Abstract
A taurine/beta-alanine transporter was cloned from a mouse brain cDNA library by screening with a partial cDNA probe of the glycine transporter at low stringency. The deduced amino acid sequence predicts 590 amino acids with typical characteristics of the sodium-dependent neurotransmitter transporters such as sequence homology and membrane topography. However, the calculated isoelectric point of the taurine/beta-alanine transporter is more acidic (pI = 5.98) than those (pI > 8.0) of other cloned neurotransmitter transporters. Xenopus oocytes injected with cRNA of the cloned transporter expressed uptake activities with Km = 4.5 microM for taurine and Km = 56 microM for beta-alanine. Northern hybridization showed a single transcript of 7.5 kilobases that was highly enriched in kidney and distributed evenly in various parts of the brain. In situ hybridization showed the mRNA of the taurine/beta-alanine transporter to be localized in the corpus callosum, striatum, and anterior commisure. Specific localization of the taurine/beta-alanine transporter in mouse brain suggests a potential function for taurine and beta-alanine as neurotransmitters.
Full text
PDF

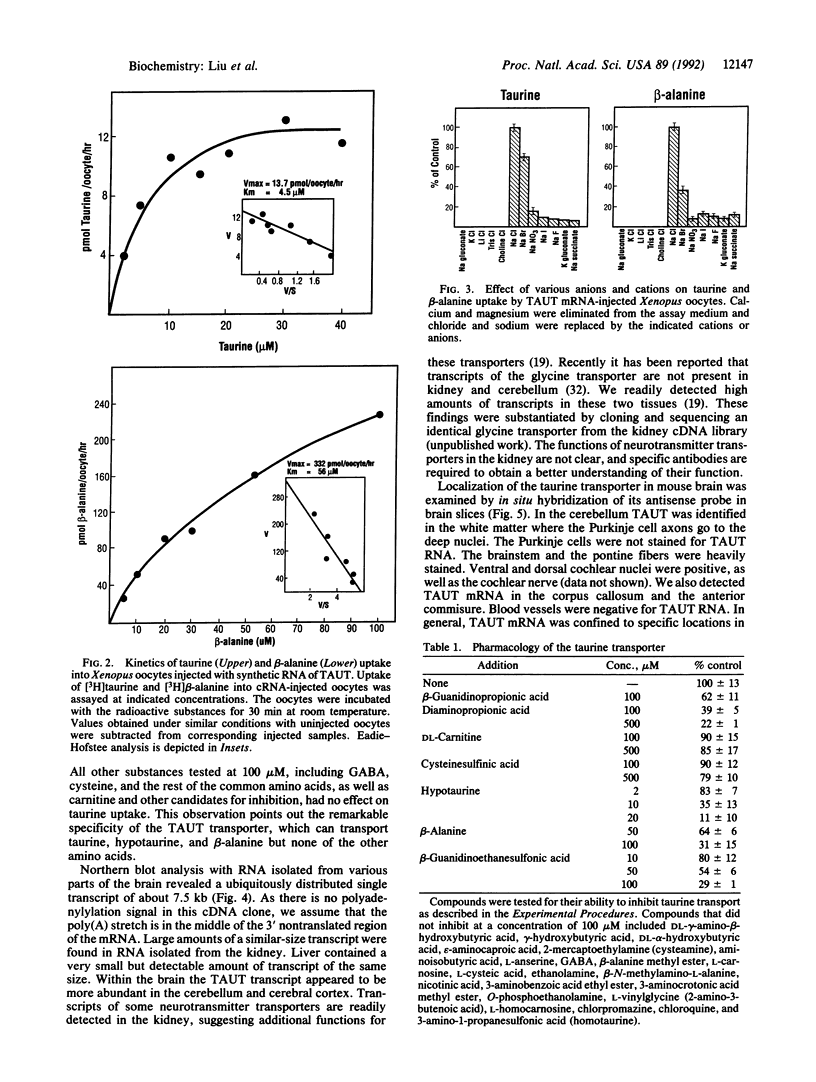


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Airaksinen E. M., Oja S. S., Marnela K. M., Sihvola P. Taurine and other amino acids of platelets and plasma in retinitis pigmentosa. Ann Clin Res. 1980 Apr;12(2):52–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almarghini K., Remy A., Tappaz M. Immunocytochemistry of the taurine biosynthesis enzyme, cysteine sulfinate decarboxylase, in the cerebellum: evidence for a glial localization. Neuroscience. 1991;43(1):111–119. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90421-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berson E. L., Schmidt S. Y., Rabin A. R. Plasma amino-acids in hereditary retinal disease. Ornithine, lysine, and taurine. Br J Ophthalmol. 1976 Feb;60(2):142–147. doi: 10.1136/bjo.60.2.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakely R. D., Berson H. E., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Caron M. G., Peek M. M., Prince H. K., Bradley C. C. Cloning and expression of a functional serotonin transporter from rat brain. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):66–70. doi: 10.1038/354066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Snyder S. H. Localization of nitric oxide synthase indicating a neural role for nitric oxide. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):768–770. doi: 10.1038/347768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney R. W., Gusowski N., Dabbagh S., Theissen M., Padilla M., Diehl A. Factors affecting the transport of beta-amino acids in rat renal brush-border membrane vesicles. The role of external chloride. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 14;812(3):702–712. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90264-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choquet D., Korn H. Does beta-alanine activate more than one chloride channel associated receptor? Neurosci Lett. 1988 Feb 3;84(3):329–334. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90530-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilley J. V. The origin of urinary taurine excretion during chronic radiation injury. Radiat Res. 1972 Apr;50(1):191–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fremeau R. T., Jr, Caron M. G., Blakely R. D. Molecular cloning and expression of a high affinity L-proline transporter expressed in putative glutamatergic pathways of rat brain. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):915–926. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90206-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A., Albright P. W., Chesney R. W. Dietary adaptation of taurine transport by rat renal epithelium. Life Sci. 1981 Dec 7;29(23):2415–2419. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90478-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guastella J., Nelson N., Nelson H., Czyzyk L., Keynan S., Miedel M. C., Davidson N., Lester H. A., Kanner B. I. Cloning and expression of a rat brain GABA transporter. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1303–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.1975955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. J., Mezey E., Brownstein M. J. Cloning of a serotonin transporter affected by antidepressants. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):579–580. doi: 10.1126/science.1948036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxtable R. J. Taurine in the central nervous system and the mammalian actions of taurine. Prog Neurobiol. 1989;32(6):471–533. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(89)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen J. G., Smith L. H. Biochemistry and physiology of taurine and taurine derivatives. Physiol Rev. 1968 Apr;48(2):424–511. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.2.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner B. I., Bendahan A. Two pharmacologically distinct sodium- and chloride-coupled high-affinity gamma-aminobutyric acid transporters are present in plasma membrane vesicles and reconstituted preparations from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2550–2554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilty J. E., Lorang D., Amara S. G. Cloning and expression of a cocaine-sensitive rat dopamine transporter. