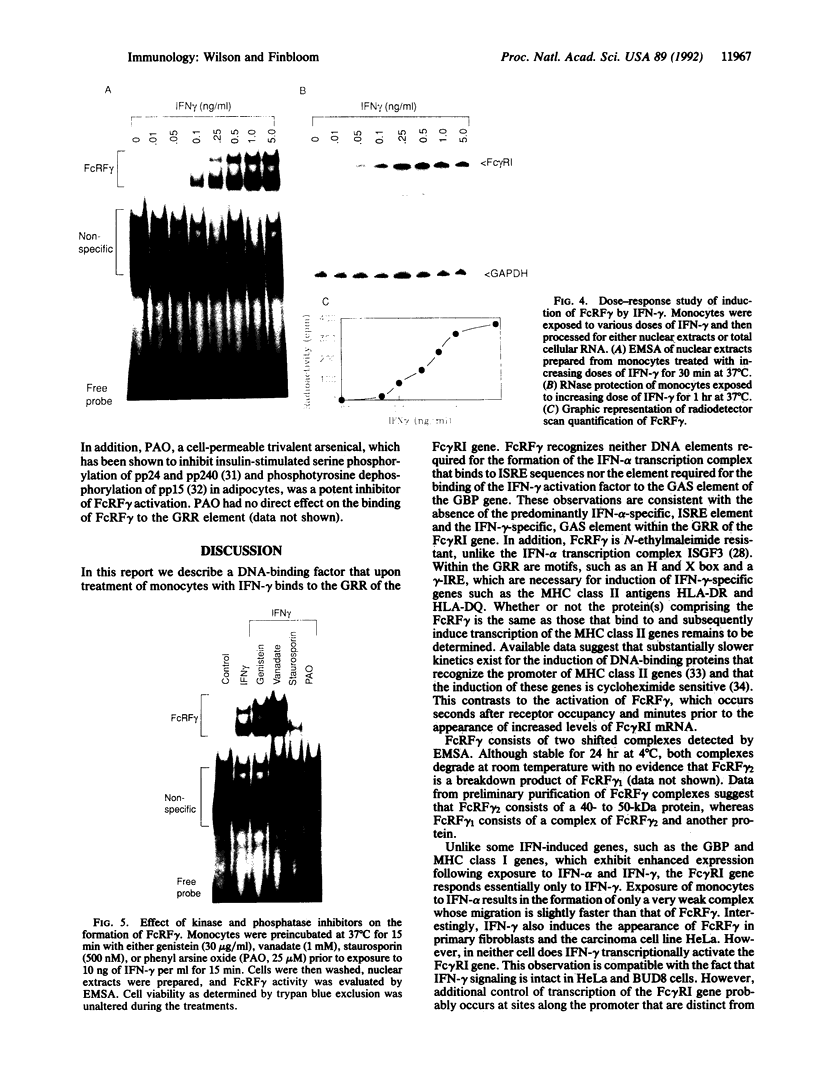

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguet M., Dembić Z., Merlin G. Molecular cloning and expression of the human interferon-gamma receptor. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akai H., Larner A. C. Phorbol ester-mediated down-regulation of an interferon-inducible gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3252–3255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. M., Seed B. Isolation and expression of functional high-affinity Fc receptor complementary DNAs. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):378–381. doi: 10.1126/science.2911749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr C. L., Saunders G. F. Interferon-gamma-inducible regulation of the human invariant chain gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3475–3481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernier M., Laird D. M., Lane M. D. Insulin-activated tyrosine phosphorylation of a 15-kilodalton protein in intact 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1844–1848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Boettger E. C., Flavell R. A. Transcriptional activation of HLA-DR alpha by interferon gamma requires a trans-acting protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4672–4676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bono M. R., Benech P., Couillin P., Alcaide-Loridan C., Grisard M. C., Jouin H., Fischer D. G., Fellous M. Characterization of human IFN-gamma response using somatic cell hybrids of hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic origin. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1989 Nov;15(6):513–523. doi: 10.1007/BF01534912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boot J. H., Geerts M. E., Aarden L. A. Functional polymorphisms of Fc receptors in human monocyte-mediated cytotoxicity towards erythrocytes induced by murine isotype switch variants. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1217–1223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassatella M. A., Bazzoni F., Calzetti F., Guasparri I., Rossi F., Trinchieri G. Interferon-gamma transcriptionally modulates the expression of the genes for the high affinity IgG-Fc receptor and the 47-kDa cytosolic component of NADPH oxidase in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22079–22082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celada A., Maki R. A. IFN-gamma induces the expression of the genes for MHC class II I-A beta and tumor necrosis factor through a protein kinase C-independent pathway. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):114–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Cheng Y. S., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Interactions of alpha- and gamma-interferon in the transcriptional regulation of the gene encoding a guanylate-binding protein. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2009–2014. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Sazer S., Tjian R., Schimke R. T. Transcription factor Sp1 recognizes a DNA sequence in the mouse dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):246–248. doi: 10.1038/319246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan X. D., Goldberg M., Bloom B. R. Interferon-gamma-induced transcriptional activation is mediated by protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5122–5125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar M. A., Fernandez-Luna J., Schreiber R. D. Identification of two regions within the cytoplasmic domain of the human interferon-gamma receptor required for function. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19626–19635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finbloom D. S., Hoover D. L., Wahl L. M. The characteristics of binding of human recombinant interferon-gamma to its receptor on human monocytes and human monocyte-like cell lines. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):300–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finbloom D. S. Internalization and degradation of human recombinant interferon-gamma in the human histiocytic lymphoma cell line, U937: relationship to Fc receptor enhancement and antiproliferation. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Apr;47(1):93–105. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90148-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finbloom D. S., Wahl L. M., Winestock K. D. The receptor for interferon-gamma on human peripheral blood monocytes consists of multiple distinct subunits. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22545–22548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost S. C., Kohanski R. A., Lane M. D. Effect of phenylarsine oxide on insulin-dependent protein phosphorylation and glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9872–9876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Morales P., Minami Y., Luong E., Klausner R. D., Samelson L. E. Tyrosine phosphorylation in T cells is regulated by phosphatase activity: studies with phenylarsine oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9255–9259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geppert T. D., Lipsky P. E. Antigen presentation at the inflammatory site. Crit Rev Immunol. 1989;9(4):313–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard T. L., Jurgensen C. H., Fauci A. S. Differential effect of monoclonal anti-DR antibody on monocytes in antigen- and mitogen-stimulated responses: mechanism of inhibition and relationship to interleukin 1 secretion. Cell Immunol. 1983 Dec;82(2):394–402. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs V. C., Williams S. R., Gray P. W., Schreiber R. D., Pennica D., Rice G., Goeddel D. V. The extracellular domain of the human interferon gamma receptor interacts with a species-specific signal transducer. