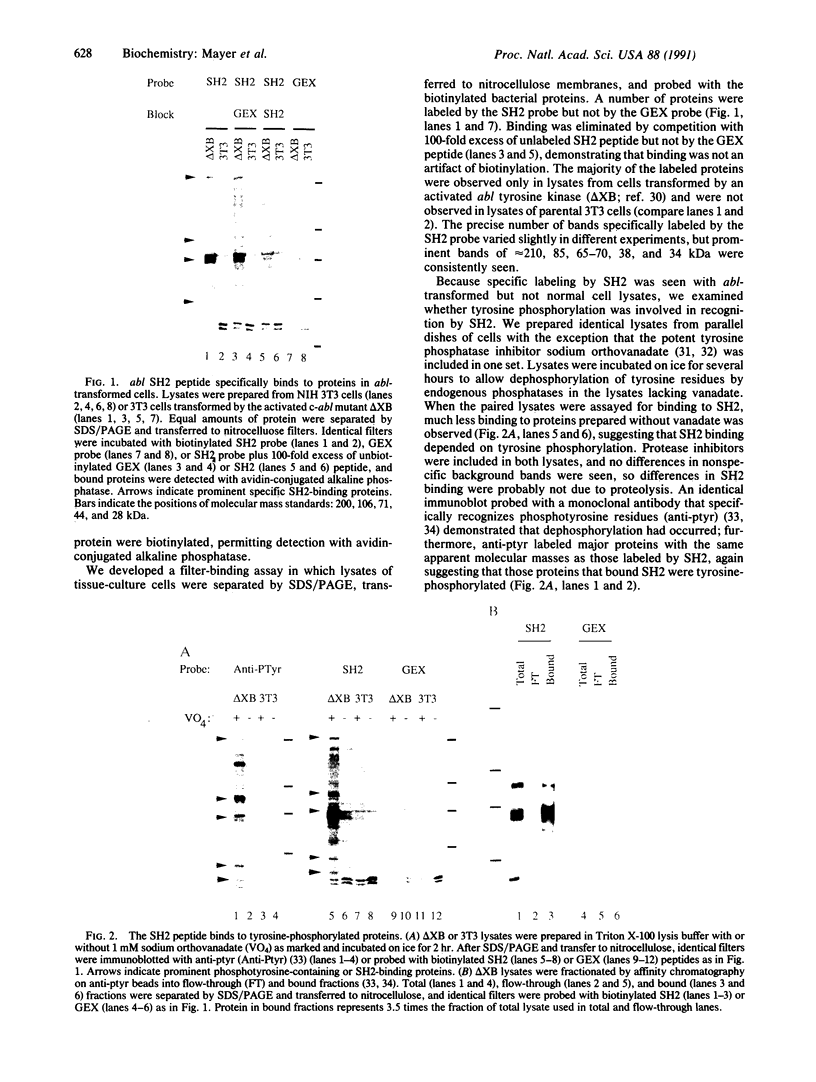
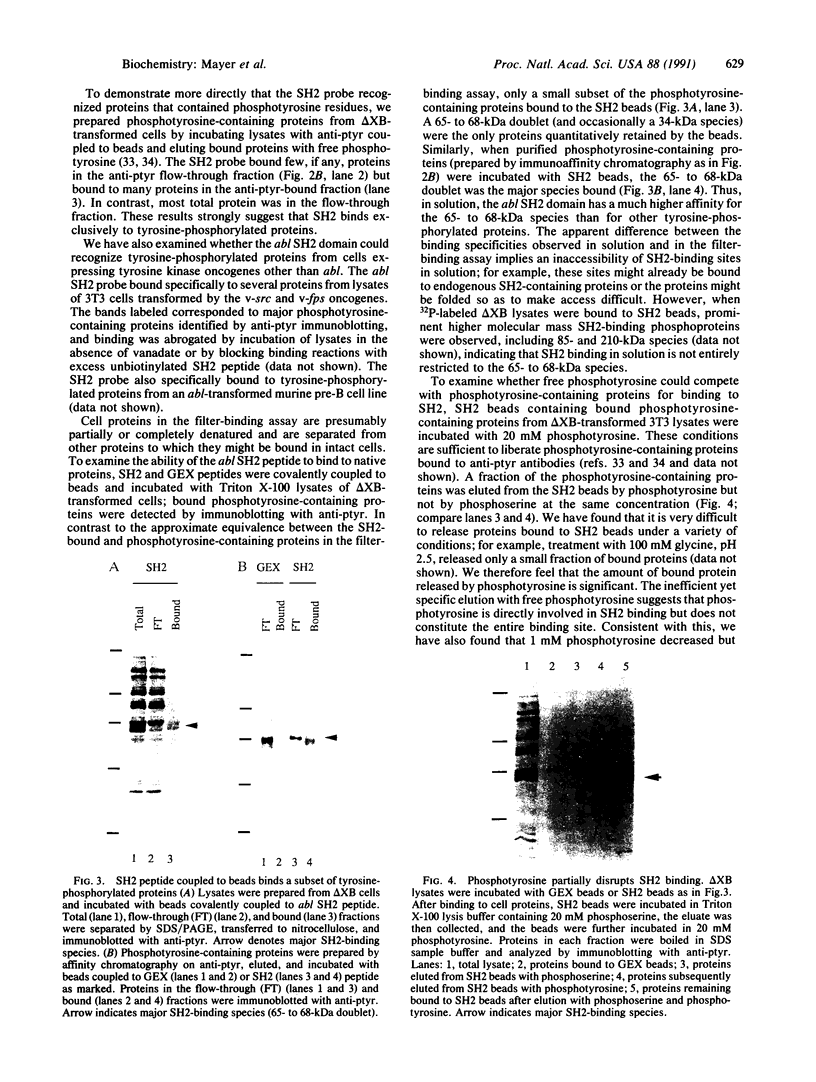
Abstract
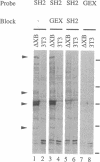
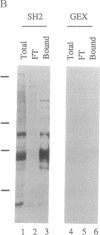
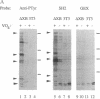
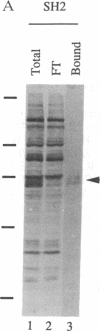
Several proteins implicated in the regulation of cell proliferation contain a common noncatalytic domain, src homology region 2 (SH2). We have used the bacterially expressed SH2 domain of abl protein-tyrosine kinase to evaluate the ability of this domain to bind to cellular proteins. ablSH2 specifically bound to a number of tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins from cells transformed by tyrosine kinase oncogenes in a filter-binding assay and to a subset of those proteins in solution. The SH2 probe bound almost exclusively to tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins, and binding was eliminated by dephosphorylation of cell proteins. Free phosphotyrosine could partially disrupt SH2 binding, suggesting that phosphotyrosine is directly involved in the binding interaction. These results demonstrate that an SH2 domain is sufficient to confer direct, high-affinity phosphotyrosine-dependent binding to proteins and suggest a general role for SH2 domains in cellular signaling pathways.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D., Koch C. A., Grey L., Ellis C., Moran M. F., Pawson T. Binding of SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma 1, GAP, and Src to activated growth factor receptors. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):979–982. doi: 10.1126/science.2173144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristol A., Hall S. M., Kriz R. W., Stahl M. L., Fan Y. S., Byers M. G., Eddy R. L., Shows T. B., Knopf J. L. Phospholipase C-148: chromosomal location and deletion mapping of functional domains. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):915–920. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. J., Gordon J. A. The stimulation of pp60v-src kinase activity by vanadate in intact cells accompanies a new phosphorylation state of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9580–9586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Darrow D. Analysis of the catalytic domain of phosphotransferase activity of two avian sarcoma virus-transforming proteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4550–4557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Belzer S. K., Purchio A. F. Structurally and functionally modified forms of pp60v-src in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cell lysates. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1213–1220. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daley G. Q., Van Etten R. A., Baltimore D. Induction of chronic myelogenous leukemia in mice by the P210bcr/abl gene of the Philadelphia chromosome. Science. 1990 Feb 16;247(4944):824–830. doi: 10.1126/science.2406902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C., Moran M., McCormick F., Pawson T. Phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins by transforming and mitogenic tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):377–381. doi: 10.1038/343377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori Y., Homma Y., Sorimachi H., Kawasaki H., Nakanishi O., Suzuki K., Takenawa T. A second type of rat phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C containing a src-related sequence not essential for phosphoinositide-hydrolyzing activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21885–21890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Zokas L., Kamps M. P. Monoclonal antibodies to phosphotyrosine. J Immunol Methods. 1988 May 9;109(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90253-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Zokas L. Novel tyrosine kinase substrates from Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells are present in the membrane skeleton. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2401–2408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Varmus H. E. Site-directed mutagenesis of the SH2- and SH3-coding domains of c-src produces varied phenotypes, including oncogenic activation of p60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1307–1318. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P., Baltimore D. N-terminal mutations activate the leukemogenic potential of the myristoylated form of c-abl. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):449–456. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03397.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Morrison D. K., Wong G., McCormick F., Williams L. T. PDGF beta-receptor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of GAP and association of GAP with a signaling complex. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Ellis C., Pawson T., Cooper J. A. Binding of GAP to activated PDGF receptors. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1578–1581. doi: 10.1126/science.2157284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Moran M., Sadowski I., Pawson T. The common src homology region 2 domain of cytoplasmic signaling proteins is a positive effector of v-fps tyrosine kinase function. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4131–4140. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumjian D. A., Wahl M. I., Rhee S. G., Daniel T. O. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) binding promotes physical association of PDGF receptor with phospholipase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8232–8236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kypta R. M., Goldberg Y., Ulug E. T., Courtneidge S. A. Association between the PDGF receptor and members of the src family of tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Courtneidge S. A., Bishop J. M. Structural and functional domains of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein (pp60src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Bellot F., Honegger A. M., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Zilberstein A. Tyrosine kinase activity is essential for the association of phospholipase C-gamma with the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):435–441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall M. S., Hill W. S., Ng A. S., Vogel U. S., Schaber M. D., Scolnick E. M., Dixon R. A., Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B. A C-terminal domain of GAP is sufficient to stimulate ras p21 GTPase activity. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1105–1110. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03480.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Mayer B. J., Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Binding of transforming protein, P47gag-crk, to a broad range of phosphotyrosine-containing proteins. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1537–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.1694307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. A novel viral oncogene with structural similarity to phospholipase C. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):272–275. doi: 10.1038/332272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hanafusa H. Association of the v-crk oncogene product with phosphotyrosine-containing proteins and protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2638–2642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hanafusa H. Mutagenic analysis of the v-crk oncogene: requirement for SH2 and SH3 domains and correlation between increased cellular phosphotyrosine and transformation. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3581–3589. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3581-3589.