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):578–579. doi: 10.1126/science.1948035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishtal O. A., Osipchuk YuV, Vrublevsky S. V. Properties of glycine-activated conductances in rat brain neurones. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Feb 3;84(3):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90519-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson O. M., Griffiths R., Allen I. C., Schousboe A. Mutual inhibition kinetic analysis of gamma-aminobutyric acid, taurine, and beta-alanine high-affinity transport into neurons and astrocytes: evidence for similarity between the taurine and beta-alanine carriers in both cell types. J Neurochem. 1986 Aug;47(2):426–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb04519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann A., Carlström C., Nagelhus E. A., Ottersen O. P. Elevation of taurine in hippocampal extracellular fluid and cerebrospinal fluid of acutely hypoosmotic rats: contribution by influx from blood? J Neurochem. 1991 Feb;56(2):690–697. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. P., Lombardini J. B. Taurine inhibits protein kinase C-catalyzed phosphorylation of specific proteins in a rat cortical P2 fraction. J Neurochem. 1991 May;56(5):1747–1753. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02076.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Q. R., Mandiyan S., Nelson H., Nelson N. A family of genes encoding neurotransmitter transporters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6639–6643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Q. R., Nelson H., Mandiyan S., López-Corcuera B., Nelson N. Cloning and expression of a glycine transporter from mouse brain. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jun 29;305(2):110–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80875-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Corcuera B., Liu Q. R., Mandiyan S., Nelson H., Nelson N. Expression of a mouse brain cDNA encoding novel gamma-aminobutyric acid transporter. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17491–17493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson H., Mandiyan S., Nelson N. Cloning of the human brain GABA transporter. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 20;269(1):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81149-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr H. T., Cohen A. I., Lowry O. H. The distribution of taurine in the vertebrate retina. J Neurochem. 1976 Mar;26(3):609–611. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb01519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacholczyk T., Blakely R. D., Amara S. G. Expression cloning of a cocaine- and antidepressant-sensitive human noradrenaline transporter. Nature. 1991 Mar 28;350(6316):350–354. doi: 10.1038/350350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasantes-Morales H., Klethi J., Ledig M., Mandel P. Free amino acids of chicken and rat retina. Brain Res. 1972 Jun 22;41(2):494–497. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90523-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen R., Scriver C. R. Renal transport of taurine adapts to perturbed taurine homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2101–2105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid R., Sieghart W., Karobath M. Taurine uptake in synaptosomal fractions of rat cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1975 Jul;25(1):5–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb07686.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada S., Kitayama S., Lin C. L., Patel A., Nanthakumar E., Gregor P., Kuhar M., Uhl G. Cloning and expression of a cocaine-sensitive dopamine transporter complementary DNA. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):576–578. doi: 10.1126/science.1948034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. E., Borden L. A., Hartig P. R., Branchek T., Weinshank R. L. Cloning and expression of a glycine transporter reveal colocalization with NMDA receptors. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):927–935. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90207-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay N., Warren R., Dykes R. W. The effects of strychnine on neurons in cat somatosensory cortex and its interaction with the inhibitory amino acids, glycine, taurine and beta-alanine. Neuroscience. 1988 Sep;26(3):745–762. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vessey D. A. The biochemical basis for the conjugation of bile acids with either glycine or taurine. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 15;174(2):621–626. doi: 10.1042/bj1740621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. V., Olson J. P., Samson F. E., Nelson S. R., Pazdernik T. L. A possible role for taurine in osmoregulation within the brain. J Neurochem. 1988 Sep;51(3):740–745. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01807.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. E., Tallan H. H., Lin Y. Y., Gaull G. E. Taurine: biological update. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:427–453. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