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5860–5866. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyre P. M., Morganelli P. M., Miller R. Recombinant immune interferon increases immunoglobulin G Fc receptors on cultured human mononuclear phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):393–397. doi: 10.1172/JCI110980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmi S., Merlin G., Aguet M. Functional characterization of a hybrid human-mouse interferon gamma receptor: evidence for species-specific interaction of the extracellular receptor domain with a putative signal transducer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2737–2741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey G. K., McCourt D. W., Schreiber R. D. Ligand-induced phosphorylation of the human interferon-gamma receptor. Dependence on the presence of a functionally active receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17868–17875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung V., Rashidbaigi A., Jones C., Tischfield J. A., Shows T. B., Pestka S. Human chromosomes 6 and 21 are required for sensitivity to human interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4151–4155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of ISGF3, the positive regulator of interferon-alpha-stimulated transcription, reconstituted in vitro. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1362–1371. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao K., Hoffman R. D., Lane M. D. Phosphotyrosyl turnover in insulin signaling. Characterization of two membrane-bound pp15 protein tyrosine phosphatases from 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6544–6553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luster A. D., Unkeless J. C., Ravetch J. V. Gamma-interferon transcriptionally regulates an early-response gene containing homology to platelet proteins. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):672–676. doi: 10.1038/315672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao C., Merlin G., Ballotti R., Metzler M., Aguet M. Rapid increase of the human IFN-gamma receptor phosphorylation in response to human IFN-gamma and phorbol myristate acetate. Involvement of different serine/threonine kinases. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4257–4264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medema R. H., Burgering B. M., Bos J. L. Insulin-induced p21ras activation does not require protein kinase C, but a protein sensitive to phenylarsine oxide. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):21186–21189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger H. Fc receptors and membrane immunoglobulin. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(1):40–46. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90074-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Interferon-gamma, the activated macrophage, and host defense against microbial challenge. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Apr;108(4):595–608. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-4-595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse R. N., Feinman R., Ravetch J. V. Characterization of the promoter of the human gene encoding the high-affinity IgG receptor: transcriptional induction by gamma-interferon is mediated through common DNA response elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11305–11309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piechaczyk M., Blanchard J. M., Marty L., Dani C., Panabieres F., El Sabouty S., Fort P., Jeanteur P. Post-transcriptional regulation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase gene expression in rat tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):6951–6963. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.6951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Kinet J. P. Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:457–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.002325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N., Evans B., Levy D., Fahey D., Knight E., Jr, Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced transcription of a gene encoding a 15-kDa protein depends on an upstream enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6394–6398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D. Identification of gamma-interferon as a murine macrophage-activating factor for tumor cytotoxicity. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1984;13:171–198. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-1445-6_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standiford T. J., Strieter R. M., Chensue S. W., Westwick J., Kasahara K., Kunkel S. L. IL-4 inhibits the expression of IL-8 from stimulated human monocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 1;145(5):1435–1439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T. Use and specificity of staurosporine, UCN-01, and calphostin C as protein kinase inhibitors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:340–347. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01030-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Scigliano E., Freedman V. H. Structure and function of human and murine receptors for IgG. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:251–281. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Winkel J. G., Anderson C. L. Biology of human immunoglobulin G Fc receptors. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 May;49(5):511–524. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.5.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]