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy C. J., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Aaronson S. A. PDGF induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of GTPase activating protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):711–714. doi: 10.1038/342711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Koch C. A., Anderson D., Ellis C., England L., Martin G. S., Pawson T. Src homology region 2 domains direct protein-protein interactions in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8622–8626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien M. C., Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Activation of the proto-oncogene p60c-src by point mutations in the SH2 domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2855–2862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Non-catalytic domains of cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases: regulatory elements in signal transduction. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):491–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponticelli A. S., Whitlock C. A., Rosenberg N., Witte O. N. In vivo tyrosine phosphorylations of the Abelson virus transforming protein are absent in its normal cellular homolog. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):953–960. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. P., Smith M. J., Srinivasan A. Nucleotide sequence of Abelson murine leukemia virus genome: structural similarity of its transforming gene product to other onc gene products with tyrosine-specific kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg N., Witte O. N. The viral and cellular forms of the Abelson (abl) oncogene. Adv Virus Res. 1988;35:39–81. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60708-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Stone J. C., Pawson T. A noncatalytic domain conserved among cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases modifies the kinase function and transforming activity of Fujinami sarcoma virus P130gag-fps. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4396–4408. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Ferenz C. R., Kelleher K. L., Kriz R. W., Knopf J. L. Sequence similarity of phospholipase C with the non-catalytic region of src. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):269–272. doi: 10.1038/332269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Moon K. H., Suh H. W., Rhee S. G. Inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C: complete cDNA and protein sequences and sequence homology to tyrosine kinase-related oncogene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5419–5423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., Wong G., Halenbeck R., Rubinfeld B., Martin G. A., Ladner M., Long C. M., Crosier W. J., Watt K., Koths K. Molecular cloning of two types of GAP complementary DNA from human placenta. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1697–1700. doi: 10.1126/science.3201259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Etten R. A., Jackson P., Baltimore D. The mouse type IV c-abl gene product is a nuclear protein, and activation of transforming ability is associated with cytoplasmic localization. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):669–678. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel U. S., Dixon R. A., Schaber M. D., Diehl R. E., Marshall M. S., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B. Cloning of bovine GAP and its interaction with oncogenic ras p21. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):90–93. doi: 10.1038/335090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Nishibe S., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Epidermal growth factor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II independently of receptor internalization and extracellular calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1568–1572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmaster G., Hinze E., Pawson T. Mapping of multiple phosphorylation sites within the structural and catalytic domains of the Fujinami avian sarcoma virus transforming protein. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):29–41. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.29-41.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]